Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields▲ | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
06 Jul 2018

Variation in competitive ability with mating system, ploidy and range expansion in four Capsella speciesXuyue Yang, Martin Lascoux and Sylvain Glémin https://doi.org/10.1101/214866When ecology meets genetics: Towards an integrated understanding of mating system transitions and diversityRecommended by Sylvain Billiard and Henrique Teotonio based on reviews by Yaniv Brandvain, Henrique Teotonio and 1 anonymous reviewerIn the 19th century, C. Darwin and F. Delpino engaged in a debate about the success of species with different reproduction modes, with the later favouring the idea that monoecious plants capable of autonomous selfing could spread more easily than dioecious plants (or self-incompatible hermaphroditic plants) if cross-pollination opportunities were limited [1]. Since then, debate has never faded about how natural selection is responsible for transitions to selfing and can explain the diversity and distribution of reproduction modes we observe in the natural world [2, 3]. References [1] Darwin, C. R. (1876). The effects of cross and self fertilization in the vegetable kingdom. London: Murray.
[2] Stebbins, G. L. (1957). Self fertilization and population variability in the higher plants. The American Naturalist, 91, 337-354. doi: 10.1086/281999 | Variation in competitive ability with mating system, ploidy and range expansion in four Capsella species | Xuyue Yang, Martin Lascoux and Sylvain Glémin | <p>Self-fertilization is often associated with ecological traits corresponding to the ruderal strategy in Grime’s Competitive-Stress-tolerant-Ruderal (CSR) classification of ecological strategies. Consequently, selfers are expected to be less comp... |  | Evolutionary Ecology, Population Genetics / Genomics, Reproduction and Sex, Species interactions | Sylvain Billiard | 2017-11-06 19:54:52 | View | |
11 Jul 2022
Mutualists construct the ecological conditions that trigger the transition from parasitismLeo Ledru, Jimmy Garnier, Matthias Rohr, Camille Nous, Sebastien Ibanez https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.08.18.456759Give them some space: how spatial structure affects the evolutionary transition towards mutualistic symbiosisRecommended by Francois Massol based on reviews by Eva Kisdi and 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Eva Kisdi and 3 anonymous reviewers
The evolution of mutualistic symbiosis is a puzzle that has fascinated evolutionary ecologist for quite a while. Data on transitions between symbiotic bacterial ways of life has evidenced shifts from mutualism towards parasitism and vice versa (Sachs et al., 2011), so there does not seem to be a strong determinism on those transitions. From the host’s perspective, mutualistic symbiosis implies at the very least some form of immune tolerance, which can be costly (e.g. Sorci, 2013). Empirical approaches thus raise very important questions: How can symbiosis turn from parasitism into mutualism when it seemingly needs such a strong alignment of selective pressures on both the host and the symbiont? And yet why is mutualistic symbiosis so widespread and so important to the evolution of macro-organisms (Margulis, 1998)? While much of the theoretical literature on the evolution of symbiosis and mutualism has focused on either the stability of such relationships when non-mutualists can invade the host-symbiont system (e.g. Ferrière et al., 2007) or the effect of the mode of symbiont transmission on the evolutionary dynamics of mutualism (e.g. Genkai-Kato and Yamamura, 1999), the question remains whether and under which conditions parasitic symbiosis can turn into mutualism in the first place. Earlier results suggested that spatial demographic heterogeneity between host populations could be the leading determinant of evolution towards mutualism or parasitism (Hochberg et al., 2000). Here, Ledru et al. (2022) investigate this question in an innovative way by simulating host-symbiont evolutionary dynamics in a spatially explicit context. Their hypothesis is intuitive but its plausibility is difficult to gauge without a model: Does the evolution towards mutualism depend on the ability of the host and symbiont to evolve towards close-range dispersal in order to maintain clusters of efficient host-symbiont associations, thus outcompeting non-mutualists? I strongly recommend reading this paper as the results obtained by the authors are very clear: competition strength and the cost of dispersal both affect the likelihood of the transition from parasitism to mutualism, and once mutualism has set in, symbiont trait values clearly segregate between highly dispersive parasites and philopatric mutualists. The demonstration of the plausibility of their hypothesis is accomplished with brio and thoroughness as the authors also examine the conditions under which the transition can be reversed, the impact of the spatial range of competition and the effect of mortality. Since high dispersal cost and strong, long-range competition appear to be the main factors driving the evolutionary transition towards mutualistic symbiosis, now is the time for empiricists to start investigating this question with spatial structure in mind. References Ferrière, R., Gauduchon, M. and Bronstein, J. L. (2007) Evolution and persistence of obligate mutualists and exploiters: competition for partners and evolutionary immunization. Ecology Letters, 10, 115-126. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.01008.x Genkai-Kato, M. and Yamamura, N. (1999) Evolution of mutualistic symbiosis without vertical transmission. Theoretical Population Biology, 55, 309-323. https://doi.org/10.1006/tpbi.1998.1407 Hochberg, M. E., Gomulkiewicz, R., Holt, R. D. and Thompson, J. N. (2000) Weak sinks could cradle mutualistic symbioses - strong sources should harbour parasitic symbioses. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 13, 213-222. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1420-9101.2000.00157.x Ledru L, Garnier J, Rohr M, Noûs C and Ibanez S (2022) Mutualists construct the ecological conditions that trigger the transition from parasitism. bioRxiv, 2021.08.18.456759, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.18.456759 Margulis, L. (1998) Symbiotic planet: a new look at evolution, Basic Books, Amherst. Sachs, J. L., Skophammer, R. G. and Regus, J. U. (2011) Evolutionary transitions in bacterial symbiosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108, 10800-10807. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1100304108 Sorci, G. (2013) Immunity, resistance and tolerance in bird–parasite interactions. Parasite Immunology, 35, 350-361. https://doi.org/10.1111/pim.12047 | Mutualists construct the ecological conditions that trigger the transition from parasitism | Leo Ledru, Jimmy Garnier, Matthias Rohr, Camille Nous, Sebastien Ibanez | <p>The evolution of mutualism between hosts and initially parasitic symbionts represents a major transition in evolution. Although vertical transmission of symbionts during host reproduction and partner control both favour the stability of mutuali... |  | Evolutionary Ecology, Species interactions | Francois Massol | 2021-08-20 12:25:40 | View | |
05 Oct 2022
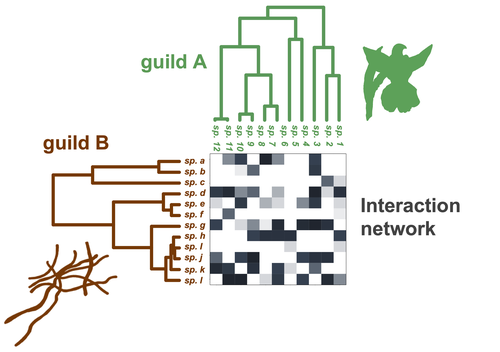
Do closely related species interact with similar partners? Testing for phylogenetic signal in bipartite interaction networksBenoît Perez-Lamarque, Odile Maliet, Benoît Pichon, Marc-André Selosse, Florent Martos, Hélène Morlon https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.30.458192Testing for phylogenetic signal in species interaction networksRecommended by Alejandro Gonzalez Voyer based on reviews by Joaquin Calatayud and Thomas GuillermeSpecies are immersed within communities in which they interact mutualistically, as in pollination or seed dispersal, or nonreciprocally, such as in predation or parasitism, with other species and these interactions play a paramount role in shaping biodiversity (Bascompte and Jordano 2013). Researchers have become increasingly interested in the processes that shape these interactions and how these influence community structure and responses to disturbances. Species interactions are often described using bipartite interaction networks and one important question is how the evolutionary history of the species involved influences the network, including whether there is phylogenetic signal in interactions, in other words whether closely related species interact with other closely related species (Bascompte and Jordano 2013, Perez-Lamarque et al. 2022). To address this question different approaches, correlative and model-based, have been developed to test for phylogenetic signal in interactions, although comparative analyses of the performance of these different metrics are lacking. In their article Perez-Lamarque et al. (2022) set out to test the statistical performance of two widely-used methods, Mantel tests and Phylogenetic Bipartite Linear Models (PBLM; Ives and Godfray 2006) using simulations. Phylogenetic signal is measured as the degree to which distance to the nearest common ancestor predicts the observed similarity in trait values among species. In species interaction networks, the data are actually the between-species dissimilarity among interacting species (Perez-Lamarque et al. 2022), and typical approaches to test for phylogenetic signal cannot be used. However, the Mantel test provides a useful means of analyzing the correlation between two distance matrices, the between-species phylogenetic distance and the between-species dissimilarity in interactions. The PBLM approach, on the other hand, assumes that interactions between species are influenced by unobserved traits that evolve along the phylogenies following a given phenotypic evolution model and the parameters of this model are interpreted in terms of phylogenetic signal (Ives and Godfray 2006). Perez-Lamarque et al (2022) found that the model-based PBLM approach has a high type-I error rate, in other words it often detected phylogenetic signal when there was none. The simple Mantel test was found to present a low type-I error rate and moderate statistical power. However, it tended to overestimate the degree to which species interact with dissimilar partners. In addition to the aforementioned analyses, the authors also tested whether the simple Mantel test was able to detect phylogenetic signal in interactions among species within a given clade in the phylogeny, as phylogenetic signal in species interactions may be localized within specific clades. The article concludes with general guidelines for users wishing to test phylogenetic signal in their interaction networks and illustrates them with an example of an orchid-mycorrhizal fungus network from the oceanic island of La Réunion (Martos et al 2012). This broadly accessible article provides a valuable analysis of the performance of tests of phylogenetic signal in interaction networks enabling users to make informed choices of the analytical methods they wish to employ, and provide useful and detailed guidelines. Therefore, the work should be of broad interest to researchers studying species interactions. References Bascompte J, Jordano P (2013) Mutualistic Networks. Princeton University Press. https://doi.org/10.1515/9781400848720 Ives AR, Godfray HCJ (2006) Phylogenetic Analysis of Trophic Associations. The American Naturalist, 168, E1–E14. https://doi.org/10.1086/505157 Martos F, Munoz F, Pailler T, Kottke I, Gonneau C, Selosse M-A (2012) The role of epiphytism in architecture and evolutionary constraint within mycorrhizal networks of tropical orchids. Molecular Ecology, 21, 5098–5109. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05692.x Perez-Lamarque B, Maliet O, Pichon B, Selosse M-A, Martos F, Morlon H (2022) Do closely related species interact with similar partners? Testing for phylogenetic signal in bipartite interaction networks. bioRxiv, 2021.08.30.458192, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.30.458192 | Do closely related species interact with similar partners? Testing for phylogenetic signal in bipartite interaction networks | Benoît Perez-Lamarque, Odile Maliet, Benoît Pichon, Marc-André Selosse, Florent Martos, Hélène Morlon | <p style="text-align: justify;">Whether interactions between species are conserved on evolutionary time-scales has spurred the development of both correlative and process-based approaches for testing phylogenetic signal in interspecific interactio... |  | Evolutionary Ecology, Species interactions | Alejandro Gonzalez Voyer | 2022-03-10 13:48:15 | View | |
02 Feb 2024
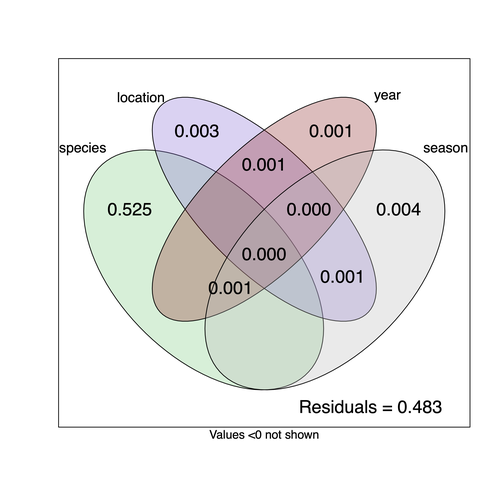
Community structure of heritable viruses in a Drosophila-parasitoids complexJulien Varaldi, David Lepetit, Nelly Burlet, Camille Faber, Bérénice Baretje, Roland Allemand https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.29.551099The virome of a Drosophilidae-parasitoid communityRecommended by Ben Longdon based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers
Understanding the factors that shape the virome of a host is key to understanding virus ecology and evolution (Obbard, 2018; French & Holmes, 2020). There is still much to learn about the diversity and distribution of viruses in a host community (Wille et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2023). The viruses of parasitoid wasps are well studied, and their viruses, or integrated viral genes, are known to suppress their insect host’s immune response to enhance parasitoid survival (Herniou et al., 2013; Coffman et al., 2022). Likewise, the insect virome is being increasingly well studied (Shi et al., 2016), with the virome of Drosophila species being particularly well characterised over the best part of the last century (L'Heritier & Teissier, 1937; L'Heritier, 1970; Brun & Plus, 1980; Longdon et al., 2010; Longdon et al., 2011; Longdon et al., 2012; Webster et al., 2015; Webster et al., 2016; Medd et al., 2018; Wallace et al., 2021). However, the viromes of parasitoids and their insect host communities have been less well studied (Leigh et al., 2018; Caldas-Garcia et al., 2023), and the inherent connectivity between parasitoids and their hosts provides an interesting system to study virus host range and cross-species transmission. Here, Varaldi et al (Varaldi et al., 2024) have examined the viruses associated with a community of nine Drosophilidae hosts and six parasitoids. Using both RNA and DNA sequencing of insects reared for two generations, they selected viruses that are maintained in the lab either via vertical transmission or contamination of rearing medium. From 55 pools of insects they found 53 virus-like sequences, 37 of which were novel. Parasitoids were host to nearly twice as many viruses as their Drosophila hosts, although they note this could be due to differences in the rearing temperatures of the hosts. They next quantified if species, year, season, or location played a role in structuring the virome, finding only a significant effect of host species, which explained just over 50% of the variation in virus distribution. No evidence was found of related species sharing more similar virus communities. Although looking at a limited number of species, this suggests that these viruses are not co-speciating or preferentially host switching between closely related species. Finally, they carried out crosses between lines of the parasitoid Leptopilina heterotoma that were infected and uninfected for a novel Iflavirus found in their sequencing data. They found evidence of high levels of maternal transmission and lower level horizontal transmission between wasp larvae parasitising the same host. No evidence of changes in parasitoid-induced mortality, developmental success or the sex ratio was found in iflavirus-infected parasitoids. Interestingly individuals infected with this RNA virus also contained viral DNA, but this did not appear to be integrated into the wasp genome. Overall, this work has taken the first steps in examining the community structure of the virome of parasitoids together with their Drosophilidae hosts. This work will not doubt stimulate follow-up studies to explore the evolution and ecology of these novel virus communities. References Brun G, Plus N (1980) The viruses of Drosophila. In: The genetics and biology of Drosophila eds Ashburner M & Wright TRF), pp. 625-702. Academic Press, New York. | Community structure of heritable viruses in a *Drosophila*-parasitoids complex | Julien Varaldi, David Lepetit, Nelly Burlet, Camille Faber, Bérénice Baretje, Roland Allemand | <p style="text-align: justify;">The diversity and phenotypic impacts related to the presence of heritable bacteria in insects have been extensively studied in the last decades. On the contrary, heritable viruses have been overlooked for several re... |  | Evolutionary Ecology, Species interactions | Ben Longdon | 2023-08-03 01:07:43 | View | |
22 May 2017
Can Ebola Virus evolve to be less virulent in humans?Mircea T. Sofonea, Lafi Aldakak, Luis Fernando Boullosa, Samuel Alizon 10.1101/108589A new hypothesis to explain Ebola's high virulenceRecommended by Virginie Ravigné and François Blanquart based on reviews by Virginie Ravigné and François Blanquart
The tragic 2014-2016 Ebola outbreak that resulted in more than 28,000 cases and 11,000 deaths in West Africa [1] has been a surprise to the scientific community. Before 2013, the Ebola virus (EBOV) was known to produce recurrent outbreaks in remote villages near tropical rainforests in Central Africa, never exceeding a few hundred cases with very high virulence. Both EBOV’s ability to circulate for several months in large urban human populations and its important mutation rate suggest that EBOV’s virulence could evolve and to some extent adapt to human hosts [2]. Up to now, the high virulence of EBOV in humans was generally thought to be maladaptive, the virus being adapted to circulating in wild animal populations (e.g. fruit bats [3]). As a logical consequence, EBOV virulence could be expected to decrease during long epidemics in humans. The present paper by Sofonea et al. [4] challenges this view and explores how, given EBOV’s life cycle and known epidemiological parameters, virulence is expected to evolve in the human host during long epidemics. The main finding of the paper is that there is no chance that EBOV’s virulence decreases in the short and long terms. The main underlying mechanism is that EBOV is also transmitted by dead bodies, which limits the cost of virulence. In itself the idea that selection should select for higher virulence in diseases that are also transmitted after host death will sound intuitive for most evolutionary epidemiologists. The accomplishment of the paper is to make a very strong case that the parameter range where virulence could decrease is very small. The paper further provides scientifically grounded arguments in favor of the safe management of corpses. Safe burial of corpses is culturally difficult to impose. The present paper shows that in addition to instantaneously decreasing the spread of the virus, safe burial may limit virulence increase in the short term and favor of less virulent strains in the long term. Altogether these results make a timely and important contribution to the knowledge and understanding of EBOV. References [1] World Health Organization. 2016. WHO: Ebola situation report - 10 June 2016. [2] Kupferschmidt K. 2014. Imagining Ebola’s next move. Science 346: 151–152. doi: 10.1126/science.346.6206.151 [3] Leroy EM, Kumulungui B, Pourrut X, Rouquet P, Hassanin A, Yaba P, Délicat A, Paweska, Gonzalez JP and Swanepoel R. 2005. Fruit bats as reservoirs of Ebola virus. Nature 438: 575–576. doi: 10.1038/438575a [4] Sofonea MT, Aldakak L, Boullosa LFVV and Alizon S. 2017. Can Ebola Virus evolve to be less virulent in humans? bioRxiv 108589, ver. 3 of 19th May 2017; doi: 10.1101/108589 | Can Ebola Virus evolve to be less virulent in humans? | Mircea T. Sofonea, Lafi Aldakak, Luis Fernando Boullosa, Samuel Alizon | Understanding Ebola Virus (EBOV) virulence evolution is not only timely but also raises specific questions because it causes one pf the most virulent human infections and it is capable of transmission after the death of its host. Using a compartme... |  | Evolutionary Epidemiology | Virginie Ravigné | 2017-02-15 13:25:58 | View | |
18 Aug 2020
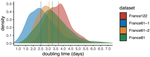
Early phylodynamics analysis of the COVID-19 epidemics in FranceGonché Danesh, Baptiste Elie,Yannis Michalakis, Mircea T. Sofonea, Antonin Bal, Sylvie Behillil, Grégory Destras, David Boutolleau, Sonia Burrel, Anne-Geneviève Marcelin, Jean-Christophe Plantier, Vincent Thibault, Etienne Simon-Loriere, Sylvie van der Werf, Bruno Lina, Laurence Josset, Vincent Enouf, Samuel Alizon and the COVID SMIT PSL group https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.03.20119925SARS-Cov-2 genome sequence analysis suggests rapid spread followed by epidemic slowdown in FranceRecommended by B. Jesse Shapiro based on reviews by Luca Ferretti and 2 anonymous reviewersSequencing and analyzing SARS-Cov-2 genomes in nearly real time has the potential to quickly confirm (and inform) our knowledge of, and response to, the current pandemic [1,2]. In this manuscript [3], Danesh and colleagues use the earliest set of available SARS-Cov-2 genome sequences available from France to make inferences about the timing of the major epidemic wave, the duration of infections, and the efficacy of lockdown measures. Their phylodynamic estimates -- based on fitting genomic data to molecular clock and transmission models -- are reassuringly close to estimates based on 'traditional' epidemiological methods: the French epidemic likely began in mid-January or early February 2020, and spread relatively rapidly (doubling every 3-5 days), with people remaining infectious for a median of 5 days [4,5]. These transmission parameters are broadly in line with estimates from China [6,7], but are currently unknown in France (in the absence of contact tracing data). By estimating the temporal reproductive number (Rt), the authors detected a slowing down of the epidemic in the most recent period of the study, after mid-March, supporting the efficacy of lockdown measures. References [1] Grubaugh, N. D., Ladner, J. T., Lemey, P., Pybus, O. G., Rambaut, A., Holmes, E. C., & Andersen, K. G. (2019). Tracking virus outbreaks in the twenty-first century. Nature microbiology, 4(1), 10-19. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0296-2 | Early phylodynamics analysis of the COVID-19 epidemics in France | Gonché Danesh, Baptiste Elie,Yannis Michalakis, Mircea T. Sofonea, Antonin Bal, Sylvie Behillil, Grégory Destras, David Boutolleau, Sonia Burrel, Anne-Geneviève Marcelin, Jean-Christophe Plantier, Vincent Thibault, Etienne Simon-Loriere, Sylvie va... | <p>France was one of the first countries to be reached by the COVID-19 pandemic. Here, we analyse 196 SARS-Cov-2 genomes collected between Jan 24 and Mar 24 2020, and perform a phylodynamics analysis. In particular, we analyse the doubling time, r... |  | Evolutionary Epidemiology, Molecular Evolution, Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics | B. Jesse Shapiro | 2020-06-04 13:13:57 | View | |
11 Dec 2020
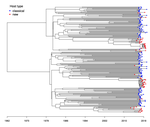
Quantifying transmission dynamics of acute hepatitis C virus infections in a heterogeneous population using sequence dataGonche Danesh, Victor Virlogeux, Christophe Ramière, Caroline Charre, Laurent Cotte, Samuel Alizon https://doi.org/10.1101/689158Phylodynamics of hepatitis C virus reveals transmission dynamics within and between risk groups in LyonRecommended by David Rasmussen based on reviews by Chris Wymant and Louis DuPlessisGenomic epidemiology seeks to better understand the transmission dynamics of infectious pathogens using molecular sequence data. Phylodynamic methods have given genomic epidemiology new power to track the transmission dynamics of pathogens by combining phylogenetic analyses with epidemiological modeling. In recent year, applications of phylodynamics to chronic viral infections such as HIV and hepatitis C virus (HVC) have provided some of the best examples of how phylodynamic inference can provide valuable insights into transmission dynamics within and between different subpopulations or risk groups, allowing for more targeted interventions. References [1] Rasmussen, D. A., Volz, E. M., and Koelle, K. (2014). Phylodynamic inference for structured epidemiological models. PLoS Comput Biol, 10(4), e1003570. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003570 | Quantifying transmission dynamics of acute hepatitis C virus infections in a heterogeneous population using sequence data | Gonche Danesh, Victor Virlogeux, Christophe Ramière, Caroline Charre, Laurent Cotte, Samuel Alizon | <p>Opioid substitution and syringes exchange programs have drastically reduced hepatitis C virus (HCV) spread in France but HCV sexual transmission in men having sex with men (MSM) has recently arisen as a significant public health concern. The fa... |  | Evolutionary Epidemiology, Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics | David Rasmussen | 2019-07-11 13:37:23 | View | |
11 Sep 2017

POSTPRINT
Less effective selection leads to larger genomesTristan Lefébure, Claire Morvan, Florian Malard, Clémentine François, Lara Konecny-Dupré, Laurent Guéguen, Michèle Weiss-Gayet, Andaine Seguin-Orlando, Luca Ermini, Clio Der Sarkissian, N. Pierre Charrier, David Eme, Florian Mermillod-Blondin, Laurent Duret, Cristina Vieira, Ludovic Orlando and Christophe Douady 10.1101/gr.212589.116Colonisation of subterranean ecosystems leads to larger genome in waterlouse (Aselloidea)Recommended by Benoit Nabholz and Jochen B. W. WolfThe total amount of DNA utilized to store hereditary information varies immensely among eukaryotic organisms. Single copy genome sizes – disregarding differences due to ploidy - differ by more than three orders of magnitude ranging from a few million nucleotides (Mb) to hundreds of billions (Gb). With the ever-increasing availability of fully sequenced genomes we now know that most of the difference is due either to whole genome duplication or to variation in the abundance of repetitive elements. Regarding repetitive elements, the evolutionary forces underlying the large variation 'allowing' more or less elements in a genome remain largely elusive. A tentative correlation between an organism's complexity (however this may be adequately measured) and genome size, the so called C-value paradox [1], has long been dismissed. Studies testing for selection on secondary phenotypic effects associated with genome size (cell size, metabolic rates, nutrient availability) have yielded mixed results. Nonadaptive theories capitalizing on a role of deleterious insertion-deletion mutations and genetic drift as the main drivers have likewise received mixed support [2-3]. Overall, most evidence was derived from analyses across broad taxonomical scales [4-6]. Lefébure and colleagues [7] take a different approach. They confine their considerations to a homogeneous, restricted taxonomical group, isopod crustaceans of the superfamily Aselloidea. This taxonomic focus allows the authors to circumvent many of the confounding factors such as phylogenetic inertia, life history divergence and mutation rate variation that tend to trouble analyses across broad taxonomic timescales. Another important feature of the chosen system is the evolutionary independent transition of habitat use that has occurred at least 11 times. One group of species inhabits subterranean ecosystems (groundwater), another group thrives on surface water. Populations of the former live in low-energy habitats and are expected to be outnumbered by their surface dwelling relatives. Interestingly – and a precondition for the study - the groundwater species have significantly larger genomes (up to 137%). With this unique set-up, the authors are able to investigate the link between genome size and evolutionary forces related to a proxy of long-term population size by removing many of the confounding factors a priori. Upfront, we learn that the dN/dS ratio is higher in the groundwater species. This may either suggest prevalent positive selection or lower efficacy of purifying selection (relaxed constraint) in the group of species in which population sizes are expected to be low. Using a series of population genetic analyses the authors provide compelling evidence for the latter. Analyses are carefully conducted and include models for estimating the intensity and frequency of purifying and positive selection, the DoS (direction of selection) and α statistic. Next the authors also exclude the possibility that increased dN/dS of the subterranean groundwater species may be due to nonfunctionalization, which may result from the subterranean lifestyle. Overall, these analyses suggest relaxed constraint in smaller populations as the most plausible alternative to explain increased dN/dS ratios. In addition to the efficacy of selection, the authors estimate the timing of the ecological transition under the rationale that the amount of time a species may have been exposed to the subterranean habitat may reflect long term population sizes. To calibrate the 'colonization clock' they apply a neat trick based on the degree of degeneration of the opsin gene (as vision tends to get lost in these habitats). When finally testing which parameters may explain differences in genome size all factors – ecological status, selection efficiency as measured by dN/dS and colonization time - turned out to be significant predictors. Direct estimates of the short term effective population size Ne from polymorphism data, however, did not correlate with genome size. Ruling out the effect of other co-variates such as body size and growth rate the authors conclude that genome size was overall best predicted by long-term population size change upon habitat shift. In that the authors provide convincing evidence that the increase in genome size is linked to a decrease in long-term reduction of selection efficiency of subterranean species. Assuming a bias for insertion mutations over deletion mutations (which is usually the case in eukaryotes) this result is in agreement with the theory of mutational hazard [4-6]. This theory proposed by Michael Lynch postulates that the accumulation of non-functional DNA has a weak deleterious effect that can only be efficiently opposed by natural selection in species with high Ne. In conclusion, Lefébure and colleagues provide novel and welcome evidence supporting a 'neutralist' hypothesis of genome size evolution without the need to invoke an adaptive component. Methodologically, the study cautions against the common use of polymorphism-based estimates of Ne which are often obfuscated by transitory demographic change. Instead, alternative measures of selection efficacy linked to long-term population size may serve as better predictors of genome size. We hope that this study will stimulate additional work testing the link between Ne and genome size variation in other taxonomical groups [8-9]. Using genome sequences instead of the transcriptome approach applied here may concomitantly further our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying genome size change. References [1] Thomas, CA Jr. 1971. The genetic organization of chromosomes. Annual Review of Genetics 5: 237–256. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.05.120171.001321 [2] Ågren JA, Greiner S, Johnson MTJ, Wright SI. 2015. No evidence that sex and transposable elements drive genome size variation in evening primroses. Evolution 69: 1053–1062. doi: 10.1111/evo.12627 [3] Bast J, Schaefer I, Schwander T, Maraun M, Scheu S, Kraaijeveld K. 2016. No accumulation of transposable elements in asexual arthropods. Molecular Biology and Evolution 33: 697–706. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv261 [4] Lynch M. 2007. The Origins of Genome Architecture. Sinauer Associates. [5] Lynch M, Bobay LM, Catania F, Gout JF, Rho M. 2011. The repatterning of eukaryotic genomes by random genetic drift. Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics 12: 347–366. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-082410-101412 [6] Lynch M, Conery JS. 2003. The origins of genome complexity. Science 302: 1401–1404. doi: 10.1126/science.1089370 [7] Lefébure T, Morvan C, Malard F, François C, Konecny-Dupré L, Guéguen L, Weiss-Gayet M, Seguin-Orlando A, Ermini L, Der Sarkissian C, Charrier NP, Eme D, Mermillod-Blondin F, Duret L, Vieira C, Orlando L, and Douady CJ. 2017. Less effective selection leads to larger genomes. Genome Research 27: 1016-1028. doi: 10.1101/gr.212589.116 [8] Lower SS, Johnston JS, Stanger-Hall KF, Hjelmen CE, Hanrahan SJ, Korunes K, Hall D. 2017. Genome size in North American fireflies: Substantial variation likely driven by neutral processes. Genome Biolology and Evolution 9: 1499–1512. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx097 [9] Sessegolo C, Burlet N, Haudry A. 2016. Strong phylogenetic inertia on genome size and transposable element content among 26 species of flies. Biology Letters 12: 20160407. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2016.0407 | Less effective selection leads to larger genomes | Tristan Lefébure, Claire Morvan, Florian Malard, Clémentine François, Lara Konecny-Dupré, Laurent Guéguen, Michèle Weiss-Gayet, Andaine Seguin-Orlando, Luca Ermini, Clio Der Sarkissian, N. Pierre Charrier, David Eme, Florian Mermillod-Blondin, Lau... | The evolutionary origin of the striking genome size variations found in eukaryotes remains enigmatic. The effective size of populations, by controlling selection efficacy, is expected to be a key parameter underlying genome size evolution. However... |  | Evolutionary Theory, Genome Evolution, Molecular Evolution, Population Genetics / Genomics | Benoit Nabholz | 2017-09-08 09:39:23 | View | |
06 Feb 2024
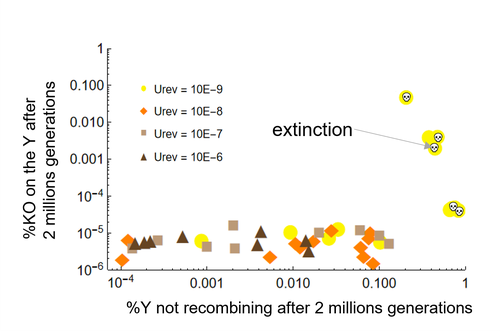
Can mechanistic constraints on recombination reestablishment explain the long-term maintenance of degenerate sex chromosomes?Thomas Lenormand, Denis Roze https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.17.528909New modelling results help understanding the evolution and maintenance of recombination suppression involving sex chromosomesRecommended by Jos Käfer based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewersDespite advances in genomic research, many views of genome evolution are still based on what we know from a handful of species, such as humans. This also applies to our knowledge of sex chromosomes. We've apparently been too much used to the situation in which a highly degenerate Y chromosome coexists with an almost normal X chromosome to be able to fully grasp all the questions implied by this situation. Lately, many more sex chromosomes have been studied in other organisms, such as in plants, and the view is changing radically: there is a large diversity of situations, ranging from young highly divergent sex chromosomes to old ones that are so similar that they're hard to detect. Undoubtedly inspired by these recent findings, a few theoretical studies have been published around 2 years ago that put an entirely new light on the evolution of sex chromosomes. The differences between these models have however remained somewhat difficult to appreciate by non-specialists. In particular, the models by Lenormand & Roze (2022) and by Jay et al. (2022) seemed quite similar. Indeed, both rely on the same mechanism for initial recombination suppression: a ``lucky'' inversion, i.e. one with less deleterious mutations than the population average, encompassing the sex-determination locus, is initially selected. However, as it doesn't recombine, it will quickly accumulate deleterious mutations lowering its fitness. And it's at this point the models diverge: according to Lenormand & Roze (2022), nascent dosage compensation not only limits the deleterious effects on fitness by the ongoing degeneration, but it actually opposes recombination restoration as this would lead gene expression away from the optimum that has been reached. On the other hand, in the model by Jay et al. (2022), no additional ingredient is required: they argue that once an inversion had been fixed, reversions that restore recombination are extremely unlikely. This is what Lenormand & Roze (2024) now call a ``constraint'': in Jay et al.'s model, recombination restoration is impossible for mechanistic reasons. Lenormand & Roze (2024) argue such constraints cannot explain long-term recombination suppression. Instead, a mechanism should evolve to limit the negative fitness effects of recombination arrest, otherwise recombination is either restored, or the population goes extinct due to a dramatic drop in the fitness of the heterogametic sex. These two arguments work together: given the huge fitness cost of the lack of ongoing degeneration of the non-recombining Y, in the absence of compensatory mechanisms, there is a very strong selection for the restoration of recombination, so that even when restoration a priori is orders of magnitude less likely than inversion (leading to recombination suppression), it will eventually happen. One way the negative fitness effects of recombination suppression can be limited, is the way the authors propose in their own model: dosage compensation evolves through regulatory evolution right at the start of recombination suppression. This changes our classical, simplistic view that dosage compensation evolves in response to degeneration: rather, Lenormand & Roze (2024) argue, that degeneration can only happen when dosage compensation is effective. The reasoning is convincing and exposes the difference between the models to readers without a firm background in mathematical modelling. Although Lenormand & Roze (2024) target the "constraint theory", it seems likely that other theories for the maintenance of recombination suppression that don't imply the compensation of early degeneration are subject to the same criticism. Indeed, they mention the widely-cited "sexual antagonism" theory, in which mutations with a positive effect in males but a negative in females will select for recombination suppression that will link them to the sex-determining gene on the Y. However, once degeneration starts, the sexually-antagonistic benefits should be huge to overcome the negative effects of degeneration, and it's unlikely they'll be large enough. A convincing argument by Lenormand & Roze (2024) is that there are many ways recombination could be restored, allowing to circumvent the possible constraints that might be associated with reverting an inversion. First, reversions don't have to be exact to restore recombination. Second, the sex-determining locus can be transposed to another chromosome pair, or an entirely new sex-determining locus might evolve, leading to sex-chromosome turnover which has effectively been observed in several groups. These modelling studies raise important questions that need to be addressed with both theoretical and empirical work. First, is the regulatory hypothesis proposed by Lenormand & Roze (2022) the only plausible mechanism for the maintenance of long-term recombination suppression? The female- and male-specific trans regulators of gene expression that are required for this model, are they readily available or do they need to evolve first? Both theoretical work and empirical studies of nascent sex chromosomes will help to answer these questions. However, nascent sex chromosomes are difficult to detect and dosage compensation is difficult to reveal. Second, how many species today actually have "stable" recombination suppression? Maybe many species are in a transient phase, with different populations having different inversions that are either on their way to being fixed or starting to get counterselected. The models have now shown us some possibilities qualitatively but can they actually be quantified to be able to fit the data and to predict whether an observed case of recombination suppression is transient or stable? The debate will continue, and we need the active contribution of theoretical biologists to help clarify the underlying hypotheses of the proposed mechanisms. Conflict of interest statement: I did co-author a manuscript with D. Roze in 2023, but do not consider this a conflict of interest. The manuscript is the product of discussions that have taken place in a large consortium mainly in 2019. It furthermore deals with an entirely different topic of evolutionary biology. References Jay P, Tezenas E, Véber A, and Giraud T. (2022) Sheltering of deleterious mutations explains the stepwise extension of recombination suppression on sex chromosomes and other supergenes. PLoS Biol.;20:e3001698. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3001698 | Can mechanistic constraints on recombination reestablishment explain the long-term maintenance of degenerate sex chromosomes? | Thomas Lenormand, Denis Roze | <p style="text-align: justify;">Y and W chromosomes often stop recombining and degenerate. Most work on recombination suppression has focused on the mechanisms favoring recombination arrest in the short term. Yet, the long-term maintenance of reco... |  | Evolutionary Theory, Genome Evolution, Population Genetics / Genomics, Reproduction and Sex | Jos Käfer | 2023-10-27 21:52:06 | View | |
25 Mar 2019

The joint evolution of lifespan and self-fertilisationThomas Lesaffre, Sylvain Billiard https://doi.org/10.1101/420877Evolution of selfing & lifespan 2.0Recommended by Thomas Bataillon based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersFlowering plants display a staggering diversity of both mating systems and life histories, ranging from almost exclusively selfers to obligate outcrossers, very short-lived annual herbs to super long lived trees. One pervasive pattern that has attracted considerable attention is the tight correlation that is found between mating systems and lifespan [1]. Until recently, theoretical explanations for these patterns have relied on static models exploring the consequences of several non-mutually exclusive important process: levels of inbreeding depression and ability to successfully were center stage. This make sense: successful colonization after long‐distance dispersal is far more likely to happen for self‐compatible than for self‐incompatible individuals in a sexually reproducing species. Furthermore, inbreeding depression (essentially a genetically driven phenomenon) and reproductive insurance are expected to shape the evolution of both mating system and lifespan. References | The joint evolution of lifespan and self-fertilisation | Thomas Lesaffre, Sylvain Billiard | <p>In Angiosperms, there exists a strong association between mating system and lifespan. Most self-fertilising species are short-lived and most predominant or obligate outcrossers are long-lived. This association is generally explained by the infl... |  | Evolutionary Theory, Life History, Reproduction and Sex | Thomas Bataillon | 2018-09-19 10:03:51 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Guillaume Achaz
Juan Arroyo
Trine Bilde
Dustin Brisson
Marianne Elias
Inês Fragata
Matteo Fumagalli
Tatiana Giraud
Frédéric Guillaume
Ruth Hufbauer
Sara Magalhaes
Caroline Nieberding
Michael David Pirie
Tanja Pyhäjärvi
Tanja Schwander
Alejandro Gonzalez Voyer










