
JOUSSELIN Emmanuelle
- Centre de Biologie pour la Gestion des Populations, INRAe, Montpellier, France
- Adaptation, Macroevolution, Molecular Evolution, Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics, Phylogeography & Biogeography, Species interactions
- recommender
Recommendations: 2
Reviews: 0
Recommendations: 2
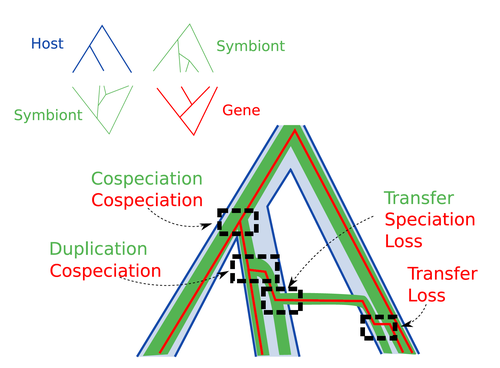
Host-symbiont-gene phylogenetic reconciliation
Reconciling molecular evolution and evolutionary ecology studies: a phylogenetic reconciliation method for gene-symbiont-host systems
Recommended by Emmanuelle Jousselin based on reviews by Vincent Berry and Catherine MatiasInteractions between species are a driving force in evolution. Many organisms host symbiotic partners that live all or part of their life in or on their host. Whether they are mutualistic or parasitic, these symbiotic associations impose strong selective pressures on both partners and affect their evolutionary trajectories. In fine, they can have a significant impact on the diversification patterns of both host and symbiont lineages, with symbiotic lineages sometimes speciating simultaneously with their hosts and/or switching from one host species to another. Long-term associations between species can also result in gene transfers between the involved organisms. Those lateral gene transfers are a source of ecological innovation but can obscure the phylogenetic signals and render the process of phylogenetic reconstructions complex (Lerat et al. 2003).
Methods known as reconciliations explore similarities and differences between phylogenetic trees. They have been widely used to both compare the diversification patterns of hosts and symbionts and identify lateral gene transfers between species. Though the reconciliation approaches used in host/ symbiont and species/ gene phylogenetic studies are identical, they are always applied separately to solve either molecular evolution questions or investigate the evolution of ecological interactions. However, the two questions are often intimately linked and the current interest in multi-level systems (e.g. the holobiont concept) calls for a unique model that will take into account three-level nested organization (gene/symbiont/ host) where both symbiont and genes can transfer among hosts.
Here Menet and collaborators (2023) provide such a model to produce three-level reconciliations. In order to do so, they extend the two-level reconciliation model implemented in “ALE” software (Szöllősi et al. 2013), one of the most used and proven reconciliation methods. Briefly, given a symbiont gene tree, a symbiont tree and a host tree, as in previous reconciliation models, the symbiont tree is mapped onto the host tree by mixing three types of events: Duplication, Transfer or Loss (DTL), with a possibility of the symbiont evolving temporarily outside the host phylogeny (in a “ghost” host lineage). The gene tree evolves similarly inside the symbiont tree, but horizontal transfers are constrained to symbionts co-occurring within the same host. Joint reconciliation scenarios are reconstructed and DTL event rates and likelihoods are estimated according to the model. As a nice addition, the authors propose a method to infer the symbiont phylogeny through amalgamation from gene trees and a host tree.
The authors then explore the diverse possibilities offered by this method by testing it on both simulated datasets and biological datasets in order to check whether considering three nested levels is worthwhile. They convincingly show that three-level reconciliation has a better capacity to retrieve the symbiont donors and receivers of horizontal gene transfers, probably because transfers are constrained by additional elements relevant to the biological systems. Using, aphids, their obligate endosymbionts, and the symbiont genes involved in their nutritional functions, they identify horizontal gene transfers between aphid symbionts that are missed by two-level reconciliations but detected by expertise (Manzano-Marín et al. 2020). The other dataset presented here is on the human pathogen Helicobacter pylori, which history is supposed to reflect human migration. They use more than 1000 H. pylori gene families, and four populations, and use likelihood computations to compare different hypotheses on the diversification of the host.
In summary, this study is a proof-of-concept of a 3-level reconciliation, where the authors manage to convey the applicability of their framework to many biological systems. Reported complexities, confirmed by reported running times, show that the method is computationally efficient. Without a doubt, the tool presented here will be very useful to evolutionary biologists who want to investigate multi-scale cophylogenies and it will move forward the study of associations between host and symbionts when symbiont genomic data are available.
REFERENCES
Lerat, E., Daubin, V., & Moran, N. A. (2003). From gene trees to organismal phylogeny in prokaryotes: the case of the γ-Proteobacteria. PLoS biology, 1(1), e19.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0000019
Manzano-Marın, A., Coeur d'acier, A., Clamens, A. L., Orvain, C., Cruaud, C., Barbe, V., & Jousselin, E. (2020). Serial horizontal transfer of vitamin-biosynthetic genes enables the establishment of new nutritional symbionts in aphids' di-symbiotic systems. The ISME Journal, 14(1), 259-273.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-019-0533-6
Menet H, Trung AN, Daubin V, Tannier E (2023) Host-symbiont-gene phylogenetic reconciliation. bioRxiv, 2022.07.01.498457, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.01.498457
Szöllősi, G. J., Rosikiewicz, W., Boussau, B., Tannier, E., & Daubin, V. (2013). Efficient exploration of the space of reconciled gene trees. Systematic biology, 62(6), 901-912.
https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syt054

Repeated replacements of an intrabacterial symbiont in the tripartite nested mealybug symbiosis
Obligate dependence does not preclude changing partners in a Russian dolls symbiotic system
Recommended by Emmanuelle Jousselin and Fabrice VavreSymbiotic associations with bacterial partners have facilitated important evolutionary transitions in the life histories of eukaryotes. For instance, many insects have established long-term interactions with intracellular bacteria that provide them with essential nutrients lacking in their diet. However, despite the high level of interdependency among organisms involved in endosymbiotic systems, examples of symbiont replacements along the evolutionary history of insect hosts are numerous.
In their paper, Husnik and McCutcheon [1] test the stability of symbiotic systems in a particularly imbricated Russian-doll type interaction, where one bacterium lives insides another bacterium, which itself lives inside insect cells. For their study, they chose representative species of mealybugs (Pseudococcidae), a species rich group of sap-feeding insects that hosts diverse and complex symbiotic systems. In species of the subfamily Pseudococcinae, data published so far suggest that the primary symbiont, a ß-proteobacterium named Tremblaya princeps, is supplemented by a second bacterial symbiont (a ϒ-proteobaterium) that lives within its cytoplasm; both participate to the metabolic pathways that provide essential amino acids and vitamins to their hosts. Here, Husnik and McCutcheon generate host and endosymbiont genome data for five phylogenetically divergent species of Pseudococcinae in order to better understand: 1) the evolutionary history of the symbiotic associations; 2) the metabolic roles of each partner, 3) the timing and origin of Horizontal Gene Transfers (HGT) between the hosts and their symbionts.
Their results show that all species harbour the primary and at least one secondary symbiont, whose intra-bacterial localization was verified using fluorescence in situ hybridization. In one species (Pseudococcus longispinus), Tremblaya even hosts two intracellular bacteria each with a large genome (even though it is not entirely clear whether these two symbionts are indeed found within Tremblaya). The obligate presence of an intra-bacterial symbiont is best explained by the loss in Tremblaya princeps of critical genes for translation that require “intracellular complementation”.
The most striking result concerns the identity of the intra-bacterial symbiont: genome sizes and structures of the “secondary” (intra-Tremblaya) symbionts vary drastically according to the host species. Phylogenetic analyses based on 80 conserved proteins, place all these ϒ-proteoacteria (except one of the P. longispinus symbionts) in a Sodalis allied clade. However, their relationships do not mirror the one of their hosts, and some of them show signs of very recent acquisition. Altogether these results provide strong evidence for several independent acquisitions of these highly intra-bacterial integrated symbionts. Scenarios for the history of the symbiosis are clearly laid out and discussed by the authors, and the scenario involving several independent replacements of a the intra-Tremblaya symbiont by diverse Sodalis-like bacteria appears the most likely given the data presented here.
Selected biosynthetic functions are then mapped onto the host and symbiont genomes, showing the high level of interdependency of the partners for the synthesis of essential amino acids and vitamin. These maps also identify genes in the host genome that might have been acquired through HGT from bacteria and show that many of them are shared by all mealybug species sequenced so far. HGT events have thus predated the acquisitions of the current “intra-Tremblaya“ symbionts and have probably been acquired from previous symbiont infections.
Overall, this is a thorough study, using a diverse set of data and meticulous analyses that present convincing evidence that replacements of symbionts occurred repeatedly even in an imbricated symbiotic system. The phylogenetic analyses inferring the timing of HGTs also depict a highly dynamic history of gene losses and retentions in both host and symbiont genomes. Altogether these results demonstrate how the chimeric nature of individuals allows shuffling at different levels of organisation: organisms like symbionts can be replaced, genes can be exchanged among the partners of the chimera. The surprise is that constraints arising from interdependencies do not impede these exchanges. In the discussion, the authors present a very interesting parallel with the evolution of organelles: if the story presented here mirrors the one of mitochondria, it supports a gradualist view where mitochondria arrived late in the evolution of eukaryotic cells that already contained many bacterial genes resulting from HGT from previous symbionts.
Reference
[1] Husnik F., McCutcheon JP. 2016. Repeated replacements of an intrabacterial symbiont in the tripartite nested mealybug symbiosis. PNAS 113: E5416-E5424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603910113