Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields▲ | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
20 Dec 2017
Renewed diversification following Miocene landscape turnover in a Neotropical butterfly radiationNicolas Chazot, Keith R. Willmott, Gerardo Lamas, André V.L. Freitas, Florence Piron-Prunier, Carlos F. Arias, James Mallet, Donna Lisa De-Silva, Marianne Elias 10.1101/148189The influence of environmental change over geological time on the tempo and mode of biological diversification, revealed by Neotropical butterfliesRecommended by Richard H Ree based on reviews by Delano Lewis and 1 anonymous reviewerThe influence of environmental change over geological time on the tempo and mode of biological diversification is a hot topic in biogeography. Of central interest are questions about where, when, and how fast lineages proliferated, suffered extinction, and migrated in response to tectonic events, the waxing and waning of dominant biomes, etc. In this context, the dynamic conditions of the Miocene have received much attention, from studies of many clades and biogeographic regions. Here, Chazot et al. [1] present an exemplary analysis of butterflies (tribe Ithomiini) in the Neotropics, examining their diversification across the Andes and Amazon. They infer sharp contrasts between these regions in the late Miocene: accelerated diversification during orogeny of the Andes, and greater extinction in the Amazon associated during the Pebas system, with interchange and local diversification increasing following the Pebas during the Pliocene. References [1] Chazot N, Willmott KR, Lamas G, Freitas AVL, Piron-Prunier F, Arias CF, Mallet J, De-Silva DL and Elias M. 2017. Renewed diversification following Miocene landscape turnover in a Neotropical butterfly radiation. BioRxiv 148189, ver 4 of 19th December 2017. doi: 10.1101/148189 [2] Xing Y, and Ree RH. 2017. Uplift-driven diversification in the Hengduan Mountains, a temperate biodiversity hotspot. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114: E3444-E3451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616063114 | Renewed diversification following Miocene landscape turnover in a Neotropical butterfly radiation | Nicolas Chazot, Keith R. Willmott, Gerardo Lamas, André V.L. Freitas, Florence Piron-Prunier, Carlos F. Arias, James Mallet, Donna Lisa De-Silva, Marianne Elias | The Neotropical region has experienced a dynamic landscape evolution throughout the Miocene, with the large wetland Pebas occupying western Amazonia until 11-8 my ago and continuous uplift of the Andes mountains along the western edge of South Ame... |  | Macroevolution, Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics, Phylogeography & Biogeography | Richard H Ree | 2017-06-12 11:55:14 | View | |
03 Oct 2018
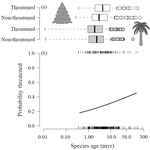
Range size dynamics can explain why evolutionarily age and diversification rate correlate with contemporary extinction risk in plantsAndrew J. Tanentzap, Javier Igea, Matthew G. Johnston, Matthew J. Larcombe https://doi.org/10.1101/152215Are both very young and the very old plant lineages at heightened risk of extinction?Recommended by Arne Mooers based on reviews by Dan Greenberg and 1 anonymous reviewerHuman economic activity is responsible for the vast majority of ongoing extinction, but that does not mean lineages are being affected willy-nilly. For amphibians [1] and South African flowering plants [2], young species have a somewhat higher than expected chance of being threatened with extinction. In contrast, older Australian marsupial lineages seem to be more at risk [3]. Both of the former studies suggested that situations leading to peripheral isolation might simultaneously increase ongoing speciation and current threat via small geographic range, while the authors of the latter study suggested that older species might have evolved increasingly narrow niches. Here, Andrew Tanentzap and colleagues [4] dig deeper into the putative links between species age, niche breadth and threat status. Across 500-some plant genera worldwide, they find that, indeed, ""younger"" species (i.e. from younger and faster-diversifying genera) were more likely to be listed as imperiled by the IUCN, consistent with patterns for amphibians and African plants. Given this, results from their finer-level analyses of conifers are initially bemusing: here, ""older"" (i.e., on longer terminal branches) species were at higher risk. This would make conifers more like Australian marsupials, with the rest of the plants being more like amphibians. However, here where the data were more finely grained, the authors detected a second interesting pattern: using an intriguing matched-pair design, they detect a signal of conifer species niches seemingly shrinking as a function of age. The authors interpret this as consistent with increasing specialization, or loss of ancestral warm wet habitat, over paleontological time. It is true that conifers in general are older than plants more generally, with some species on branches that extend back many 10s of millions of years, and so a general loss of suitable habitat makes some sense. If so, both the pattern for all plants (small initial ranges heightening extinction) and the pattern for conifers (eventual increasing specialization or habitat contraction heightening extinction) could occur, each on a different time scale. As a coda, the authors detected no effect of age on threat status in palms; however, this may be both because palms have already lost species to climate-change induced extinction, and because they are thought to speciate more via long-distance dispersal and adaptive divergence then via peripheral isolation. References [1] Greenberg, D. A., & Mooers, A. Ø. (2017). Linking speciation to extinction: Diversification raises contemporary extinction risk in amphibians. Evolution Letters, 1, 40–48. doi: 10.1002/evl3.4 | Range size dynamics can explain why evolutionarily age and diversification rate correlate with contemporary extinction risk in plants | Andrew J. Tanentzap, Javier Igea, Matthew G. Johnston, Matthew J. Larcombe | <p>Extinction threatens many species, yet few factors predict this risk across the plant Tree of Life (ToL). Taxon age is one factor that may associate with extinction if occupancy of geographic and adaptive zones varies with time, but evidence fo... |  | Macroevolution, Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics, Phylogeography & Biogeography | Arne Mooers | 2018-02-01 21:01:19 | View | |
24 Oct 2019
Testing host-plant driven speciation in phytophagous insects : a phylogenetic perspectiveEmmanuelle Jousselin, Marianne Elias https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.09510v1Phylogenetic approaches for reconstructing macroevolutionary scenarios of phytophagous insect diversificationRecommended by Hervé Sauquet based on reviews by Brian O'Meara and 1 anonymous reviewerPlant-animal interactions have long been identified as a major driving force in evolution. However, only in the last two decades have rigorous macroevolutionary studies of the topic been made possible, thanks to the increasing availability of densely sampled molecular phylogenies and the substantial development of comparative methods. In this extensive and thoughtful perspective [1], Jousselin and Elias thoroughly review current hypotheses, data, and available macroevolutionary methods to understand how plant-insect interactions may have shaped the diversification of phytophagous insects. First, the authors review three main hypotheses that have been proposed to lead to host-plant driven speciation in phytophagous insects: the ‘escape and radiate’, ‘oscillation’, and ‘musical chairs’ scenarios, each with their own set of predictions. Jousselin and Elias then synthesize a vast core of recent studies on different clades of insects, where explicit phylogenetic approaches have been used. In doing so, they highlight heterogeneity in both the methods being used and predictions being tested across these studies and warn against the risk of subjective interpretation of the results. Lastly, they advocate for standardization of phylogenetic approaches and propose a series of simple tests for the predictions of host-driven speciation scenarios, including the characterization of host-plant range history and host breadth history, and diversification rate analyses. This helpful review will likely become a new point of reference in the field and undoubtedly help many researchers formalize and frame questions of plant-insect diversification in future studies of phytophagous insects. References [1] Jousselin, E., Elias, M. (2019). Testing Host-Plant Driven Speciation in Phytophagous Insects: A Phylogenetic Perspective. arXiv, 1910.09510, ver. 1 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol. https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.09510v1 | Testing host-plant driven speciation in phytophagous insects : a phylogenetic perspective | Emmanuelle Jousselin, Marianne Elias | During the last two decades, ecological speciation has been a major research theme in evolutionary biology. Ecological speciation occurs when reproductive isolation between populations evolves as a result of niche differentiation. Phytophagous ins... |  | Macroevolution, Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics, Speciation, Species interactions | Hervé Sauquet | 2019-02-25 17:31:33 | View | |
27 Jul 2020
Evolution of the DAN gene family in vertebratesJuan C. Opazo, Federico G. Hoffmann, Kattina Zavala, Scott V. Edwards https://doi.org/10.1101/794404An evolutionary view of a biomedically important gene familyRecommended by Kateryna Makova based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersThis manuscript [1] investigates the evolutionary history of the DAN gene family—a group of genes important for embryonic development of limbs, kidneys, and left-right axis speciation. This gene family has also been implicated in a number of diseases, including cancer and nephropathies. DAN genes have been associated with the inhibition of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway. Despite this detailed biochemical and functional knowledge and clear importance for development and disease, evolution of this gene family has remained understudied. The diversification of this gene family was investigated in all major groups of vertebrates. The monophyly of the gene members belonging to this gene family was confirmed. A total of five clades were delineated, and two novel lineages were discovered. The first lineage was only retained in cephalochordates (amphioxus), whereas the second one (GREM3) was retained by cartilaginous fish, holostean fish, and coelanth. Moreover, the patterns of chromosomal synteny in the chromosomal regions harboring DAN genes were investigated. Additionally, the authors reconstructed the ancestral gene repertoires and studied the differential retention/loss of individual gene members across the phylogeny. They concluded that the ancestor of gnathostome vertebrates possessed eight DAN genes that underwent differential retention during the evolutionary history of this group. During radiation of vertebrates, GREM1, GREM2, SOST, SOSTDC1, and NBL1 were retained in all major vertebrate groups. At the same time, GREM3, CER1, and DAND5 were differentially lost in some vertebrate lineages. At least two DAN genes were present in the common ancestor of vertebrates, and at least three DAN genes were present in the common ancestor of chordates. Therefore the patterns of retention and diversification in this gene family appear to be complex. Evolutionary slowdown for the DAN gene family was observed in mammals, suggesting selective constraints. Overall, this article puts the biomedical importance of the DAN family in the evolutionary perspective. References [1] Opazo JC, Hoffmann FG, Zavala K, Edwards SV (2020) Evolution of the DAN gene family in vertebrates. bioRxiv, 794404, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/794404 | Evolution of the DAN gene family in vertebrates | Juan C. Opazo, Federico G. Hoffmann, Kattina Zavala, Scott V. Edwards | <p>The DAN gene family (DAN, Differential screening-selected gene Aberrant in Neuroblastoma) is a group of genes that is expressed during development and plays fundamental roles in limb bud formation and digitation, kidney formation and morphogene... |  | Molecular Evolution | Kateryna Makova | 2019-10-15 16:43:13 | View | |
29 Sep 2022
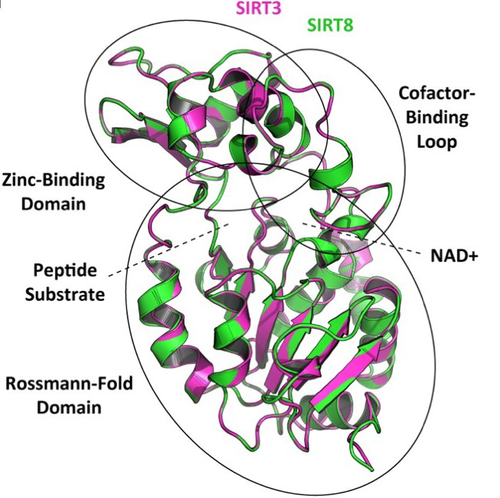
How many sirtuin genes are out there? evolution of sirtuin genes in vertebrates with a description of a new family memberJuan C. Opazo, Michael W. Vandewege, Federico G. Hoffmann, Kattina Zavala, Catalina Meléndez, Charlotte Luchsinger, Viviana A. Cavieres, Luis Vargas-Chacoff, Francisco J. Morera, Patricia V. Burgos, Cheril Tapia-Rojas, Gonzalo A. Mardones https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.17.209510Making sense of vertebrate sirtuin genesRecommended by Frédéric Delsuc based on reviews by Filipe Castro, Nicolas Leurs and 1 anonymous reviewerSirtuin proteins are class III histone deacetylases that are involved in a variety of fundamental biological functions mostly related to aging. These proteins are located in different subcellular compartments and are associated with different biological functions such as metabolic regulation, stress response, and cell cycle control [1]. In mammals, the sirtuin gene family is composed of seven paralogs (SIRT1-7) grouped into four classes [2]. Due to their involvement in maintaining cell cycle integrity, sirtuins have been studied as a way to understand fundamental mechanisms governing longevity [1]. Indeed, the downregulation of sirtuin genes with aging seems to explain much of the pathophysiology that accumulates with aging [3]. Biomedical studies have thus explored the potential therapeutic implications of sirtuins [4] but whether they can effectively be used as molecular targets for the treatment of human diseases remains to be demonstrated [1]. Despite this biomedical interest and some phylogenetic analyses of sirtuin paralogs mostly conducted in mammals, a comprehensive evolutionary analysis of the sirtuin gene family at the scale of vertebrates was still lacking. In this preprint, Opazo and collaborators [5] took advantage of the increasing availability of whole-genome sequences for species representing all main groups of vertebrates to unravel the evolution of the sirtuin gene family. To do so, they undertook a phylogenomic approach in its original sense aimed at improving functional predictions by evolutionary analysis [6] in order to inventory the full vertebrate sirtuin gene repertoire and reconstruct its precise duplication history. Harvesting genomic databases, they extracted all predicted sirtuin proteins and performed phylogenetic analyses based on probabilistic inference methods. Maximum likelihood and Bayesian analyses resulted in well-resolved and congruent phylogenetic trees dividing vertebrate sirtuin genes into three major clades. These analyses also revealed an additional eighth paralog that was previously overlooked because of its restricted phyletic distribution. This newly identified sirtuin family member (named SIRT8) was recovered with unambiguous statistical support as a sister-group to the SIRT3 clade. Comparative genomic analyses based on conserved gene synteny confirmed that SIRT8 was present in all sampled non-amniote vertebrate genomes (cartilaginous fish, bony fish, coelacanth, lungfish, and amphibians) except cyclostomes. SIRT8 has thus most likely been lost in the last common ancestor of amniotes (mammals, reptiles, and birds). Discovery of such previously unknown genes in vertebrates is not completely surprising given the plethora of high-quality genomes now available. However, this study highlights the importance of considering a broad taxonomic sampling to infer evolutionary patterns of gene families that have been mostly studied in mammals because of their potential importance for human biology. Based on its phylogenetic position as closely related to SIRT3 within class I, it could be predicted that the newly identified SIRT8 paralog likely has a deacetylase activity and is probably located in mitochondria. To test these evolutionary predictions, Opazo and collaborators [5] conducted further bioinformatics analyses and functional experiments using the elephant shark (Callorhinchus milii) as a model species. RNAseq expression data were analyzed to determine tissue-specific transcription of sirtuin genes in vertebrates, including SIRT8 found to be mainly expressed in the ovary, which suggests a potential role in biological processes associated with reproduction. The elephant shark SIRT8 protein sequence was used with other vertebrates for comparative analyses of protein structure modeling and subcellular localization prediction both pointing to a probable mitochondrial localization. The protein localization and its function were further characterized by immunolocalization in transfected cells, and enzymatic and functional assays, which all confirmed the prediction that SIRT8 proteins are targeted to the mitochondria and have deacetylase activity. The extensive experimental efforts made in this study to shed light on the function of this newly discovered gene are both rare and highly commendable. Overall, this work by Opazo and collaborators [5] provides a comprehensive phylogenomic study of the sirtuin gene family in vertebrates based on detailed evolutionary analyses using state-of-the-art phylogenetic reconstruction methods. It also illustrates the power of adopting an integrative comparative approach supplementing the reconstruction of the duplication history of the gene family with complementary functional experiments in order to elucidate the function of the newly discovered SIRT8 family member. These results provide a reference phylogenetic framework for the evolution of sirtuin genes and the further functional characterization of the eight vertebrate paralogs with potential relevance for understanding the cellular biology of aging and its associated diseases in human. References [1] Vassilopoulos A, Fritz KS, Petersen DR, Gius D (2011) The human sirtuin family: Evolutionary divergences and functions. Human Genomics, 5, 485. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-7364-5-5-485 [2] Yamamoto H, Schoonjans K, Auwerx J (2007) Sirtuin Functions in Health and Disease. Molecular Endocrinology, 21, 1745–1755. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2007-0079 [3] Morris BJ (2013) Seven sirtuins for seven deadly diseases ofaging. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 56, 133–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.10.525 [4] Bordo D Structure and Evolution of Human Sirtuins. Current Drug Targets, 14, 662–665. http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/1389450111314060007 [5] Opazo JC, Vandewege MW, Hoffmann FG, Zavala K, Meléndez C, Luchsinger C, Cavieres VA, Vargas-Chacoff L, Morera FJ, Burgos PV, Tapia-Rojas C, Mardones GA (2022) How many sirtuin genes are out there? evolution of sirtuin genes in vertebrates with a description of a new family member. bioRxiv, 2020.07.17.209510, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.17.209510 [6] Eisen JA (1998) Phylogenomics: Improving Functional Predictions for Uncharacterized Genes by Evolutionary Analysis. Genome Research, 8, 163–167. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.8.3.163 | How many sirtuin genes are out there? evolution of sirtuin genes in vertebrates with a description of a new family member | Juan C. Opazo, Michael W. Vandewege, Federico G. Hoffmann, Kattina Zavala, Catalina Meléndez, Charlotte Luchsinger, Viviana A. Cavieres, Luis Vargas-Chacoff, Francisco J. Morera, Patricia V. Burgos, Cheril Tapia-Rojas, Gonzalo A. Mardones | <p style="text-align: justify;">Studying the evolutionary history of gene families is a challenging and exciting task with a wide range of implications. In addition to exploring fundamental questions about the origin and evolution of genes, disent... |  | Molecular Evolution | Frédéric Delsuc | Filipe Castro, Anonymous, Nicolas Leurs | 2022-05-12 16:06:04 | View |
11 Jun 2019

A bird’s white-eye view on neosex chromosome evolutionThibault Leroy, Yoann Anselmetti, Marie-Ka Tilak, Sèverine Bérard, Laura Csukonyi, Maëva Gabrielli, Céline Scornavacca, Borja Milá, Christophe Thébaud, Benoit Nabholz https://doi.org/10.1101/505610Young sex chromosomes discovered in white-eye birdsRecommended by Kateryna Makova based on reviews by Gabriel Marais, Melissa Wilson and 1 anonymous reviewerRecent advances in next-generation sequencing are allowing us to uncover the evolution of sex chromosomes in non-model organisms. This study [1] represents an example of this application to birds of two Sylvioidea species from the genus Zosterops (commonly known as white-eyes). The study is exemplary in the amount and types of data generated and in the thoroughness of the analysis applied. Both male and female genomes were sequenced to allow the authors to identify sex-chromosome specific scaffolds. These data were augmented by generating the transcriptome (RNA-seq) data set. The findings after the analysis of these extensive data are intriguing: neoZ and neoW chromosome scaffolds and their breakpoints were identified. Novel sex chromosome formation appears to be accompanied by translocation events. The timing of formation of novel sex chromosomes was identified using molecular dating and appears to be relatively recent. Yet first signatures of distinct evolutionary patterns of sex chromosomes vs. autosomes could be already identified. These include the accumulation of transposable elements and changes in GC content. The changes in GC content could be explained by biased gene conversion and altered recombination landscape of the neo sex chromosomes. The authors also study divergence and diversity of genes located on the neo sex chromosomes. Here their findings appear to be surprising and need further exploration. The neoW chromosome already shows unique patterns of divergence and diversity at protein-coding genes as compared with genes on either neoZ or autosomes. In contrast, the genes on the neoZ chromosome do not display divergence or diversity patterns different from those for autosomes. This last observation is puzzling and I believe should be explored in further studies. Overall, this study significantly advances our knowledge of the early stages of sex chromosome evolution in vertebrates, provides an example of how such a study could be conducted in other non-model organisms, and provides several avenues for future work. References [1] Leroy T., Anselmetti A., Tilak M.K., Bérard S., Csukonyi L., Gabrielli M., Scornavacca C., Milá B., Thébaud C. and Nabholz B. (2019). A bird’s white-eye view on neo-sex chromosome evolution. bioRxiv, 505610, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/505610 | A bird’s white-eye view on neosex chromosome evolution | Thibault Leroy, Yoann Anselmetti, Marie-Ka Tilak, Sèverine Bérard, Laura Csukonyi, Maëva Gabrielli, Céline Scornavacca, Borja Milá, Christophe Thébaud, Benoit Nabholz | <p>Chromosomal organization is relatively stable among avian species, especially with regards to sex chromosomes. Members of the large Sylvioidea clade however have a pair of neo-sex chromosomes which is unique to this clade and originate from a p... |  | Molecular Evolution, Population Genetics / Genomics | Kateryna Makova | 2019-01-24 14:17:15 | View | |
18 Jan 2021

Trait plasticity and covariance along a continuous soil moisture gradientJ Grey Monroe, Haoran Cai, David L Des Marais https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.17.952853Another step towards grasping the complexity of the environmental response of traitsRecommended by Benoit Pujol based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersOne can only hope that one day, we will be able to evaluate how the ecological complexity surrounding natural populations affects their ability to adapt. This is more like a long term quest than a simple scientific aim. Many steps are heading in the right direction. This paper by Monroe and colleagues (2021) is one of them. References Gienapp P. & J.E. Brommer. 2014. Evolutionary dynamics in response to climate change. In: Charmentier A, Garant D, Kruuk LEB, editors. Quantitative genetics in the wild. Oxford: Oxford University Press, Oxford. pp. 254–273. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199674237.003.0015 | Trait plasticity and covariance along a continuous soil moisture gradient | J Grey Monroe, Haoran Cai, David L Des Marais | <p>Water availability is perhaps the greatest environmental determinant of plant yield and fitness. However, our understanding of plant-water relations is limited because it is primarily informed by experiments considering soil moisture variabilit... |  | Phenotypic Plasticity | Benoit Pujol | 2020-02-20 16:34:40 | View | |
29 Sep 2017

Parallel diversifications of Cremastosperma and Mosannona (Annonaceae), tropical rainforest trees tracking Neogene upheaval of the South American continentMichael D. Pirie, Paul J. M. Maas, Rutger A. Wilschut, Heleen Melchers-Sharrott & Lars W. Chatrou 10.1101/141127Unravelling the history of Neotropical plant diversificationRecommended by Hervé Sauquet based on reviews by Thomas Couvreur and Hervé SauquetSouth American rainforests, particularly the Tropical Andes, have been recognized as the hottest spot of plant biodiversity on Earth, while facing unprecedented threats from human impact [1,2]. Considerable research efforts have recently focused on unravelling the complex geological, bioclimatic, and biogeographic history of the region [3,4]. While many studies have addressed the question of Neotropical plant diversification using parametric methods to reconstruct ancestral areas and patterns of dispersal, Pirie et al. [5] take a distinct, complementary approach. Based on a new, near-complete molecular phylogeny of two Neotropical genera of the flowering plant family Annonaceae, the authors modelled the ecological niche of each species and reconstructed the history of niche differentiation across the region. The main conclusion is that, despite similar current distributions and close phylogenetic distance, the two genera experienced rather distinct processes of diversification, responding differently to the major geological events marking the history of the region in the last 20 million years (Andean uplift, drainage of Lake Pebas, and closure of the Panama Isthmus). As a researcher who has not personally worked on Neotropical biogeography, I found this paper captivating and especially enjoyed very much reading the Introduction, which sets out the questions very clearly. The strength of this paper is the near-complete diversity of species the authors were able to sample in each clade and the high-quality data compiled for the niche models. I would recommend this paper as a nice example of a phylogenetic study aimed at unravelling the detailed history of Neotropical plant diversification. While large, synthetic meta-analyses of many clades should continue to seek general patterns [4,6], careful studies restricted on smaller, but well controlled and sampled datasets such as this one are essential to really understand tropical plant diversification in all its complexity. References [1] Antonelli A, and Sanmartín I. 2011. Why are there so many plant species in the Neotropics? Taxon 60, 403–414. [2] Mittermeier RA, Robles-Gil P, Hoffmann M, Pilgrim JD, Brooks TB, Mittermeier CG, Lamoreux JL and Fonseca GAB. 2004. Hotspots revisited: Earths biologically richest and most endangered ecoregions. CEMEX, Mexico City, Mexico 390pp [3] Antonelli A, Nylander JAA, Persson C and Sanmartín I. 2009. Tracing the impact of the Andean uplift on Neotropical plant evolution. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the USA 106, 9749–9754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811421106 [4] Hoorn C, Wesselingh FP, ter Steege H, Bermudez MA, Mora A, Sevink J, Sanmartín I, Sanchez-Meseguer A, Anderson CL, Figueiredo JP, Jaramillo C, Riff D, Negri FR, Hooghiemstra H, Lundberg J, Stadler T, Särkinen T and Antonelli A. 2010. Amazonia through time: Andean uplift, climate change, landscape evolution, and biodiversity. Science 330, 927–931. doi: 10.1126/science.1194585 [5] Pirie MD, Maas PJM, Wilschut R, Melchers-Sharrott H and Chatrou L. 2017. Parallel diversifications of Cremastosperma and Mosannona (Annonaceae), tropical rainforest trees tracking Neogene upheaval of the South American continent. bioRxiv, 141127, ver. 3 of 28th Sept 2017. doi: 10.1101/141127 [6] Bacon CD, Silvestro D, Jaramillo C, Tilston Smith B, Chakrabartye P and Antonelli A. 2015. Biological evidence supports an early and complex emergence of the Isthmus of Panama. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the USA 112, 6110–6115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1423853112 | Parallel diversifications of Cremastosperma and Mosannona (Annonaceae), tropical rainforest trees tracking Neogene upheaval of the South American continent | Michael D. Pirie, Paul J. M. Maas, Rutger A. Wilschut, Heleen Melchers-Sharrott & Lars W. Chatrou | Much of the immense present day biological diversity of Neotropical rainforests originated from the Miocene onwards, a period of geological and ecological upheaval in South America. We assess the impact of the Andean orogeny, drainage of lake Peba... |  | Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics, Phylogeography & Biogeography | Hervé Sauquet | Hervé Sauquet, Thomas Couvreur | 2017-06-03 21:25:48 | View |
09 Feb 2018
Phylodynamic assessment of intervention strategies for the West African Ebola virus outbreakSimon Dellicour, Guy Baele, Gytis Dudas, Nuno R. Faria, Oliver G. Pybus, Marc A. Suchard, Andrew Rambaut, Philippe Lemey https://doi.org/10.1101/163691Simulating the effect of public health interventions using dated virus sequences and geographical dataRecommended by Samuel Alizon based on reviews by Christian Althaus, Chris Wymant and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Christian Althaus, Chris Wymant and 1 anonymous reviewer
Perhaps because of its deadliness, the 2013-2016 Ebola Virus (EBOV) epidemics in West-Africa has led to unprecedented publication and sharing of full virus genome sequences. This was both rapid (90 full genomes were shared within weeks [1]) and important (more than 1500 full genomes have been released overall [2]). Furthermore, the availability of the metadata (especially GPS location) has led to depth analyses of the geographical spread of the epidemics [3]. References [1] Gire et al. 2014. Genomic surveillance elucidates Ebola virus origin and transmission during the 2014 outbreak. Science 345: 1369–1372. doi: 10.1126/science.1259657. | Phylodynamic assessment of intervention strategies for the West African Ebola virus outbreak | Simon Dellicour, Guy Baele, Gytis Dudas, Nuno R. Faria, Oliver G. Pybus, Marc A. Suchard, Andrew Rambaut, Philippe Lemey | <p>This preprint has been reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Evolutionary Biology (https://doi.org/10.24072/pci.evolbiol.100046). The recent Ebola virus (EBOV) outbreak in West Africa witnessed considerable efforts to obtain viral genom... |  | Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics, Phylogeography & Biogeography | Samuel Alizon | 2017-09-30 13:49:57 | View | |
13 Dec 2016

POSTPRINT
Repeated replacements of an intrabacterial symbiont in the tripartite nested mealybug symbiosisHusnik F, McCutcheon JP doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603910113Obligate dependence does not preclude changing partners in a Russian dolls symbiotic systemRecommended by Emmanuelle Jousselin and Fabrice VavreSymbiotic associations with bacterial partners have facilitated important evolutionary transitions in the life histories of eukaryotes. For instance, many insects have established long-term interactions with intracellular bacteria that provide them with essential nutrients lacking in their diet. However, despite the high level of interdependency among organisms involved in endosymbiotic systems, examples of symbiont replacements along the evolutionary history of insect hosts are numerous.
In their paper, Husnik and McCutcheon [1] test the stability of symbiotic systems in a particularly imbricated Russian-doll type interaction, where one bacterium lives insides another bacterium, which itself lives inside insect cells. For their study, they chose representative species of mealybugs (Pseudococcidae), a species rich group of sap-feeding insects that hosts diverse and complex symbiotic systems. In species of the subfamily Pseudococcinae, data published so far suggest that the primary symbiont, a ß-proteobacterium named Tremblaya princeps, is supplemented by a second bacterial symbiont (a ϒ-proteobaterium) that lives within its cytoplasm; both participate to the metabolic pathways that provide essential amino acids and vitamins to their hosts. Here, Husnik and McCutcheon generate host and endosymbiont genome data for five phylogenetically divergent species of Pseudococcinae in order to better understand: 1) the evolutionary history of the symbiotic associations; 2) the metabolic roles of each partner, 3) the timing and origin of Horizontal Gene Transfers (HGT) between the hosts and their symbionts. Reference [1] Husnik F., McCutcheon JP. 2016. Repeated replacements of an intrabacterial symbiont in the tripartite nested mealybug symbiosis. PNAS 113: E5416-E5424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603910113 | Repeated replacements of an intrabacterial symbiont in the tripartite nested mealybug symbiosis | Husnik F, McCutcheon JP | Stable endosymbiosis of a bacterium into a host cell promotes cellular and genomic complexity. The mealybug *Planococcus citri* has two bacterial endosymbionts with an unusual nested arrangement: the γ-proteobacterium *Moranella endobia* lives in ... |  | Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics, Species interactions | Emmanuelle Jousselin | 2016-12-13 14:27:09 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Guillaume Achaz
Juan Arroyo
Trine Bilde
Dustin Brisson
Marianne Elias
Inês Fragata
Matteo Fumagalli
Tatiana Giraud
Frédéric Guillaume
Ruth Hufbauer
Sara Magalhaes
Caroline Nieberding
Michael David Pirie
Tanja Pyhäjärvi
Tanja Schwander
Alejandro Gonzalez Voyer










