Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields▼ | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
07 Nov 2017

MaxTiC: Fast ranking of a phylogenetic tree by Maximum Time Consistency with lateral gene transfersCédric Chauve, Akbar Rafiey, Adrian A. Davin, Celine Scornavacca, Philippe Veber, Bastien Boussau, Gergely J Szöllosi, Vincent Daubin, and Eric Tannier 10.1101/127548Dating nodes in a phylogeny using inferred horizontal gene transfersRecommended by Tatiana Giraud and Toni Gabaldon based on reviews by Alexandros Stamatakis, Mukul Bansal and 2 anonymous reviewersDating nodes in a phylogeny is an important problem in evolution and is typically performed by using molecular clocks and fossil age estimates [1]. The manuscript by Chauve et al. [2] reports a novel method, which uses lateral gene transfers to help ordering nodes in a species tree. The idea is that a lateral gene transfer can only occur between two species living at the same time, which indirectly informs on node relative ages in a phylogeny: the donor species cannot be more recent than the recipient species. Horizontal gene transfers are increasingly recognized as frequent, even in eukaryotes, and especially in micro-organisms that have little fossil records [3-7]. Yet, such an important source of information has been very rarely used so far for inferring relative node ages in phylogenies. In this context, the method by Chauve et al. [2] represents an innovative and original approach to a difficult problem. An obvious limitation of the approach is that it relies on inferences of horizontal transfers, which detection is in itself a difficult problem. Incomplete taxon sampling, or the extinction of the true donor lineage may render patterns difficult to interpret in a temporary fashion. Yet, for clades with no fossils this may be the only piece of information we have at hand, and the growing amount of sequence data is likely to minimize issues derived from incomplete sampling. The developed method, MaxTiC (for Maximal Time Consistency) [2], represents a very nice application of theoretical developments on the well-known « Feedback Arc Set » computer science problem to the evolutionary question of ordering nodes in a phylogeny. MaxTiC uses as input a species tree and a set of time constraints based on lateral gene transfers inferred using other softwares, and minimizes conflicts between node ordering and these time constraints. The application of MaxTiC on simulated datasets indicated that node ordering was fairly accurate [2]. MaxTiC is implemented in a freely available software, which represents original and relevant contribution to the field of evolutionary biology. References [1] Donoghue P and Smith M, editors. 2003. Telling the evolutionary time. CRC press. [2] Chauve C, Rafiey A, Davin AA, Scornavacca C, Veber P, Boussau B, Szöllősi GJ, Daubin V and Tannier E. 2017. MaxTiC: Fast ranking of a phylogenetic tree by Maximum Time Consistency with lateral gene transfers. bioRxiv 127548, ver. 6 of 6th November 2017. doi: 10.1101/127548 [3] Ropars J, Rodríguez de la Vega RC, Lopez-Villavicencio M, Gouzy J, Sallet E, Debuchy R, Dupont J, Branca A and Giraud T. 2015. Adaptive horizontal gene transfers between multiple cheese-associated fungi. Current Biology 19, 2562–2569. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.08.025 [4] Novo M, Bigey F, Beyne E, Galeote V, Gavory F, Mallet S, Cambon B, Legras JL, Wincker P, Casaregola S and Dequin S. 2009. Eukaryote-to-eukaryote gene transfer events revealed by the genome sequence of the wine yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae EC1118. Proceeding of the National Academy of Science USA, 106, 16333–16338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904673106 [5] Naranjo-Ortíz MA, Brock M, Brunke S, Hube B, Marcet-Houben M, Gabaldón T. 2016. Widespread inter- and intra-domain horizontal gene transfer of d-amino acid metabolism enzymes in Eukaryotes. Frontiers in Microbiology 7, 2001. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.02001 [6] Alexander WG, Wisecaver JH, Rokas A, Hittinger CT. 2016. Horizontally acquired genes in early-diverging pathogenic fungi enable the use of host nucleosides and nucleotides. Proceeding of the National Academy of Science USA. 113, 4116–4121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1517242113 [7] Marcet-Houben M, Gabaldón T. 2010. Acquisition of prokaryotic genes by fungal genomes. Trends in Genetics. 26, 5–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2009.11.007 | MaxTiC: Fast ranking of a phylogenetic tree by Maximum Time Consistency with lateral gene transfers | Cédric Chauve, Akbar Rafiey, Adrian A. Davin, Celine Scornavacca, Philippe Veber, Bastien Boussau, Gergely J Szöllosi, Vincent Daubin, and Eric Tannier | Lateral gene transfers (LGTs) between ancient species contain information about the relative timing of species diversification. Specifically, the ancestors of a donor species must have existed before the descendants of the recipient species. Hence... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Evolutionary Dynamics, Genome Evolution, Life History, Molecular Evolution, Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics | Tatiana Giraud | 2017-06-28 13:40:52 | View | |
28 Mar 2024
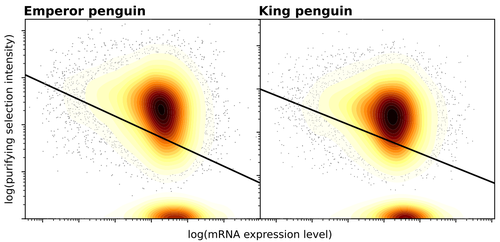
Gene expression is the main driver of purifying selection in large penguin populationsEmiliano Trucchi, Piergiorgio Massa, Francesco Giannelli, Thibault Latrille, Flavia A.N. Fernandes, Lorena Ancona, Nils Chr Stenseth, Joan Ferrer Obiol, Josephine Paris, Giorgio Bertorelle, Celine Le Bohec https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.08.552445Purifying selection on highly expressed genes in PenguinsRecommended by Bruce Rannala based on reviews by Tanja Pyhäjärvi and 1 anonymous reviewerGiven the general importance of protein expression levels, in cells it is widely accepted that gene expression levels are often a target of natural selection and that most mutations affecting gene expression levels are therefore likely to be deleterious [1]. However, it is perhaps less obvious that the strength of selection on the regulated genes themselves may be influenced by their expression levels. This might be due to harmful effects of misfolded proteins, for example, when higher protein concentrations exist in cells [2]. Recent studies have suggested that highly expressed genes accumulate fewer deleterious mutations; thus a positive relationship appears to exist between gene expression levels and the relative strength of purifying selection [3]. The recommended paper by Trucchi et al. [4] examines the relationship between gene expression, purifying selection and a third variable -- effective population size -- in populations of two species of penguin with different population sizes, the Emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri) and the King penguin (A. patagonicus). Using transcriptomic data and computer simulations modeling selection, they examine patterns of nonsynonymous and synonymous segregating polymorphisms (p) across genes in the two populations, concluding that even in relatively small populations purifying selection has an important effect in eliminating deleterious mutations. References 1] Gilad Y, Oshlack A, and Rifkin SA. 2006. Natural selection on gene expression. Trends in Genetics 22: 456-461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2006.06.002 [4] Trucchi E, Massa P, Giannelli F, Latrille T, Fernandes FAN, Ancona L, Stenseth NC, Obiol JF, Paris J, Bertorelle G, and Le Bohec, C. 2023. Gene expression is the main driver of purifying selection in large penguin populations. bioRxiv 2023.08.08.552445, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.08.552445
| Gene expression is the main driver of purifying selection in large penguin populations | Emiliano Trucchi, Piergiorgio Massa, Francesco Giannelli, Thibault Latrille, Flavia A.N. Fernandes, Lorena Ancona, Nils Chr Stenseth, Joan Ferrer Obiol, Josephine Paris, Giorgio Bertorelle, Celine Le Bohec | <p style="text-align: justify;">Purifying selection is the most pervasive type of selection, as it constantly removes deleterious mutations arising in populations, directly scaling with population size. Highly expressed genes appear to accumulate ... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Evolutionary Dynamics, Evolutionary Theory, Population Genetics / Genomics | Bruce Rannala | 2023-08-09 17:53:03 | View | |
03 Oct 2023
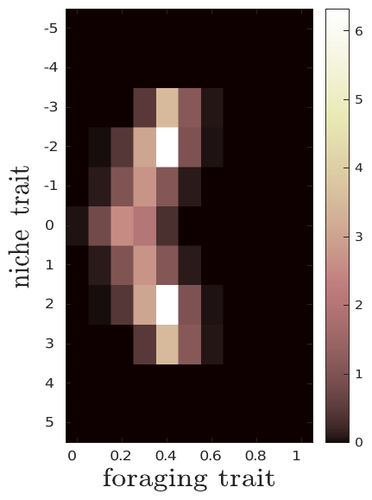
The evolutionary dynamics of plastic foraging and its ecological consequences: a resource-consumer modelLéo Ledru, Jimmy Garnier, Océane Guillot, Erwan Faou, Camille Noûs, Sébastien Ibanez https://doi.org/10.32942/X2QG7MEvolution and consequences of plastic foraging behavior in consumer-resource ecosystemsRecommended by François Rousset based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersPlastic responses of organisms to their environment may be maladaptive in particular when organisms are exposed to new environments. Phenotypic plasticity may also have opposite effects on the adaptive response of organisms to environmental changes: whether phenotypic plasticity favors or hinders such adaptation depends on a balance between the ability of the population to respond to the change non-genetically in the short term, and the weakened genetic response to environmental change. These topics have received continued attention, particularly in the context of climate change (e.g., Chevin et al. 2013, Duputié et al., 2015, Vinton et al . 2022). In their work, Ledru et al. focus on the adaptive nature of plastic behavior and on its consequences in a consumer-resource ecosystem. As they emphasize, previous works have found that plastic foraging promotes community stability, but these did not consider plasticity as an evolving trait, so Ledru et al. set out to test whether this conclusion holds when both plastic foraging and niche traits of consumers and resources evolve (though ultimately, their new conclusions may not all depend on plasticity evolving). Along the way, they first seek to clarify when such plasticity will evolve, and how it affects the evolution of the niche diversity of consumers and resources, before turning to the question of consumer persistence. The model is rather complex, as three traits are allowed to evolve, and the resource uptake expressed through plastic behavior has its own dynamics affected by some form of social learning. Classically, in models of niche evolution, a consumer's efficiency in exploiting a resource characterized by a trait y (here, the resource's individual niche trait), has been described in terms of location-scale (typically Gaussian) kernels, with mean x (the consumer's individual niche trait) specifying the most efficiently exploited resource, and with variance characterizing individual niche breadth. The evolution of the variance has been considered in some previous models but is assumed to be fixed here. Rather, the new model considers the evolution of the distribution of resource traits, of the consumer's individual niche trait (which is not plastic), and of a "plastic foraging trait" that controls the relative time spent foraging plastically versus foraging randomly. When foraging plastically, the consumers modify their foraging effort towards the type of resource that maximizes their energy intake. in some previous models, the effect of variation in the extent of plastic foraging was already considered, but the evolution of allocation to a plastic foraging strategy versus random foraging was not considered. The model is formulated through reaction-diffusion equations, and its dynamics is investigated by numerical integration. Foraging plasticity readily evolves, when resources vary widely enough, competition for resources is strong, and the cost of plasticity is weak. This means in particular that a large individual niche width of consumers selects for increased plastic foraging, as the evolution of plastic foraging leads to reduced niche overlap between consumers. The evolution of plastic foraging itself generally, though not always, favors the diversification of the niche traits of consumers and of resources. There is thus a positive feedback loop between plastic foraging and resource diversity. Ledru et al. conclude that the total niche width of the consumer population should also correlate with the evolution of plastic foraging, an implication which they relate to the so-called niche variation hypothesis and to empirical tests of it. The joint evolution of the consumer's individual niche trait and plastic foraging trait generates a striking pattern within populations: consumers whose individual niche trait is at an edge of the resource distribution forage more plastically. The authors observe that this relatively simple prediction has not been subjected to any empirical test. Returning to the question of consumer persistence, Ledru et al. evaluate this persistence when consumer mortality increases, and in response to either gradual or sudden environmental changes. These different perturbations all reduce the benefits of plastic foraging. The effect of plastic foraging on stability are complex, being negative or positive effect depending on the type of disturbance, and in particular the ecosystem has a lower sustainable rate of environmental change in the presence of plastic foraging. However, allowing the evolutionary regression of plastic foraging then has a comparatively positive effect on persistence. Despite the substantial effort devoted to analyzing this complex model, relaxing some of its assumptions would likely reveal further complexities. Notably, the overall effect of plasticity on consumer persistence depends on effects already encountered in models of the adaptive response of single species to environmental change: a fast non-genetic response in the short term versus a weakened genetic response in the longer term. The overall balance between these opposite effects on adaptation may be difficult to predict robustly. In the case of a constant rate of environmental change, the results of the present model depend on a lag load between the trait changes of consumer and resource populations, and the extent of the lag may also depend on many factors, such as the extent of genetic variation (e.g., Bürger & Lynch, 1995) for niche traits in consumers and resources. Here, the same variance of mutational effects was assumed for all three evolving traits. Further, spatial environmental variation, a central issue in studies of adaptive responses to environmental changes (e.g., Parmesan, 2006, Zhu et al., 2012), was not considered. Finally, the rate of adjustment of effort by consumers with given niche trait and plastic foraging trait values was assumed proportional to the density of consumers with such trait values. This was justified as a way of accounting for the use of social cues during foraging, but to the extent that they occur, social effects could manifest themselves through other learning dynamics. In conclusion, Ledru et al. have addressed a broad range of questions, suggesting new empirical tests of behavioural patterns on one side, and recovering in the context of community response to environmental changes a complexity that could be expected from earlier works on adaptive responses of organisms but that has been overlooked by previous works on community effects of phenotypic plasticity. References Bürger, R. and Lynch, M. (1995), Evolution and extinction in a changing environment: a quantitative-genetic analysis. Evolution, 49: 151-163. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1995.tb05967.x Chevin, L.-M., Collins, S. and Lefèvre, F. (2013), Phenotypic plasticity and evolutionary demographic responses to climate change: taking theory out to the field. Funct Ecol, 27: 967-979. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2435.2012.02043.x Duputié, A., Rutschmann, A., Ronce, O. and Chuine, I. (2015), Phenological plasticity will not help all species adapt to climate change. Glob Change Biol, 21: 3062-3073. https://doi-org.inee.bib.cnrs.fr/10.1111/gcb.12914 Ledru, L., Garnier, J., Guillot, O., Faou, E., & Ibanez, S. (2023). The evolutionary dynamics of plastic foraging and its ecological consequences: a resource-consumer model. EcoEvoRxiv, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.32942/X2QG7M Parmesan, C. (2006) Ecological and evolutionary responses to recent climate change Vinton, A.C., Gascoigne, S.J.L., Sepil, I., Salguero-Gómez, R., (2022) Plasticity’s role in adaptive evolution depends on environmental change components. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 37: 1067-1078. Zhu, K., Woodall, C.W. and Clark, J.S. (2012), Failure to migrate: lack of tree range expansion in response to climate change. Glob Change Biol, 18: 1042-1052. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02571.x | The evolutionary dynamics of plastic foraging and its ecological consequences: a resource-consumer model | Léo Ledru, Jimmy Garnier, Océane Guillot, Erwan Faou, Camille Noûs, Sébastien Ibanez | <p style="text-align: justify;">Phenotypic plasticity has important ecological and evolutionary consequences. In particular, behavioural phenotypic plasticity such as plastic foraging (PF) by consumers, may enhance community stability. Yet little ... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Evolutionary Dynamics, Evolutionary Ecology, Phenotypic Plasticity | François Rousset | 2023-03-25 12:04:08 | View | |
20 Jan 2020

A young age of subspecific divergence in the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria, inferred by ABC Random ForestMarie-Pierre Chapuis, Louis Raynal, Christophe Plantamp, Christine N. Meynard, Laurence Blondin, Jean-Michel Marin, Arnaud Estoup https://doi.org/10.1101/671867Estimating recent divergence history: making the most of microsatellite data and Approximate Bayesian Computation approachesRecommended by Takeshi Kawakami and Concetta Burgarella based on reviews by Michael D Greenfield and 2 anonymous reviewersThe present-day distribution of extant species is the result of the interplay between their past population demography (e.g., expansion, contraction, isolation, and migration) and adaptation to the environment. Shedding light on the timing and magnitude of key demographic events helps identify potential drivers of such events and interaction of those drivers, such as life history traits and past episodes of environmental shifts. The understanding of the key factors driving species evolution gives important insights into how the species may respond to changing conditions, which can be particularly relevant for the management of harmful species, such as agricultural pests (e.g. [1]). Meaningful demographic inferences present major challenges. These include formulating evolutionary scenarios fitting species biology and the eco-geographical context and choosing informative molecular markers and accurate quantitative approaches to statistically compare multiple demographic scenarios and estimate the parameters of interest. A further issue comes with result interpretation. Accurately dating the inferred events is far from straightforward since reliable calibration points are necessary to translate the molecular estimates of the evolutionary time into absolute time units (i.e. years). This can be attempted in different ways, such as by using fossil and archaeological records, heterochronous samples (e.g. ancient DNA), and/or mutation rate estimated from independent data (e.g. [2], [3] for review). Nonetheless, most experimental systems rarely meet these conditions, hindering the comprehensive interpretation of results. The contribution of Chapuis et al. [4] addresses these issues to investigate the recent history of the African insect pest Schistocerca gregaria (desert locust). They apply Approximate Bayesian Computation-Random Forest (ABC-RF) approaches to microsatellite markers. Owing to their fast mutation rate microsatellite markers offer at least two advantages: i) suitability for analyzing recently diverged populations, and ii) direct estimate of the germline mutation rate in pedigree samples. The work of Chapuis et al. [4] benefits of both these advantages, since they have estimates of mutation rate and allele size constraints derived from germline mutations in the species [5]. The main aim of the study is to infer the history of divergence of the two subspecies of the desert locust, which have spatially disjoint distribution corresponding to the dry regions of North and West-South Africa. They first use paleo-vegetation maps to formulate hypotheses about changes in species range since the last glacial maximum. Based on them, they generate 12 divergence models. For the selection of the demographic model and parameter estimation, they apply the recently developed ABC-RF approach, a powerful inferential tool that allows optimizing the use of summary statistics information content, among other advantages [6]. Some methodological novelties are also introduced in this work, such as the computation of the error associated with the posterior parameter estimates under the best scenario. The accuracy of timing estimate is assured in two ways: i) by the use of microsatellite markers with known evolutionary dynamics, as underlined above, and ii) by assessing the divergence time threshold above which posterior estimates are likely to be biased by size homoplasy and limits in allele size range [7]. The best-supported model suggests a recent divergence event of the subspecies of S. gregaria (around 2.6 kya) and a reduction of populations size in one of the subspecies (S. g. flaviventris) that colonized the southern distribution area. As such, results did not support the hypothesis that the southward colonization was driven by the expansion of African dry environments associated with the last glacial maximum, as it has been postulated for other arid-adapted species with similar African disjoint distributions [8]. The estimated time of divergence points at a much more recent origin for the two subspecies, during the late Holocene, in a period corresponding to fairly stable arid conditions similar to current ones [9,10]. Although the authors cannot exclude that their microsatellite data bear limited information on older colonization events than the last one, they bring arguments in favour of alternative explanations. The hypothesis privileged does not involve climatic drivers, but the particularly efficient dispersal behaviour of the species, whose individuals are able to fly over long distances (up to thousands of kilometers) under favourable windy conditions. A single long-distance dispersal event by a few individuals would explain the genetic signature of the bottleneck. There is a growing number of studies in phylogeography in arid regions in the Southern hemisphere, but the impact of past climate changes on the species distribution in this region remains understudied relative to the Northern hemisphere [11,12]. The study presented by Chapuis et al. [4] offers several important insights into demographic changes and the evolutionary history of an agriculturally important pest species in Africa, which could also mirror the history of other organisms in the continent. As the authors point out, there are necessarily some uncertainties associated with the models of past ecosystems and climate, especially for Africa. Interestingly, the authors argue that the information on paleo-vegetation turnover was more informative than climatic niche modeling for the purpose of their study since it made them consider a wider range of bio-geographical changes and in turn a wider range of evolutionary scenarios (see discussion in Supplementary Material). Microsatellite markers have been offering a useful tool in population genetics and phylogeography for decades, but their popularity is perhaps being taken over by single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotyping and whole-genome sequencing (WGS) (the peak year of the number of the publication with “microsatellite” is in 2012 according to PubMed). This study reaffirms the usefulness of these classic molecular markers to estimate past demographic events, especially when species- and locus-specific microsatellite mutation features are available and a powerful inferential approach is adopted. Nonetheless, there are still hurdles to overcome, such as the limitations in scenario choice associated with the simulation software used (e.g. not allowing for continuous gene flow in this particular case), which calls for further improvement of simulation tools allowing for more flexible modeling of demographic events and mutation patterns. In sum, this work not only contributes to our understanding of the makeup of the African biodiversity but also offers a useful statistical framework, which can be applied to a wide array of species and molecular markers (microsatellites, SNPs, and WGS). References [1] Lehmann, P. et al. (2018). Complex responses of global insect pests to climate change. bioRxiv, 425488. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1101/425488 [2] Donoghue, P. C., & Benton, M. J. (2007). Rocks and clocks: calibrating the Tree of Life using fossils and molecules. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 22(8), 424-431. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2007.05.005 [3] Ho, S. Y., Lanfear, R., Bromham, L., Phillips, M. J., Soubrier, J., Rodrigo, A. G., & Cooper, A. (2011). Time‐dependent rates of molecular evolution. Molecular ecology, 20(15), 3087-3101. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05178.x [4] Chapuis, M.-P., Raynal, L., Plantamp, C., Meynard, C. N., Blondin, L., Marin, J.-M. and Estoup, A. (2020). A young age of subspecific divergence in the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria, inferred by ABC Random Forest. bioRxiv, 671867, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evolutionary Biology. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1101/671867 5] Chapuis, M.-P., Plantamp, C., Streiff, R., Blondin, L., & Piou, C. (2015). Microsatellite evolutionary rate and pattern in Schistocerca gregaria inferred from direct observation of germline mutations. Molecular ecology, 24(24), 6107-6119. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1111/mec.13465 [6] Raynal, L., Marin, J. M., Pudlo, P., Ribatet, M., Robert, C. P., & Estoup, A. (2018). ABC random forests for Bayesian parameter inference. Bioinformatics, 35(10), 1720-1728. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty867 [7] Estoup, A., Jarne, P., & Cornuet, J. M. (2002). Homoplasy and mutation model at microsatellite loci and their consequences for population genetics analysis. Molecular ecology, 11(9), 1591-1604. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294X.2002.01576.x [8] Moodley, Y. et al. (2018). Contrasting evolutionary history, anthropogenic declines and genetic contact in the northern and southern white rhinoceros (Ceratotherium simum). Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 285(1890), 20181567. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2018.1567 [9] Kröpelin, S. et al. (2008). Climate-driven ecosystem succession in the Sahara: the past 6000 years. science, 320(5877), 765-768. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1154913 [10] Maley, J. et al. (2018). Late Holocene forest contraction and fragmentation in central Africa. Quaternary Research, 89(1), 43-59. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1017/qua.2017.97 [11] Beheregaray, L. B. (2008). Twenty years of phylogeography: the state of the field and the challenges for the Southern Hemisphere. Molecular Ecology, 17(17), 3754-3774. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03857.x [12] Dubey, S., & Shine, R. (2012). Are reptile and amphibian species younger in the Northern Hemisphere than in the Southern Hemisphere?. Journal of evolutionary biology, 25(1), 220-226. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1420-9101.2011.02417.x ***** A video about this preprint is available here: | A young age of subspecific divergence in the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria, inferred by ABC Random Forest | Marie-Pierre Chapuis, Louis Raynal, Christophe Plantamp, Christine N. Meynard, Laurence Blondin, Jean-Michel Marin, Arnaud Estoup | <p>Dating population divergence within species from molecular data and relating such dating to climatic and biogeographic changes is not trivial. Yet it can help formulating evolutionary hypotheses regarding local adaptation and future responses t... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Evolutionary Applications, Phylogeography & Biogeography, Population Genetics / Genomics | Takeshi Kawakami | 2019-06-20 10:31:15 | View | |
17 Nov 2017

ABC random forests for Bayesian parameter inferenceLouis Raynal, Jean-Michel Marin, Pierre Pudlo, Mathieu Ribatet, Christian P. Robert, Arnaud Estoup https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.05537Machine learning methods are useful for Approximate Bayesian Computation in evolution and ecologyRecommended by Michael Blum based on reviews by Dennis Prangle and Michael BlumIt is my pleasure to recommend the paper by Raynal et al. [1] about using random forest for parameter inference. There are two reviews about the paper, one review written by Dennis Prangle and another review written by myself. Both reviews were positive and included comments that have been addressed in the current version of the preprint. The paper nicely shows that modern machine learning approaches are useful for Approximate Bayesian Computation (ABC) and more generally for simulation-driven parameter inference in ecology and evolution. The authors propose to consider the random forest approach, proposed by Meinshausen [2] to perform quantile regression. The numerical implementation of ABC with random forest, available in the abcrf package, is based on the RANGER R package that provides a fast implementation of random forest for high-dimensional data. According to my reading of the manuscript, there are 3 main advantages when using random forest (RF) for parameter inference with ABC. The first advantage is that RF can handle many summary statistics and that dimension reduction is not needed when using RF. The second advantage is very nicely displayed in Figure 5, which shows the main result of the paper. If correct, 95% posterior credibility intervals (C.I.) should contain 95% of the parameter values used in simulations. Figure 5 shows that posterior C.I. obtained with rejection are too large compared to other methods. By contrast, C.I. obtained with regression methods have been shrunken. However, the shrinkage can be excessive for the smallest tolerance rates, with coverage values that can be equal to 85% instead of the expected 95% value. The attractive property of RF is that C.I. have been shrunken but the coverage is of 100% resulting in a conservative decision about parameter values. The last advantage is that no hyperparameter should be chosen. It is a parameter free approach, which is desirable because of the potential difficulty of choosing an appropriate acceptance rate. The main drawback of the proposed approach concerns joint parameter inference. There are many settings where the joint parameter distribution is of interest and the proposed RF approach cannot handle that. In population genetics for example, estimation of the severity and of the duration of the bottleneck should be estimated jointly because of identifiability issues. The challenge of performing joint parameter inference with RF might constitute a useful research perspective. References [1] Raynal L, Marin J-M, Pudlo P, Ribatet M, Robert CP, Estoup A. 2017. ABC random forests for Bayesian parameter inference. arXiv 1605.05537v4, https://arxiv.org/pdf/1605.05537 | ABC random forests for Bayesian parameter inference | Louis Raynal, Jean-Michel Marin, Pierre Pudlo, Mathieu Ribatet, Christian P. Robert, Arnaud Estoup | This preprint has been reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Evolutionary Biology (http:// dx.doi.org/ 10.24072/ pci.evolbiol.100036). Approximate Bayesian computation (ABC) has grown into a standard methodology that manages Bayesian infer... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Evolutionary Applications, Other, Population Genetics / Genomics | Michael Blum | 2017-07-06 07:42:00 | View | |
21 Nov 2018
Convergent evolution as an indicator for selection during acute HIV-1 infectionFrederic Bertels, Karin J Metzner, Roland R Regoes https://doi.org/10.1101/168260Is convergence an evidence for positive selection?Recommended by Guillaume Achaz based on reviews by Jeffrey Townsend and 1 anonymous reviewerThe preprint by Bertels et al. [1] reports an interesting application of the well-accepted idea that positively selected traits (here variants) can appear several times independently; think about the textbook examples of flight capacity. Hence, the authors assume that reciprocally convergence implies positive selection. The methodology becomes then, in principle, straightforward as one can simply count variants in independent datasets to detect convergent mutations. References [1] Bertels, F., Metzner, K. J., & Regoes R. R. (2018). Convergent evolution as an indicator for selection during acute HIV-1 infection. BioRxiv, 168260, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol. doi: 10.1101/168260 | Convergent evolution as an indicator for selection during acute HIV-1 infection | Frederic Bertels, Karin J Metzner, Roland R Regoes | <p>Convergent evolution describes the process of different populations acquiring similar phenotypes or genotypes. Complex organisms with large genomes only rarely and only under very strong selection converge to the same genotype. In contrast, ind... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Evolutionary Applications, Genome Evolution, Molecular Evolution | Guillaume Achaz | 2017-07-26 08:39:17 | View | |
17 Dec 2016
POSTPRINT
Evolution of HIV virulence in response to widespread scale up of antiretroviral therapy: a modeling studyHerbeck JT, Mittler JE, Gottlieb GS, Goodreau SM, Murphy JT, Cori A, Pickles M, Fraser C 10.1093/ve/vew028Predicting HIV virulence evolution in response to widespread treatmentRecommended by Samuel Alizon and Roger Kouyos and Roger Kouyos
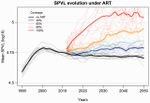
It is a classical result in the virulence evolution literature that treatments decreasing parasite replication within the host should select for higher replication rates, thus driving increased levels of virulence if the two are correlated. There is some evidence for this in vitro but very little in the field. HIV infections in humans offer a unique opportunity to go beyond the simple predictions that treatments should favour more virulent strains because many details of this host-parasite system are known, especially the link between set-point virus load, transmission rate and virulence. To tackle this question, Herbeck et al. [1] used a detailed individual-based model. This is original because it allows them to integrate existing knowledge from the epidemiology and evolution of HIV (e.g. recent estimates of the ‘heritability’ of set-point virus load from one infection to the next). This detailed model allows them to formulate predictions regarding the effect of different treatment policies; especially regarding the current policy switch away from treatment initiation based on CD4 counts towards universal treatment. The results show that, perhaps as expected from the theory, treatments based on the level of remaining host target cells (CD4 T cells) do not affect virulence evolution because they do not strongly affect the virulence level that maximizes HIV’s transmission potential. However, early treatments can lead to moderate increase in virulence within several years if coverage is high enough. These results seem quite robust to variation of all the parameters in realistic ranges. The great step forward in this model is the ability to obtain quantitative prediction regarding how a virus may evolve in response to public health policies. Here the main conclusion is that given our current knowledge in HIV biology, the risk of virulence evolution is perhaps more limited than expected from a direct application of virulence evolution model. Interestingly, the authors also conclude that recently observed increased in HIV virulence [2-3] cannot be explained by the impact of antiretroviral therapy alone; which raises the question about the main mechanism behind this increase. Finally, the authors make the interesting suggestion that “changing virulence is amenable to being monitored alongside transmitted drug resistance in sentinel surveillance”. References [1] Herbeck JT, Mittler JE, Gottlieb GS, Goodreau SM, Murphy JT, Cori A, Pickles M, Fraser C. 2016. Evolution of HIV virulence in response to widespread scale up of antiretroviral therapy: a modeling study. Virus Evolution 2:vew028. doi: 10.1093/ve/vew028 [2] Herbeck JT, Müller V, Maust BS, Ledergerber B, Torti C, et al. 2012. Is the virulence of HIV changing? A meta-analysis of trends in prognostic markers of HIV disease progression and transmission. AIDS 26:193-205. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32834db418 [3] Pantazis N, Porter K, Costagliola D, De Luca A, Ghosn J, et al. 2014. Temporal trends in prognostic markers of HIV-1 virulence and transmissibility: an observational cohort study. Lancet HIV 1:e119-26. doi: 10.1016/s2352-3018(14)00002-2 | Evolution of HIV virulence in response to widespread scale up of antiretroviral therapy: a modeling study | Herbeck JT, Mittler JE, Gottlieb GS, Goodreau SM, Murphy JT, Cori A, Pickles M, Fraser C | There are global increases in the use of HIV antiretroviral therapy (ART), guided by clinical benefits of early ART initiation and the efficacy of treatment as prevention of transmission. Separately, it has been shown theoretically and empirically... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Evolutionary Applications, Evolutionary Epidemiology | Samuel Alizon | 2016-12-16 20:54:08 | View | |
26 Nov 2019
Pleiotropy or linkage? Their relative contributions to the genetic correlation of quantitative traits and detection by multi-trait GWA studiesJobran Chebib and Frédéric Guillaume https://doi.org/10.1101/656413Understanding the effects of linkage and pleiotropy on evolutionary adaptationRecommended by Kathleen Lotterhos based on reviews by Pär Ingvarsson and 1 anonymous reviewerGenetic correlations among traits are ubiquitous in nature. However, we still have a limited understanding of the genetic architecture of trait correlations. Some genetic correlations among traits arise because of pleiotropy - single mutations or genotypes that have effects on multiple traits. Other genetic correlations among traits arise because of linkage among mutations that have independent effects on different traits. Teasing apart the differential effects of pleiotropy and linkage on trait correlations is difficult, because they result in very similar genetic patterns. However, understanding these differential effects gives important insights into how ubiquitous pleiotropy may be in nature. References [1] Chebib, J. and Guillaume, F. (2019). Pleiotropy or linkage? Their relative contributions to the genetic correlation of quantitative traits and detection by multi-trait GWA studies. bioRxiv, 656413, v3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/656413 | Pleiotropy or linkage? Their relative contributions to the genetic correlation of quantitative traits and detection by multi-trait GWA studies | Jobran Chebib and Frédéric Guillaume | <p>Genetic correlations between traits may cause correlated responses to selection depending on the source of those genetic dependencies. Previous models described the conditions under which genetic correlations were expected to be maintained. Sel... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Evolutionary Applications, Evolutionary Dynamics, Evolutionary Theory, Genome Evolution, Genotype-Phenotype, Molecular Evolution, Population Genetics / Genomics, Quantitative Genetics | Kathleen Lotterhos | 2019-06-05 13:51:43 | View | |
05 Feb 2021
Relaxation of purifying selection suggests low effective population size in eusocial Hymenoptera and solitary pollinating beesArthur Weyna, Jonathan Romiguier https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.14.038893Multi-gene and lineage comparative assessment of the strength of selection in HymenopteraRecommended by Bertanne Visser based on reviews by Michael Lattorff and 1 anonymous reviewerGenetic variation is the raw material for selection to act upon and the amount of genetic variation present within a population is a pivotal determinant of a population’s evolutionary potential. A large effective population size, i.e., the ideal number of individuals experiencing the same amount of genetic drift and inbreeding as an actual population, Ne (Wright 1931, Crow 1954), thus increases the probability of long-term survival of a population. However, natural populations, as opposed to theoretical ones, rarely adhere to the requirements of an ideal panmictic population (Sjödin et al. 2005). A range of circumstances can reduce Ne, including the structuring of populations (through space and time, as well as age and developmental stages) and inbreeding (Charlesworth 2009). In mammals, species with a larger body mass (as a proxy for lower Ne) were found to have a higher rate of nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions (that alter the amino acid sequence of a protein), as well as radical amino acid substitutions (altering the physicochemical properties of a protein) (Popadin et al. 2007). In general, low effective population sizes increase the chance of mutation accumulation and drift, while reducing the strength of selection (Sjödin et al. 2005). References Charlesworth, B. (2009). Effective population size and patterns of molecular evolution and variation. Nature Reviews Genetics, 10(3), 195-205. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2526 | Relaxation of purifying selection suggests low effective population size in eusocial Hymenoptera and solitary pollinating bees | Arthur Weyna, Jonathan Romiguier | <p>With one of the highest number of parasitic, eusocial and pollinator species among all insect orders, Hymenoptera features a great diversity of lifestyles. At the population genetic level, such life-history strategies are expected to decrease e... |  | Behavior & Social Evolution, Genome Evolution, Life History, Molecular Evolution, Population Genetics / Genomics | Bertanne Visser | 2020-04-21 17:30:57 | View | |
16 Dec 2016

POSTPRINT
Evolutionary robotics simulations help explain why reciprocity is rare in nature.André J-B, Nolfi S 10.1038/srep32785Simulated robots and the evolution of reciprocityRecommended by Michael D Greenfield and Joël Meunier
Of the various forms of cooperative and altruistic behavior, reciprocity remains the most contentious. Humans certainly exhibit reciprocity – under certain circumstances – and various non-human animals behave in ways suggesting that they do as well. Thus, evolutionary biologists have sought to explain why non-relatives might engage in altruistic transactions when a substantial delay occurs between helping and compensation; i.e. an individual may be a donor today and a beneficiary tomorrow, or vice-versa. This quest, aided by game theory and computer modeling late in the past century, identified some strategies for reciprocal behavior that could work – in theory. But when biologists looked for confirmation of these strategies in animals they found little evidence that stood up to rigorous testing. In a recent paper André and Nolfi [1] offer a compelling reason for this observed rarity of reciprocity: Reciprocal behavior that animals might exhibit is a bit more complex than any of the game theoretic strategies, and even the simplest forms of realistic behavior would entail several nearly simultaneous mutations, an unlikely occurrence. André and Nolfi [1] relied on neural networks to test actors, robots that could evolve helping and reciprocal behavior from a basal level of selfishness. In an extensive series of simulations, they found that reciprocal behavior did not take hold in a population, largely because the various intermediates to full reciprocity were eliminated before the subsequent mutations occurred. The findings are satisfying given our current knowledge of animal behavior, but questions remain. Notably, how does one account for those rare cases in which reciprocity does meet all the criteria? The authors suggest some possibilities, but an analysis will await their next study. Reference [1] André J-B, Nolfi S. 2016. Evolutionary robotics simulations help explain why reciprocity is rare in nature. Scientific Reports 6:32785. doi: 10.1038/srep32785 | Evolutionary robotics simulations help explain why reciprocity is rare in nature. | André J-B, Nolfi S | The relative rarity of reciprocity in nature, contrary to theoretical predictions that it should be widespread, is currently one of the major puzzles in social evolution theory. Here we use evolutionary robotics to solve this puzzle. We show tha... |  | Behavior & Social Evolution, Evolutionary Theory | Michael D Greenfield | 2016-12-16 18:08:31 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Guillaume Achaz
Juan Arroyo
Trine Bilde
Dustin Brisson
Marianne Elias
Inês Fragata
Matteo Fumagalli
Tatiana Giraud
Frédéric Guillaume
Ruth Hufbauer
Sara Magalhaes
Caroline Nieberding
Michael David Pirie
Tanja Pyhäjärvi
Tanja Schwander
Alejandro Gonzalez Voyer










