
MAKOVA Kateryna
- Department of Biology, Penn State University, University Park, United States of America
- Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Genome Evolution, Human Evolution, Molecular Evolution
- recommender
Recommendations: 2
Reviews: 0
Recommendations: 2
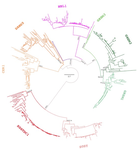
Evolution of the DAN gene family in vertebrates
An evolutionary view of a biomedically important gene family
Recommended by Kateryna Makova based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersThis manuscript [1] investigates the evolutionary history of the DAN gene family—a group of genes important for embryonic development of limbs, kidneys, and left-right axis speciation. This gene family has also been implicated in a number of diseases, including cancer and nephropathies. DAN genes have been associated with the inhibition of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway. Despite this detailed biochemical and functional knowledge and clear importance for development and disease, evolution of this gene family has remained understudied. The diversification of this gene family was investigated in all major groups of vertebrates. The monophyly of the gene members belonging to this gene family was confirmed. A total of five clades were delineated, and two novel lineages were discovered. The first lineage was only retained in cephalochordates (amphioxus), whereas the second one (GREM3) was retained by cartilaginous fish, holostean fish, and coelanth. Moreover, the patterns of chromosomal synteny in the chromosomal regions harboring DAN genes were investigated. Additionally, the authors reconstructed the ancestral gene repertoires and studied the differential retention/loss of individual gene members across the phylogeny. They concluded that the ancestor of gnathostome vertebrates possessed eight DAN genes that underwent differential retention during the evolutionary history of this group. During radiation of vertebrates, GREM1, GREM2, SOST, SOSTDC1, and NBL1 were retained in all major vertebrate groups. At the same time, GREM3, CER1, and DAND5 were differentially lost in some vertebrate lineages. At least two DAN genes were present in the common ancestor of vertebrates, and at least three DAN genes were present in the common ancestor of chordates. Therefore the patterns of retention and diversification in this gene family appear to be complex. Evolutionary slowdown for the DAN gene family was observed in mammals, suggesting selective constraints. Overall, this article puts the biomedical importance of the DAN family in the evolutionary perspective.
References
[1] Opazo JC, Hoffmann FG, Zavala K, Edwards SV (2020) Evolution of the DAN gene family in vertebrates. bioRxiv, 794404, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/794404

A bird’s white-eye view on neosex chromosome evolution
Young sex chromosomes discovered in white-eye birds
Recommended by Kateryna Makova based on reviews by Gabriel Marais, Melissa Wilson and 1 anonymous reviewerRecent advances in next-generation sequencing are allowing us to uncover the evolution of sex chromosomes in non-model organisms. This study [1] represents an example of this application to birds of two Sylvioidea species from the genus Zosterops (commonly known as white-eyes). The study is exemplary in the amount and types of data generated and in the thoroughness of the analysis applied. Both male and female genomes were sequenced to allow the authors to identify sex-chromosome specific scaffolds. These data were augmented by generating the transcriptome (RNA-seq) data set. The findings after the analysis of these extensive data are intriguing: neoZ and neoW chromosome scaffolds and their breakpoints were identified. Novel sex chromosome formation appears to be accompanied by translocation events. The timing of formation of novel sex chromosomes was identified using molecular dating and appears to be relatively recent. Yet first signatures of distinct evolutionary patterns of sex chromosomes vs. autosomes could be already identified. These include the accumulation of transposable elements and changes in GC content. The changes in GC content could be explained by biased gene conversion and altered recombination landscape of the neo sex chromosomes. The authors also study divergence and diversity of genes located on the neo sex chromosomes. Here their findings appear to be surprising and need further exploration. The neoW chromosome already shows unique patterns of divergence and diversity at protein-coding genes as compared with genes on either neoZ or autosomes. In contrast, the genes on the neoZ chromosome do not display divergence or diversity patterns different from those for autosomes. This last observation is puzzling and I believe should be explored in further studies. Overall, this study significantly advances our knowledge of the early stages of sex chromosome evolution in vertebrates, provides an example of how such a study could be conducted in other non-model organisms, and provides several avenues for future work.
References
[1] Leroy T., Anselmetti A., Tilak M.K., Bérard S., Csukonyi L., Gabrielli M., Scornavacca C., Milá B., Thébaud C. and Nabholz B. (2019). A bird’s white-eye view on neo-sex chromosome evolution. bioRxiv, 505610, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/505610