DECAESTECKER Ellen
- Aquatic biology, KU Leuven, Kortrijk
- Adaptation, Evolutionary Dynamics, Evolutionary Ecology, Species interactions
- recommender
Recommendations: 2
Reviews: 0
Recommendations: 2
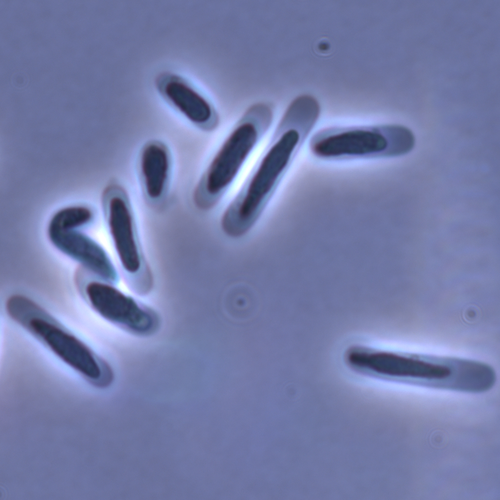
Evolution of sperm morphology in a crustacean genus with fertilization inside an open brood pouch.
Evolution of sperm morphology in Daphnia within a phyologenetic context
Recommended by Ellen Decaestecker based on reviews by Renate Matzke-Karasz and 1 anonymous reviewerIn this study sperm morphology is studied in 15 Daphnia species and the morphological data are mapped on a Daphnia phylogeny. The authors found that despite the internal fertilization mode, Daphnia have among the smallest sperm recorded, as would be expected with external fertilization. The authors also conclude that increase in sperm length has evolved twice, that sperm encapsulation has been lost in a clade, and that this clade has very polymorphic sperm with long, and often numerous, filopodia.
Daphnia is an interesting model to study sperm morphology because the biology of sexual reproduction is often ignored in (cyclical) parthenogenetic species. Daphnia is part of the very diverse and successful group of cladocerans with cyclical parthenogenetic reproduction. The success of this reproduction mode is reflected in the known 620 species that radiated within this order, this is more than half of the known Branchiopod species diversity and the estimated number of cladoceran species is even two to four times higher (Forró et al. 2008). Looking at this particular model with a good phylogeny and some particularity in the mode of fertilization/reproduction, has thus a large value. Most Daphnia species are cyclical parthenogenetic and switch between sexual and asexual reproduction depending on the environmental conditions. Within the genus Daphnia, evolution to obligate asexuality has evolved in at least four independent occasions by three different mechanisms: (i) obligate parthenogenesis through hybridisation with or without polyploidy, (ii) asexuality has been acquired de novo in some populations and (iii) in certain lineages females reproduce by obligate parthenogenesis, whereas the clonally propagated males produce functional haploid sperm that allows them to breed with sexual females of normal cyclically parthenogenetic lineages (more on this in Decaestecker et al. 2009).
This study is made in the context of a body of research on the evolution of one of the most fundamental and taxonomically diverse cell types. There is surprisingly little known about the adaptive value underlying their morphology because it is very difficult to test this experimentally. Studying sperm morphology across species is interesting to study evolution itself because it is a "simple trait". As the authors state: The understanding of the adaptive value of sperm morphology, such as length and shape, remains largely incomplete (Lüpold & Pitnick, 2018). Based on phylogenetic analyses across the animal kingdom, the general rule seems to be that fertilization mode (i.e. whether eggs are fertilized within or outside the female) is a key predictor of sperm length (Kahrl et al., 2021). There is a trade-off between sperm number and length (Immler et al., 2011). This study reports on one of the smallest sperm recorded despite the fertilization being internal. The brood pouch in Daphnia is an interesting particularity as fertilisation occurs internally, but it is not disconnected from the environment. It is also remarkable that there are two independent evolution lines of sperm size in this group. It suggests that those traits have an adaptive value.
References
Decaestecker E, De Meester L, Mergeay J (2009) Cyclical Parthenogenesis in Daphnia: Sexual Versus Asexual Reproduction. In: Lost Sex: The Evolutionary Biology of Parthenogenesis (eds Schön I, Martens K, Dijk P), pp. 295–316. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-2770-2_15
Duneau David, Möst M, Ebert D (2022) Evolution of sperm morphology in a crustacean genus with fertilization inside an open brood pouch. bioRxiv, 2020.01.31.929414, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.31.929414
Forró L, Korovchinsky NM, Kotov AA, Petrusek A (2008) Global diversity of cladocerans (Cladocera; Crustacea) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia, 595, 177–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-9013-5
Immler S, Pitnick S, Parker GA, Durrant KL, Lüpold S, Calhim S, Birkhead TR (2011) Resolving variation in the reproductive tradeoff between sperm size and number. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108, 5325–5330. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1009059108
Kahrl AF, Snook RR, Fitzpatrick JL (2021) Fertilization mode drives sperm length evolution across the animal tree of life. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 5, 1153–1164. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-021-01488-y
Lüpold S, Pitnick S (2018) Sperm form and function: what do we know about the role of sexual selection? Reproduction, 155, R229–R243. https://doi.org/10.1530/REP-17-0536
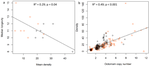
Experimental evolution of virulence and associated traits in a Drosophila melanogaster – Wolbachia symbiosis
Temperature effects on virulence evolution of wMelPop Wolbachia in Drosophila melanogaster
Recommended by Ellen Decaestecker based on reviews by Shira Houwenhuyse and 3 anonymous reviewersMonnin et al. [1] here studied how Drosophila populations are affected when exposed to a high virulent endosymbiotic wMelPop Wolbachia strain and why virulent vertically transmitting endosymbionts persist in nature. This virulent wMelPop strain has been described to be a blocker of dengue and other arboviral infections in arthropod vector species, such as Aedes aegypti. Whereas it can thus function as a mutualistic symbiont, it here acts as an antagonist along the mutualism-antagonism continuum symbionts operate. The wMelPop strain is not a natural occurring strain in Drosophila melanogaster and thus the start of this experiment can be seen as a novel host-pathogen association. Through experimental evolution of 17 generations, the authors studied how high temperature affects wMelPop Wolbachia virulence and Drosophila melanogaster survival. The authors used Drosophila strains that were selected for late reproduction, given that this should favor evolution to a lower virulence. Assumptions for this hypothesis are not given in the manuscript here, but it can indeed be assumed that energy that is assimilated to symbiont tolerance instead of reproduction may lead to reduced virulence evolution. This has equally been suggested by Reyserhove et al. [2] in a dynamics energy budget model tailored to Daphnia magna virulence evolution upon a viral infection causing White fat Cell disease, reconstructing changing environments through time.
Contrary to their expectations for vertically transmitting symbionts, the authors did not find a reduction in wMelPop Wolbachia virulence during the course of the experimental evolution experiment under high temperature. Important is what this learns for virulence evolution, also for currently horizontal transmitting disease epidemics (such as COVID-19). It mainly reflects that evolution of virulence for new host-pathogen associations is difficult to predict and that it may take multiple generations before optimal levels of virulence are reached [3,4]. These optimal levels of virulence will depend on trade-offs with other life history traits of the symbiont, but also on host demography, host heterogeneity, amongst others [5,6]. Multiple microbial interactions may affect the outcome of virulence evolution [7]. Given that no germ-free individuals were used, it can be expected that other components of the Drosophila microbiome may have played a role in the virulence evolution. In most cases, microbiota have been described as defensive or protective for virulent symbionts [8], but they may also have stimulated the high levels of virulence. Especially, given that upon higher temperatures, Wolbachia growth may have been increased, host metabolic demands increased [9], host immune responses affected and microbial communities changed [10]. This may have resulted in increased competitive interactions to retrieve host resources, sustaining high virulence levels of the symbiont.
A nice asset of this study is that the phenotypic results obtained in the experimental evolution set-up were linked with wMelPop density measurement and octomom copy number quantifications. Octomom is a specific 8-n genes region of the Wolbachia genome responsible for wMelPop virulence, so there is a link between the phenotypic and molecular functions of the involved symbiont. The authors found that density, octomom copy number and virulence were correlated to each other. An important note the authors address in their discussion is that, to exclude the possibility that octomom copy number has an effect on density, and density on virulence, the effect of these variables should be assessed independently of temperature and age. The obtained results are a valuable contribution to the ongoing debate on the relationship between wMelPop octomom copy number, density and virulence.
References
[1] Monnin, D., Kremer, N., Michaud, C., Villa, M., Henri, H., Desouhant, E. and Vavre, F. (2020) Experimental evolution of virulence and associated traits in a Drosophila melanogaster – Wolbachia symbiosis. bioRxiv, 2020.04.26.062265, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.26.062265
[2] Reyserhove, L., Samaey, G., Muylaert, K., Coppé, V., Van Colen, W., and Decaestecker, E. (2017). A historical perspective of nutrient change impact on an infectious disease in Daphnia. Ecology, 98(11), 2784-2798. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.1994
[3] Ebert, D., and Bull, J. J. (2003). Challenging the trade-off model for the evolution of virulence: is virulence management feasible?. Trends in microbiology, 11(1), 15-20. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0966-842X(02)00003-3
[4] Houwenhuyse, S., Macke, E., Reyserhove, L., Bulteel, L., and Decaestecker, E. (2018). Back to the future in a petri dish: Origin and impact of resurrected microbes in natural populations. Evolutionary Applications, 11(1), 29-41. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/eva.12538
[5] Day, T., and Gandon, S. (2007). Applying population‐genetic models in theoretical evolutionary epidemiology. Ecology Letters, 10(10), 876-888. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01091.x
[6] Alizon, S., Hurford, A., Mideo, N., and Van Baalen, M. (2009). Virulence evolution and the trade‐off hypothesis: history, current state of affairs and the future. Journal of evolutionary biology, 22(2), 245-259. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1420-9101.2008.01658.x
[7] Alizon, S., de Roode, J. C., and Michalakis, Y. (2013). Multiple infections and the evolution of virulence. Ecology letters, 16(4), 556-567. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12076
[8] Decaestecker, E., and King, K. (2019). Red queen dynamics. Reference module in earth systems and environmental sciences, 3, 185-192. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-409548-9.10550-0
[9] Kirk, D., Jones, N., Peacock, S., Phillips, J., Molnár, P. K., Krkošek, M., and Luijckx, P. (2018). Empirical evidence that metabolic theory describes the temperature dependency of within-host parasite dynamics. PLoS biology, 16(2), e2004608. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2004608
[10] Frankel-Bricker, J., Song, M. J., Benner, M. J., and Schaack, S. (2019). Variation in the microbiota associated with Daphnia magna across genotypes, populations, and temperature. Microbial ecology, 1-12. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-019-01412-9