Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender▼ | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
07 Sep 2018

Parallel pattern of differentiation at a genomic island shared between clinal and mosaic hybrid zones in a complex of cryptic seahorse lineagesFlorentine Riquet, Cathy Liautard-Haag, Lucy Woodall, Carmen Bouza, Patrick Louisy, Bojan Hamer, Francisco Otero-Ferrer, Philippe Aublanc, Vickie Béduneau, Olivier Briard, Tahani El Ayari, Sandra Hochscheid, Khalid Belkhir, Sophie Arnaud-Haond, Pierre-Alexandre Gagnaire, Nicolas Bierne https://doi.org/10.1101/161786Genomic parallelism in adaptation to orthogonal environments in sea horsesRecommended by Yaniv Brandvain based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersStudies in speciation genomics have revealed that gene flow is quite common, and that despite this, species can maintain their distinct environmental adaptations. Although researchers are still elucidating the genomic mechanisms by which species maintain their adaptations in the face of gene flow, this often appears to involve few diverged genomic regions in otherwise largely undifferentiated genomes. In this preprint [1], Riquet and colleagues investigate the genetic structuring and patterns of parallel evolution in the long-snouted seahorse. References [1] Riquet, F., Liautard-Haag, C., Woodall, L., Bouza, C., Louisy, P., Hamer, B., Otero-Ferrer, F., Aublanc, P., Béduneau, V., Briard, O., El Ayari, T., Hochscheid, S. Belkhir, K., Arnaud-Haond, S., Gagnaire, P.-A., Bierne, N. (2018). Parallel pattern of differentiation at a genomic island shared between clinal and mosaic hybrid zones in a complex of cryptic seahorse lineages. bioRxiv, 161786, ver. 4 recommended and peer-reviewed by PCI Evol Biol. doi: 10.1101/161786 | Parallel pattern of differentiation at a genomic island shared between clinal and mosaic hybrid zones in a complex of cryptic seahorse lineages | Florentine Riquet, Cathy Liautard-Haag, Lucy Woodall, Carmen Bouza, Patrick Louisy, Bojan Hamer, Francisco Otero-Ferrer, Philippe Aublanc, Vickie Béduneau, Olivier Briard, Tahani El Ayari, Sandra Hochscheid, Khalid Belkhir, Sophie Arnaud-Haond, Pi... | <p>Diverging semi-isolated lineages either meet in narrow clinal hybrid zones, or have a mosaic distribution associated with environmental variation. Intrinsic reproductive isolation is often emphasized in the former and local adaptation in the la... |  | Hybridization / Introgression, Molecular Evolution, Population Genetics / Genomics, Speciation | Yaniv Brandvain | Kathleen Lotterhos, Sarah Fitzpatrick | 2017-07-11 13:12:40 | View |
12 Jul 2017

Assortment of flowering time and defense alleles in natural Arabidopsis thaliana populations suggests co-evolution between defense and vegetative lifespan strategiesGlander S, He F, Schmitz G, Witten A, Telschow A, de Meaux J 10.1101/131136Towards an integrated scenario to understand evolutionary patterns in A. thalianaRecommended by Xavier Picó based on reviews by Rafa Rubio de Casas and Xavier PicóNobody can ignore that a full understanding of evolution requires an integrated approach from both conceptual and methodological viewpoints. Although some life-history traits, e.g. flowering time, have long been receiving more attention than others, in many cases because the former are more workable than the latter, we must acknowledge that our comprehension about how evolution works is strongly biased and limited. In the Arabidopsis community, such an integration is making good progress as an increasing number of research groups worldwide are changing the way in which evolution is put to the test. This manuscript [1] is a good example of that as the authors raise an important issue in evolutionary biology by combining gene expression and flowering time data from different sources. In particular, the authors explore how variation in flowering time, which determines lifespan, and host immunity defenses co-vary, which is interpreted in terms of co-evolution between the two traits. Interestingly, the authors go beyond that pattern by separating lifespan-dependent from lifespan–independent defense genes, and by showing that defense genes with variants known to impact fitness in the field are among the genes whose expression co-varies most strongly with flowering time. Finally, these results are supported by a simple mathematical model indicating that such a relationship can also be expected theoretically. Overall, the readers will find many conceptual and methodological elements of interest in this manuscript. The idea that evolution is better understood under the scope of life history variation is really exciting and challenging, and in my opinion on the right track for disentangling the inherent complexities of evolutionary research. However, only when we face complexity, we also face its costs and burdens. In this particular case, the well-known co-variation between seed dormancy and flowering time is a missing piece, as well as the identification of (variation in) putative selective pressures accounting for the co-evolution between defense mechanisms and life history (seed dormancy vs. flowering time) along environmental gradients. More intellectual, technical and methodological challenges that with no doubt are totally worth it. Reference [1] Glander S, He F, Schmitz G, Witten A, Telschow A, de Meaux J. 2017. Assortment of flowering time and defense alleles in natural Arabidopsis thaliana populations suggests co-evolution between defense and vegetative lifespan strategies. bioRxiv ver.1 of June 19, 2017. doi: 10.1101/131136 | Assortment of flowering time and defense alleles in natural Arabidopsis thaliana populations suggests co-evolution between defense and vegetative lifespan strategies | Glander S, He F, Schmitz G, Witten A, Telschow A, de Meaux J | The selective impact of pathogen epidemics on host defenses can be strong but remains transient. By contrast, life-history shifts can durably and continuously modify the balance between costs and benefits of immunity, which arbitrates the evolutio... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Ecology, Expression Studies, Life History, Phenotypic Plasticity, Quantitative Genetics, Species interactions | Xavier Picó | Sophie Karrenberg, Rafa Rubio de Casas, Xavier Picó | 2017-06-21 10:57:14 | View |
19 Dec 2016

POSTPRINT
Geographic body size variation in the periodical cicadas Magicicada: implications for life cycle divergence and local adaptationKoyama T, Ito H, Kakishima S, Yoshimura J, Cooley JR, Simon C, Sota T 10.1111/jeb.12653Megacicadas show a temperature-mediated converse Bergmann cline in body size (larger in the warmer south) but no body size difference between 13- and 17-year species pairsRecommended by Wolf Blanckenhorn and Thomas FlattPeriodical cicadas are a very prominent insect group in North America that are known for their large size, good looks, and loud sounds. However, they are probably known best to evolutionary ecologists because of their long juvenile periods of 13 or 17 years (prime numbers!), which they spend in the ground. Multiple related species living in the same area are often coordinated in emerging as adults during the same year, thereby presumably swamping any predators specialized on eating them. Reference [1] Koyama T, Ito H, Kakishima S, Yoshimura J, Cooley JR, Simon C, Sota T. 2015. Geographic body size variation in the periodical cicadas Magicicada: implications for life cycle divergence and local adaptation. Journal of Evolutionary Biology 28:1270-1277. doi: 10.1111/jeb.12653 | Geographic body size variation in the periodical cicadas Magicicada: implications for life cycle divergence and local adaptation | Koyama T, Ito H, Kakishima S, Yoshimura J, Cooley JR, Simon C, Sota T | Seven species in three species groups (Decim, Cassini and Decula) of periodical cicadas (*Magicicada*) occupy a wide latitudinal range in the eastern United States. To clarify how adult body size, a key trait affecting fitness, varies geographical... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Ecology, Life History, Macroevolution, Phylogeography & Biogeography, Speciation | Wolf Blanckenhorn | 2016-12-19 10:39:22 | View | |
19 Mar 2018

Natural selection on plasticity of thermal traits in a highly seasonal environmentLeonardo Bacigalupe, Juan Diego Gaitan-Espitia, Aura M Barria, Avia Gonzalez-Mendez, Manuel Ruiz-Aravena, Mark Trinder, Barry Sinervo https://doi.org/10.1101/191825Is thermal plasticity itself shaped by natural selection? An assessment with desert frogsRecommended by Wolf Blanckenhorn based on reviews by Dries Bonte, Wolf Blanckenhorn and Nadia Aubin-HorthIt is well known that climatic factors – most notably temperature, season length, insolation and humidity – shape the thermal niche of organisms on earth through the action of natural selection. But how is this achieved precisely? Much of thermal tolerance is actually mediated by phenotypic plasticity (as opposed to genetic adaptation). A prominent expectation is that environments with greater (daily and/or annual) thermal variability select for greater plasticity, i.e. better acclimation capacity. Thus, plasticity might be selected per se. A Chilean group around Leonardo Bacigalupe assessed natural selection in the wild in one marginal (and extreme) population of the four-eyed frog Pleurodema thaul (Anura: Leptodactylidae) in an isolated oasis in the Atacama Desert, permitting estimation of mortality without much potential of confounding it with migration [1]. Several thermal traits were considered: CTmax – the critical maximal temperature; CTmin – the critical minimum temperature; Tpref – preferred temperature; Q10 – thermal sensitivity of metabolism; and body mass. Animals were captured in the wild and subsequently assessed for thermal traits in the laboratory at two acclimation temperatures (10° & 20°C), defining the plasticity in all traits as the difference between the traits at the two acclimation temperatures. Thereafter the animals were released again in their natural habitat and their survival was monitored over the subsequent 1.5 years, covering two breeding seasons, to estimate viability selection in the wild. The authors found and conclude that, aside from larger body size increasing survival (an unsurprising result), plasticity does not seem to be systematically selected directly, while some of the individual traits show weak signs of selection. Despite limited sample size (ca. 80 frogs) investigated in only one marginal but very seasonal population, this study is interesting because selection on plasticity in physiological thermal traits, as opposed to selection on the thermal traits themselves, is rarely investigated. The study thus also addressed the old but important question of whether plasticity (i.e. CTmax-CTmin) is a trait by itself or an epiphenomenon defined by the actual traits (CTmax and CTmin) [2-5]. Given negative results, the main question could not be ultimately solved here, so more similar studies should be performed. References [1] Bacigalupe LD, Gaitan-Espitia, JD, Barria AM, Gonzalez-Mendez A, Ruiz-Aravena M, Trinder M & Sinervo B. 2018. Natural selection on plasticity of thermal traits in a highly seasonal environment. bioRxiv 191825, ver. 5 peer-reviewed by Peer Community In Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/191825 | Natural selection on plasticity of thermal traits in a highly seasonal environment | Leonardo Bacigalupe, Juan Diego Gaitan-Espitia, Aura M Barria, Avia Gonzalez-Mendez, Manuel Ruiz-Aravena, Mark Trinder, Barry Sinervo | <p>For ectothermic species with broad geographical distributions, latitudinal/altitudinal variation in environmental temperatures (averages and extremes) are expected to shape the evolution of physiological tolerances and the acclimation capacity ... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Ecology, Phenotypic Plasticity | Wolf Blanckenhorn | 2017-09-22 23:17:40 | View | |
21 Nov 2019
Environmental specificity in Drosophila-bacteria symbiosis affects host developmental plasticityRobin Guilhot, Antoine Rombaut, Anne Xuéreb, Kate Howell, Simon Fellous https://doi.org/10.1101/717702Nutrition-dependent effects of gut bacteria on growth plasticity in Drosophila melanogasterRecommended by Wolf Blanckenhorn based on reviews by Pedro Simões and 1 anonymous reviewerIt is well known that the rearing environment has strong effects on life history and fitness traits of organisms. Microbes are part of every environment and as such likely contribute to such environmental effects. Gut bacteria are a special type of microbe that most animals harbor, and as such they are part of most animals’ environment. Such microbial symbionts therefore likely contribute to local adaptation [1]. The main question underlying the laboratory study by Guilhot et al. [2] was: How much do particular gut bacteria affect the organismal phenotype, in terms of life history and larval foraging traits, of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, a common laboratory model species in biology? References [1] Kawecki, T. J. and Ebert, D. (2004) Conceptual issues in local adaptation. Ecology Letters 7: 1225-1241. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00684.x | Environmental specificity in Drosophila-bacteria symbiosis affects host developmental plasticity | Robin Guilhot, Antoine Rombaut, Anne Xuéreb, Kate Howell, Simon Fellous | <p>Environmentally acquired microbial symbionts could contribute to host adaptation to local conditions like vertically transmitted symbionts do. This scenario necessitates symbionts to have different effects in different environments. We investig... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Ecology, Phenotypic Plasticity, Species interactions | Wolf Blanckenhorn | 2019-02-13 15:22:23 | View | |
24 Aug 2022
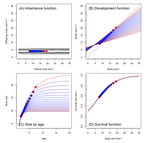
Density dependent environments can select for extremes of body sizeTim Coulson, Anja Felmy, Tomos Potter, Gioele Passoni, Robert A Montgomery, Jean-Michel Gaillard, Peter J Hudson, Joseph Travis, Ronald D Bassar, Shripad D Tuljapurkar, Dustin Marshall, Sonya M Clegg https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.17.480952A population biological modeling approach for life history and body size evolutionRecommended by Wolf Blanckenhorn based on reviews by Frédéric Guillaume and 2 anonymous reviewersBody size evolution is a central theme in evolutionary biology. Particularly the question of when and how smaller body sizes can evolve continues to interest evolutionary ecologists, because most life history models, and the empirical evidence, document that large body size is favoured by natural and sexual selection in most (even small) organisms and environments at most times. How, then, can such a large range of body size and life history syndromes evolve and coexist in nature? The paper by Coulson et al. lifts this question to the level of the population, a relatively novel approach using so-called integral projection (simulation) models (IPMs) (as opposed to individual-based or game theoretical models). As is well outlined by (anonymous) Reviewer 1, and following earlier papers spearheading this approach in other life history contexts, the authors use the well-known carrying capacity (K) of population biology as the ultimate fitness parameter to be maximized or optimized (rather than body size per se), to ultimately identify factors and conditions promoting the evolution of extreme body sizes in nature. They vary (individual or population) size-structured growth trajectories to observe age and size at maturity, surivorship and fecundity/fertility schedules upon evaluating K (see their Fig. 1). Importantly, trade-offs are introduced via density-dependence, either for adult reproduction or for juvenile survival, in two (of several conceivable) basic scenarios (see their Table 2). All other relevant standard life history variables (see their Table 1) are assumed density-independent, held constant or zero (as e.g. the heritability of body size). The authors obtain evidence for disruptive selection on body size in both scenarios, with small size and a fast life history evolving below a threshold size at maturity (at the lowest K) and large size and a slow life history beyond this threshold (see their Fig. 2). Which strategy wins ultimately depends on the fitness benefits of delaying sexual maturity (at larger size and longer lifespan) at the adult stage relative to the preceeding juvenile mortality costs, in agreement with classic life history theory (Roff 1992, Stearns 1992). The modeling approach can be altered and refined to be applied to other key life history parameters and environments. These results can ultimately explain the evolution of smaller body sizes from large body sizes, or vice versa, and their corresponding life history syndromes, depending on the precise environmental circumstances. All reviewers agreed that the approach taken is technically sound (as far as it could be evaluated), and that the results are interesting and worthy of publication. In a first round of reviews various clarifications of the manuscript were suggested by the reviewers. The new version was substantially changed by the authors in response, to the extent that it now is a quite different but much clearer paper with a clear message palatable for the general reader. The writing is now to the point, the paper's focus becomes clear in the Introduction, Methods & Results are much less technical, the Figures illustrative, and the descriptions and interpretations in the Discussion are easy to follow. In general any reader may of course question the choice and realism of the scenarios and underlying assumptions chosen by the authors for simplicity and clarity, for instance no heritability of body size and no cost of reproduction (other than mortality). But this is always the case in modeling work, and the authors acknowledge and in fact suggest concrete extensions and expansions of their approach in the Discussion. References Coulson T., Felmy A., Potter T., Passoni G., Montgomery R.A., Gaillard J.-M., Hudson P.J., Travis J., Bassar R.D., Tuljapurkar S., Marshall D.J., Clegg S.M. (2022) Density-dependent environments can select for extremes of body size. bioRxiv, 2022.02.17.480952, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.17.480952 | Density dependent environments can select for extremes of body size | Tim Coulson, Anja Felmy, Tomos Potter, Gioele Passoni, Robert A Montgomery, Jean-Michel Gaillard, Peter J Hudson, Joseph Travis, Ronald D Bassar, Shripad D Tuljapurkar, Dustin Marshall, Sonya M Clegg | <p>Body size variation is an enigma. We do not understand why species achieve the sizes they do, and this means we also do not understand the circumstances under which gigantism or dwarfism is selected. We develop size-structured integral projecti... |  | Evolutionary Dynamics, Evolutionary Ecology, Evolutionary Theory, Life History | Wolf Blanckenhorn | 2022-02-21 07:59:04 | View | |
22 May 2017
Can Ebola Virus evolve to be less virulent in humans?Mircea T. Sofonea, Lafi Aldakak, Luis Fernando Boullosa, Samuel Alizon 10.1101/108589A new hypothesis to explain Ebola's high virulenceRecommended by Virginie Ravigné and François Blanquart based on reviews by Virginie Ravigné and François Blanquart
The tragic 2014-2016 Ebola outbreak that resulted in more than 28,000 cases and 11,000 deaths in West Africa [1] has been a surprise to the scientific community. Before 2013, the Ebola virus (EBOV) was known to produce recurrent outbreaks in remote villages near tropical rainforests in Central Africa, never exceeding a few hundred cases with very high virulence. Both EBOV’s ability to circulate for several months in large urban human populations and its important mutation rate suggest that EBOV’s virulence could evolve and to some extent adapt to human hosts [2]. Up to now, the high virulence of EBOV in humans was generally thought to be maladaptive, the virus being adapted to circulating in wild animal populations (e.g. fruit bats [3]). As a logical consequence, EBOV virulence could be expected to decrease during long epidemics in humans. The present paper by Sofonea et al. [4] challenges this view and explores how, given EBOV’s life cycle and known epidemiological parameters, virulence is expected to evolve in the human host during long epidemics. The main finding of the paper is that there is no chance that EBOV’s virulence decreases in the short and long terms. The main underlying mechanism is that EBOV is also transmitted by dead bodies, which limits the cost of virulence. In itself the idea that selection should select for higher virulence in diseases that are also transmitted after host death will sound intuitive for most evolutionary epidemiologists. The accomplishment of the paper is to make a very strong case that the parameter range where virulence could decrease is very small. The paper further provides scientifically grounded arguments in favor of the safe management of corpses. Safe burial of corpses is culturally difficult to impose. The present paper shows that in addition to instantaneously decreasing the spread of the virus, safe burial may limit virulence increase in the short term and favor of less virulent strains in the long term. Altogether these results make a timely and important contribution to the knowledge and understanding of EBOV. References [1] World Health Organization. 2016. WHO: Ebola situation report - 10 June 2016. [2] Kupferschmidt K. 2014. Imagining Ebola’s next move. Science 346: 151–152. doi: 10.1126/science.346.6206.151 [3] Leroy EM, Kumulungui B, Pourrut X, Rouquet P, Hassanin A, Yaba P, Délicat A, Paweska, Gonzalez JP and Swanepoel R. 2005. Fruit bats as reservoirs of Ebola virus. Nature 438: 575–576. doi: 10.1038/438575a [4] Sofonea MT, Aldakak L, Boullosa LFVV and Alizon S. 2017. Can Ebola Virus evolve to be less virulent in humans? bioRxiv 108589, ver. 3 of 19th May 2017; doi: 10.1101/108589 | Can Ebola Virus evolve to be less virulent in humans? | Mircea T. Sofonea, Lafi Aldakak, Luis Fernando Boullosa, Samuel Alizon | Understanding Ebola Virus (EBOV) virulence evolution is not only timely but also raises specific questions because it causes one pf the most virulent human infections and it is capable of transmission after the death of its host. Using a compartme... |  | Evolutionary Epidemiology | Virginie Ravigné | 2017-02-15 13:25:58 | View | |
25 Jan 2023
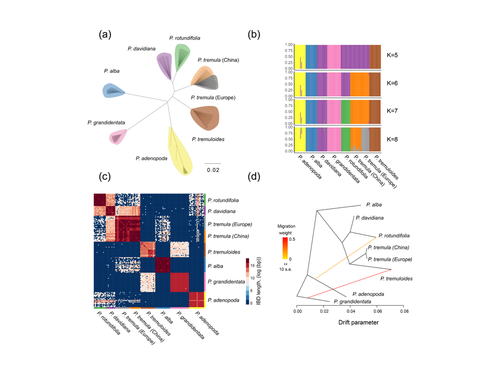
Drivers of genomic landscapes of differentiation across Populus divergence gradientHuiying Shang, Martha Rendón-Anaya, Ovidiu Paun, View David L Field, Jaqueline Hess, Claus Vogl, Jianquan Liu, Pär K. Ingvarsson, Christian Lexer, Thibault Leroy https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.26.457771Shedding light on genomic divergence along the speciation continuumRecommended by Violaine Llaurens based on reviews by Camille Roux, Steven van Belleghem and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Camille Roux, Steven van Belleghem and 1 anonymous reviewer
The article “Drivers of genomic landscapes of differentiation across Populus divergence gradient” by Shang et al. describes an amazing dataset where genomic variations among 21 pairs of diverging poplar species are compared. Such comparisons are still quite rare and are needed to shed light on the processes shaping genomic divergence along the speciation gradient. Relying on two hundred whole-genome resequenced samples from 8 species that diverged from 1.3 to 4.8 million years ago, the authors aim at identifying the key factors involved in the genomic differentiation between species. They carried out a wide range of robust statistical tests aiming at characterizing the genomic differentiation along the genome of these species pairs. They highlight in particular the role of linked selection and gene flow in shaping the divergence along the genomes of species pairs. They also confirm the significance of introgression among species with a net divergence larger than the upper boundaries of the grey zone of speciation previously documented in animals (da from 0.005 to 0.02, Roux et al. 2016). Because these findings pave the way to research about the genomic mechanisms associated with speciation in species with allopatric and parapatric distributions, I warmingly recommend this article. References Roux C, Fraïsse C, Romiguier J, Anciaux Y, Galtier N, Bierne N (2016) Shedding Light on the Grey Zone of Speciation along a Continuum of Genomic Divergence. PLOS Biology, 14, e2000234. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2000234 Shang H, Rendón-Anaya M, Paun O, Field DL, Hess J, Vogl C, Liu J, Ingvarsson PK, Lexer C, Leroy T (2023) Drivers of genomic landscapes of differentiation across Populus divergence gradient. bioRxiv, 2021.08.26.457771, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.26.457771 | Drivers of genomic landscapes of differentiation across Populus divergence gradient | Huiying Shang, Martha Rendón-Anaya, Ovidiu Paun, View David L Field, Jaqueline Hess, Claus Vogl, Jianquan Liu, Pär K. Ingvarsson, Christian Lexer, Thibault Leroy | <p style="text-align: justify;">Speciation, the continuous process by which new species form, is often investigated by looking at the variation of nucleotide diversity and differentiation across the genome (hereafter genomic landscapes). A key cha... |  | Population Genetics / Genomics, Speciation | Violaine Llaurens | 2021-09-06 14:12:27 | View | |
12 Jul 2017

Despite reproductive interference, the net outcome of reproductive interactions among spider mite species is not necessarily costlySalomé H. Clemente, Inês Santos, Rita Ponce, Leonor R. Rodrigues, Susana A. M. Varela and Sara Magalhães 10.1101/113274The pros and cons of mating with strangersRecommended by Vincent Calcagno based on reviews by Joël Meunier and Michael D Greenfield
Interspecific matings are by definition rare events in nature, but when they occur they can be very important, and not only because they might condition gene flow between species. Even when such matings have no genetic consequence, for instance if they do not yield any fertile hybrid offspring, they can still have an impact on the population dynamics of the species involved [1]. Such atypical pairings between heterospecific partners are usually regarded as detrimental or undesired; as they interfere with the occurrence or success of intraspecific matings, they are expected to cause a decline in absolute fitness. References [1] Gröning J. & Hochkirch A. 2008. Reproductive interference between animal species. The Quarterly Review of Biology 83: 257-282. doi: 10.1086/590510 [2] Clemente SH, Santos I, Ponce AR, Rodrigues LR, Varela SAM & Magalhaes S. 2017 Despite reproductive interference, the net outcome of reproductive interactions among spider mite species is not necessarily costly. bioRxiv 113274, ver. 4 of the 30th of June 2017. doi: 10.1101/113274 | Despite reproductive interference, the net outcome of reproductive interactions among spider mite species is not necessarily costly | Salomé H. Clemente, Inês Santos, Rita Ponce, Leonor R. Rodrigues, Susana A. M. Varela and Sara Magalhães | Reproductive interference is considered a strong ecological force, potentially leading to species exclusion. This supposes that the net effect of reproductive interactions is strongly negative for one of the species involved. Testing this requires... |  | Behavior & Social Evolution, Evolutionary Ecology, Species interactions | Vincent Calcagno | 2017-03-06 11:48:08 | View | |
29 Nov 2023
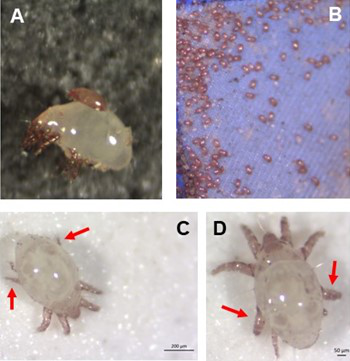
Individual differences in developmental trajectory leave a male polyphenic signature in bulb mite populationsJacques A. Deere & Isabel M. Smallegange https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.06.527265What determines whether to scramble or fight in male bulb mitesRecommended by Ulrich Karl Steiner based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
A classic textbook example in evolutionary ecology for phenotypic plasticity—the expression of different phenotypes by a genotype under different environmental conditions—is on Daphnia (Dodson 1989). If various species of this small crustacean are exposed to predation risk or cues thereof, their offspring show induced defense phenotypes including helmets, neck teeth, or head- and tail-spines. These induced morphological changes lower the risk of being eaten by a predator. As in Daphnia, induction can span over generations, while other induced phenotypic plastic changes are almost instantaneous, including many responses in physiology and behaviour (Gabriel et al. 2005). Larvae male bulb mites also show plasticity in morphologies throughout development. They can develop into a costly adult fighter morphology or a less costly, but vulnerable, scrambler type. The question Deere and Smallegange (Deere & Smallegange 2023) address is whether male bulb mite larvae can anticipate which type will likely be adaptive once they become adult, or alternatively, whether the resource availability or population density they experience during their larvae phase determines frequencies of adult scrambler and fighter types. They explore this question through experimental evolution, by removing different fractions of developing intermediate larva types. They thereby manipulate the stage structure of populations and alter selective forces on these stages. The potential shift of fixed genetics, imposed by the experimental selection regimes, is evaluated by fitness assays in green garden experiments. The exciting extension to classical experiments on phenotypic plasticity is that the authors aim at exploring eco-evolutionary feedbacks experimentally in a system that is a little more complex than basic host-parasite or predator-prey systems. The latter involve, for instance, rotifer-algae dynamics (Yoshida et al. 2003; Becks et al. 2012) or similar simple lab systems for which eco-evolutionary feedbacks have been demonstrated. The challenge for the exploration of more complex systems is revealed in the study by Deere and Smallegange. Their findings suggest that the frequencies of adult male morphotype is triggered by the environmental condition (nutrient availability) during the larval phase, i.e. a simple environmental induced plastic response. No fixed genetic shift in determining adult morphotype frequencies occurs. The trigger at the larva phase remains also not perfectly determined in their experiments, as population density and resource (food) availability are partly confounded. Additional complexity and selective aspects come into play in this system, as the targeted developmental stages that develop into fighter male morphs are also dispersal morphs. If selection on dispersal to avoid residing in food-limited environments is strong, triggering genetic shifts in fighter morphs by local population structure might be hard to experimentally achieve. Small sample sizes limit conclusions on complex interactions among duration of the experiment, population size, developmental stage types, and adult fighter frequencies. The presented study (Deere & Smallegange 2023) helps to bridge theoretical predictions and empirical evidence for eco-evolutionary feedbacks that goes beyond simple ecological-driven changes in population dynamics (Govaert et al. 2019).
References
Becks, L., Ellner, S.P., Jones, L.E. & Hairston, N.G. (2012). The functional genomics of an eco-evolutionary feedback loop: linking gene expression, trait evolution, and community dynamics. Ecol. Lett., 15, 492-501. | Individual differences in developmental trajectory leave a male polyphenic signature in bulb mite populations | Jacques A. Deere & Isabel M. Smallegange | <p style="text-align: justify;">Developmental plasticity alters phenotypes and can in that way change the response to selection. When alternative phenotypes show different life history trajectories, developmental plasticity can also affect, and be... |  | Evolutionary Ecology, Life History, Phenotypic Plasticity, Sexual Selection | Ulrich Karl Steiner | 2023-02-07 12:14:33 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Guillaume Achaz
Juan Arroyo
Trine Bilde
Dustin Brisson
Marianne Elias
Inês Fragata
Matteo Fumagalli
Tatiana Giraud
Frédéric Guillaume
Ruth Hufbauer
Sara Magalhaes
Caroline Nieberding
Michael David Pirie
Tanja Pyhäjärvi
Tanja Schwander
Alejandro Gonzalez Voyer










