Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture▼ | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
23 Jan 2020

A novel workflow to improve multi-locus genotyping of wildlife species: an experimental set-up with a known model systemGillingham, Mark A. F., Montero, B. Karina, Wilhelm, Kerstin, Grudzus, Kara, Sommer, Simone and Santos, Pablo S. C. https://doi.org/10.1101/638288Improving the reliability of genotyping of multigene families in non-model organismsRecommended by François Rousset based on reviews by Sebastian Ernesto Ramos-Onsins, Helena Westerdahl and Thomas BigotThe reliability of published scientific papers has been the topic of much recent discussion, notably in the biomedical sciences [1]. Although small sample size is regularly pointed as one of the culprits, big data can also be a concern. The advent of high-throughput sequencing, and the processing of sequence data by opaque bioinformatics workflows, mean that sequences with often high error rates are produced, and that exact but slow analyses are not feasible. References [1] Ioannidis, J. P. A, Greenland, S., Hlatky, M. A., Khoury, M. J., Macleod, M. R., Moher, D., Schulz, K. F. and Tibshirani, R. (2014) Increasing value and reducing waste in research design, conduct, and analysis. The Lancet, 383, 166-175. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62227-8 | A novel workflow to improve multi-locus genotyping of wildlife species: an experimental set-up with a known model system | Gillingham, Mark A. F., Montero, B. Karina, Wilhelm, Kerstin, Grudzus, Kara, Sommer, Simone and Santos, Pablo S. C. | <p>Genotyping novel complex multigene systems is particularly challenging in non-model organisms. Target primers frequently amplify simultaneously multiple loci leading to high PCR and sequencing artefacts such as chimeras and allele amplification... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Evolutionary Ecology, Genome Evolution, Molecular Evolution | François Rousset | Helena Westerdahl, Sebastian Ernesto Ramos-Onsins, Paul J. McMurdie , Arnaud Estoup, Vincent Segura, Jacek Radwan , Torbjørn Rognes , William Stutz , Kevin Vanneste , Thomas Bigot, Jill A. Hollenbach , Wieslaw Babik , Marie-Christin... | 2019-05-15 17:30:44 | View |
05 Feb 2019
The quiescent X, the replicative Y and the AutosomesGuillaume Achaz, Serge Gangloff, Benoit Arcangioli https://doi.org/10.1101/351288Replication-independent mutations: a universal signature ?Recommended by Nicolas Galtier based on reviews by Marc Robinson-Rechavi and Robert LanfearMutations are the primary source of genetic variation, and there is an obvious interest in characterizing and understanding the processes by which they appear. One particularly important question is the relative abundance, and nature, of replication-dependent and replication-independent mutations - the former arise as cells replicate due to DNA polymerization errors, whereas the latter are unrelated to the cell cycle. A recent experimental study in fission yeast identified a signature of mutations in quiescent (=non-replicating) cells: the spectrum of such mutations is characterized by an enrichment in insertions and deletions (indels) compared to point mutations, and an enrichment of deletions compared to insertions [2]. References [1] Achaz, G., Gangloff, S., and Arcangioli, B. (2019). The quiescent X, the replicative Y and the Autosomes. BioRxiv, 351288, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol. doi: 10.1101/351288 | The quiescent X, the replicative Y and the Autosomes | Guillaume Achaz, Serge Gangloff, Benoit Arcangioli | <p>From the analysis of the mutation spectrum in the 2,504 sequenced human genomes from the 1000 genomes project (phase 3), we show that sexual chromosomes (X and Y) exhibit a different proportion of indel mutations than autosomes (A), ranking the... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Genome Evolution, Human Evolution, Molecular Evolution, Population Genetics / Genomics, Reproduction and Sex | Nicolas Galtier | 2018-07-25 10:37:48 | View | |
04 Mar 2024
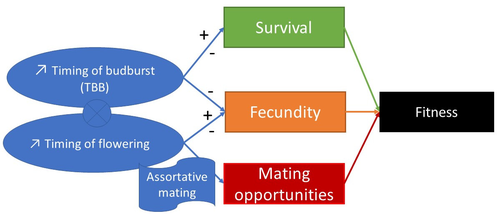
Interplay between fecundity, sexual and growth selection on the spring phenology of European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.).Sylvie Oddou-Muratorio, Aurore Bontemps, Julie Gauzere, Etienne Klein https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.27.538521Interplay between fecundity, sexual and growth selection on the spring phenology of European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.)Recommended by Santiago C. Gonzalez-Martinez based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Starting with the seminar paper by Lande & Arnold (1983), several studies have addressed phenotypic selection in natural populations of a wide variety of organisms, with a recent renewed interest in forest trees (e.g., Oddou-Muratorio et al. 2018; Alexandre et al. 2020; Westergren et al. 2023). Because of their long generation times, long-lived organisms such as forest trees may suffer the most from maladaptation due to climate change, and whether they will be able to adapt to new environmental conditions in just one or a few generations is hotly debated. In this study, Oddou-Muratorio and colleagues (2024) extend the current framework to add two additional selection components that may alter patterns of fecundity selection and the estimation of standard selection gradients, namely sexual selection (evaluated as differences in flowering phenology conducting to assortative mating) and growth (viability) selection. Notably, the study is conducted in two contrasted environments (low vs high altitude populations) providing information on how the environment may modulate selection patterns in spring phenology. Spring phenology is a key adaptive trait that has been shown to be already affected by climate change in forest trees (Alberto et al. 2013). While fecundity selection for early phenology has been extensively reported before (see Munguía-Rosas et al. 2011), the authors found that this kind of selection can be strongly modulated by sexual selection, depending on the environment. Moreover, they found a significant correlation between early phenology and seedling growth in a common garden, highlighting the importance of this trait for early survival in European beech. As a conclusion, this original research puts in evidence the need for more integrative approaches for the study of natural selection in the field, as well as the importance of testing multiple environments and the relevance of common gardens to further evaluate phenotypic changes due to real-time selection. PS: The recommender and the first author of the preprint have shared authorship in a recent paper in a similar topic (Westergren et al. 2023). Nevertheless, the recommender has not contributed in any way or was aware of the content of the current preprint before acting as recommender, and steps have been taken for a fair and unpartial evaluation. References Alberto, F. J., Aitken, S. N., Alía, R., González‐Martínez, S. C., Hänninen, H., Kremer, A., Lefèvre, F., Lenormand, T., Yeaman, S., Whetten, R., & Savolainen, O. (2013). Potential for evolutionary responses to climate change - evidence from tree populations. Global Change Biology, 19(6), 1645‑1661. Oddou-Muratorio S, Bontemps A, Gauzere J, Klein E (2024) Interplay between fecundity, sexual and growth selection on the spring phenology of European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.). bioRxiv, 2023.04.27.538521, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Evolutionary Biology https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.27.538521 Oddou-Muratorio, S., Gauzere, J., Bontemps, A., Rey, J.-F., & Klein, E. K. (2018). Tree, sex and size: Ecological determinants of male vs. female fecundity in three Fagus sylvatica stands. Molecular Ecology, 27(15), 3131‑3145. | Interplay between fecundity, sexual and growth selection on the spring phenology of European beech (*Fagus sylvatica* L.). | Sylvie Oddou-Muratorio, Aurore Bontemps, Julie Gauzere, Etienne Klein | <p>Background: Plant phenological traits such as the timing of budburst or flowering can evolve on ecological timescales through response to fecundity and viability selection. However, interference with sexual selection may arise from assortative ... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Ecology, Quantitative Genetics, Reproduction and Sex, Sexual Selection | Santiago C. Gonzalez-Martinez | 2023-05-02 11:57:23 | View | |
28 Aug 2019
Is adaptation limited by mutation? A timescale-dependent effect of genetic diversity on the adaptive substitution rate in animalsMarjolaine Rousselle, Paul Simion, Marie-Ka Tilak, Emeric Figuet, Benoit Nabholz, Nicolas Galtier https://doi.org/10.1101/643619To tinker, evolution needs a supply of spare partsRecommended by Georgii Bazykin based on reviews by Konstantin Popadin, David Enard and 1 anonymous reviewerIs evolution adaptive? Not if there is no variation for natural selection to work with. Theory predicts that how fast a population can adapt to a new environment can be limited by the supply of new mutations coming into it. This supply, in turn, depends on two things: how often mutations occur and in how many individuals. If there are few mutations, or few individuals in whom they can originate, individuals will be mostly identical in their DNA, and natural selection will be impotent. References [1] G, J. A., Visser, M. de, Zeyl, C. W., Gerrish, P. J., Blanchard, J. L., and Lenski, R. E. (1999). Diminishing Returns from Mutation Supply Rate in Asexual Populations. Science, 283(5400), 404–406. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5400.404 | Is adaptation limited by mutation? A timescale-dependent effect of genetic diversity on the adaptive substitution rate in animals | Marjolaine Rousselle, Paul Simion, Marie-Ka Tilak, Emeric Figuet, Benoit Nabholz, Nicolas Galtier | <p>Whether adaptation is limited by the beneficial mutation supply is a long-standing question of evolutionary genetics, which is more generally related to the determination of the adaptive substitution rate and its relationship with the effective... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Theory, Genome Evolution, Molecular Evolution, Population Genetics / Genomics | Georgii Bazykin | 2019-05-21 09:49:16 | View | |
14 Dec 2023

Genetic sex determination in three closely related hydrothermal vent gastropods, including one species with intersex individualsCastel J, Pradillon F, Cueff V, Leger G, Daguin-Thiébaut C, Ruault S, Mary J, Hourdez S, Jollivet D, and Broquet T https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.11.536409A shared XY sex chromosome system with variable recombination ratesRecommended by Tanja Schwander based on reviews by Hugo Darras, Daniel Jeffries and 1 anonymous reviewerMany species with separate sexes have evolved sex chromosomes, with the sex-limited chromosomes (i.e. the Y or W chromosomes) exhibiting a wide range of genetic divergences from their homologous X or Z chromosomes (Bachtrog et al., 2014). Variable divergences can result from the cessation of recombination between sex chromosomes that occurred at different time points, with the mechanisms of initiation and expansion of recombination suppression along sex chromosomes remaining poorly understood (Charlesworth, 2017). The study by Castel et al (2023) describes the serendipitous discovery of a shared XY sex chromosome system in three closely related hydrothermal vent gastropods. The X and Y chromosomes appear to still recombine but at variable rates across the three species. This variation makes the gastropod system a very promising focus for future research on sex chromosome evolution. An additional intriguing finding is that some females in one of three gastropod species contain male reproductive tissue in their gonads, providing a fascinating case of a mixed or transitory sexual system. Overall, the study by Castel et al (2023) offers the first insights into the reproduction and sex chromosome system of animals living in deep marine vents, which have remained poorly studied and open outstanding research perspectives on these creatures. References Bachtrog, D., J.E.Mank, C.L.Peichel, M.Kirkpatrick, S.P.Otto, T.L. Ashman, M.W.Hahn, J.Kitano, I.Mayrose, R.Ming, et al. 2014.Sex determination: why so many ways of doing it? PLoSBiol. 12:e1001899. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001899 Charlesworth, D. Young sex chromosomes in plants and animals. 2019. New Phytologist 224: 1095–1107. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16002 Castel J, Pradillon F, Cueff V, Leger G, Daguin-Thiébaut C, Ruault S, Mary J, Hourdez S, Jollivet D, and Broquet T 2023. Genetic sex determination in three closely related hydrothermal vent gastropods, including one species with intersex individuals. bioRxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.11.536409 | Genetic sex determination in three closely related hydrothermal vent gastropods, including one species with intersex individuals | Castel J, Pradillon F, Cueff V, Leger G, Daguin-Thiébaut C, Ruault S, Mary J, Hourdez S, Jollivet D, and Broquet T | <p style="text-align: justify;">Molluscs have a wide variety of sexual systems and have undergone many transitions from separate sexes to hermaphroditism or vice versa, which is of interest for studying the evolution of sex determination and diffe... |  | Population Genetics / Genomics, Reproduction and Sex | Tanja Schwander | 2023-04-14 11:48:25 | View | |
07 Sep 2018

Parallel pattern of differentiation at a genomic island shared between clinal and mosaic hybrid zones in a complex of cryptic seahorse lineagesFlorentine Riquet, Cathy Liautard-Haag, Lucy Woodall, Carmen Bouza, Patrick Louisy, Bojan Hamer, Francisco Otero-Ferrer, Philippe Aublanc, Vickie Béduneau, Olivier Briard, Tahani El Ayari, Sandra Hochscheid, Khalid Belkhir, Sophie Arnaud-Haond, Pierre-Alexandre Gagnaire, Nicolas Bierne https://doi.org/10.1101/161786Genomic parallelism in adaptation to orthogonal environments in sea horsesRecommended by Yaniv Brandvain based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersStudies in speciation genomics have revealed that gene flow is quite common, and that despite this, species can maintain their distinct environmental adaptations. Although researchers are still elucidating the genomic mechanisms by which species maintain their adaptations in the face of gene flow, this often appears to involve few diverged genomic regions in otherwise largely undifferentiated genomes. In this preprint [1], Riquet and colleagues investigate the genetic structuring and patterns of parallel evolution in the long-snouted seahorse. References [1] Riquet, F., Liautard-Haag, C., Woodall, L., Bouza, C., Louisy, P., Hamer, B., Otero-Ferrer, F., Aublanc, P., Béduneau, V., Briard, O., El Ayari, T., Hochscheid, S. Belkhir, K., Arnaud-Haond, S., Gagnaire, P.-A., Bierne, N. (2018). Parallel pattern of differentiation at a genomic island shared between clinal and mosaic hybrid zones in a complex of cryptic seahorse lineages. bioRxiv, 161786, ver. 4 recommended and peer-reviewed by PCI Evol Biol. doi: 10.1101/161786 | Parallel pattern of differentiation at a genomic island shared between clinal and mosaic hybrid zones in a complex of cryptic seahorse lineages | Florentine Riquet, Cathy Liautard-Haag, Lucy Woodall, Carmen Bouza, Patrick Louisy, Bojan Hamer, Francisco Otero-Ferrer, Philippe Aublanc, Vickie Béduneau, Olivier Briard, Tahani El Ayari, Sandra Hochscheid, Khalid Belkhir, Sophie Arnaud-Haond, Pi... | <p>Diverging semi-isolated lineages either meet in narrow clinal hybrid zones, or have a mosaic distribution associated with environmental variation. Intrinsic reproductive isolation is often emphasized in the former and local adaptation in the la... |  | Hybridization / Introgression, Molecular Evolution, Population Genetics / Genomics, Speciation | Yaniv Brandvain | Kathleen Lotterhos, Sarah Fitzpatrick | 2017-07-11 13:12:40 | View |
18 Nov 2022
Fitness costs and benefits in response to artificial artesunate selection in PlasmodiumVilla M, Berthomieu A, Rivero A https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.28.478164The importance of understanding fitness costs associated with drug resistance throughout the life cycle of malaria parasitesRecommended by Silvie Huijben based on reviews by Sarah Reece and Marianna SzucsAntimalarial resistance is a major hurdle to malaria eradication efforts. The spread of drug resistance follows basic evolutionary principles, with competitive interactions between resistant and susceptible malaria strains being central to the fitness of resistant parasites. These competitive interactions can be used to design resistance management strategies, whereby a fitness cost of resistant parasites can be exploited through maintaining competitive suppression of the more fit drug-susceptible parasites. This can potentially be achieved using lower drug dosages or lower frequency of drug treatments. This approach has been demonstrated to work empirically in a rodent malaria model [1,2] and has been demonstrated to have clinical success in cancer treatments [3]. However, these resistance management approaches assume a fitness cost of the resistant pathogen, and, in the case of malaria parasites in general, and for artemisinin resistant parasites in particular, there is limited information on the presence of such fitness cost. The best suggestive evidence for the presence of fitness costs comes from the discontinuation of the use of the drug, which, in the case of chloroquine, was followed by a gradual drop in resistance frequency over the following decade [see e.g. 4,5]. However, with artemisinin derivative drugs still in use, alternative ways to study the presence of fitness costs need to be undertaken. References [1] Huijben S, Bell AS, Sim DG, Tomasello D, Mideo N, Day T, et al. 2013. Aggressive chemotherapy and the selection of drug resistant pathogens. PLoS Pathog. 9(9): e1003578. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003578 [5] Mharakurwa S, Matsena-Zingoni Z, Mudare N, Matimba C, Gara TX, Makuwaza A, et al. 2021. Steep rebound of chloroquine-sensitive Plasmodium falciparum in Zimbabwe. J Infect Dis. 223(2): 306-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa368 | Fitness costs and benefits in response to artificial artesunate selection in Plasmodium | Villa M, Berthomieu A, Rivero A | <p style="text-align: justify;">Drug resistance is a major issue in the control of malaria. Mutations linked to drug resistance often target key metabolic pathways and are therefore expected to be associated with biological costs. The spread of dr... |  | Evolutionary Applications, Life History | Silvie Huijben | 2022-01-31 13:01:16 | View | |
25 Jan 2024
Sperm production and allocation in response to risk of sperm competition in the black soldier fly Hermetia illucensFrédéric Manas, Carole Labrousse, Christophe Bressac https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.20.544772Elevated sperm production and faster transfer: plastic responses to the risk of sperm competition in males of the black sodier fly Hermetia illuceRecommended by Trine Bilde based on reviews by Rebecca Boulton, Isabel Smallegange and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Rebecca Boulton, Isabel Smallegange and 1 anonymous reviewer
In this paper (Manas et al., 2023), the authors investigate male responses to risk of sperm competition in the black soldier fly Hermetia illuce, a widespread insect that has gained recent attention for its potential to be farmed for sustainable food production (Tomberlin & van Huis, 2020). Using an experimental approach that simulated low-risk (males were kept individually) and high-risk (males were kept in groups of 10) of sperm competition, they found that males reared in groups showed a significant increase in sperm production compared with males reared individually. This shows a response to the rearing environment in sperm production that is consistent with an increase in the perceived risk of sperm competition. These males were then used in mating experiments to determine whether sperm allocation to females during mating was influenced by the perceived risk of sperm competition. Mating experiments were initiated in groups, since mating only occurs when more than one male and one female are present, indicating strong sexual selection in the wild. Once a copulation began, the pair was moved to a new environment with no competition, with male competitors, or with other females, to test how social environment and potentially the sex of surrounding individuals influenced sperm allocation during mating. Copulation duration and the number of sperm transferred were subsequently counted. In these mating experiments, the number of sperm stored in the female spermathecae increased under immediate risk of sperm competition. Interestingly, this was not because males copulated for longer depending on the risk of sperm competition, indicating that males respond plastically to the risk of competition by elevating their investment in sperm production and speed of sperm transfer. There was no difference between competitive environments consisting of males or females respectively, suggesting that it is the presence of other flies per se that influence sperm allocation. The study provides an interesting new example of how males alter reproductive investment in response to social context and sexual competition in their environment. In addition, it provides new insights into the reproductive biology of the black soldier fly Hermetia illucens, which may be relevant for optimizing farming conditions. References Manas F, Labrousse C, Bressac C (2023) Sperm production and allocation in response to risks of sperm competition in the black soldier fly Hermetia illucens. bioRxiv, 2023.06.20.544772, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.20.544772 Tomberlin JK, Van Huis A (2020) Black soldier fly from pest to ‘crown jewel’ of the insects as feed industry: an historical perspective. Journal of Insects as Food and Feed, 6, 1–4. https://doi.org/10.3920/JIFF2020.0003 | Sperm production and allocation in response to risk of sperm competition in the black soldier fly Hermetia illucens | Frédéric Manas, Carole Labrousse, Christophe Bressac | <p style="text-align: justify;">In polyandrous species, competition between males for offspring paternity goes on after copulation through the competition of their ejaculates for the fertilisation of female's oocytes. Given that males allocating m... | Reproduction and Sex, Sexual Selection | Trine Bilde | 2023-06-26 09:41:07 | View | ||
03 Aug 2017
POSTPRINT
Fisher's geometrical model and the mutational patterns of antibiotic resistance across dose gradientsNoémie Harmand, Romain Gallet, Roula Jabbour-Zahab, Guillaume Martin, Thomas Lenormand 10.1111/evo.13111What doesn’t kill us makes us stronger: can Fisher’s Geometric model predict antibiotic resistance evolution?Recommended by Inês Fragata and Claudia BankThe increasing number of reported cases of antibiotic resistance is one of today’s major public health concerns. Dealing with this threat involves understanding what drives the evolution of antibiotic resistance and investigating whether we can predict (and subsequently avoid or circumvent) it [1]. References [1] Palmer AC, and Kishony R. 2013. Understanding, predicting and manipulating the genotypic evolution of antibiotic resistance. Nature Review Genetics 14: 243—248. doi: 10.1038/nrg3351 [2] Tenaillon O. 2014. The utility of Fisher’s geometric model in evolutionary genetics. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution and Systematics 45: 179—201. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-120213-091846 [3] Blanquart F and Bataillon T. 2016. Epistasis and the structure of fitness landscapes: are experimental fitness landscapes compatible with Fisher’s geometric model? Genetics 203: 847—862. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.182691 [4] Harmand N, Gallet R, Jabbour-Zahab R, Martin G and Lenormand T. 2017. Fisher’s geometrical model and the mutational patterns of antibiotic resistance across dose gradients. Evolution 71: 23—37. doi: 10.1111/evo.13111 [5] de Visser, JAGM, and Krug J. 2014. Empirical fitness landscapes and the predictability of evolution. Nature 15: 480—490. doi: 10.1038/nrg3744 [6] Palmer AC, Toprak E, Baym M, Kim S, Veres A, Bershtein S and Kishony R. 2015. Delayed commitment to evolutionary fate in antibiotic resistance fitness landscapes. Nature Communications 6: 1—8. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8385 | Fisher's geometrical model and the mutational patterns of antibiotic resistance across dose gradients | Noémie Harmand, Romain Gallet, Roula Jabbour-Zahab, Guillaume Martin, Thomas Lenormand | Fisher's geometrical model (FGM) has been widely used to depict the fitness effects of mutations. It is a general model with few underlying assumptions that gives a large and comprehensive view of adaptive processes. It is thus attractive in sever... |  | Adaptation | Inês Fragata | 2017-08-01 16:06:02 | View | |
24 Jan 2017

POSTPRINT
Birth of a W sex chromosome by horizontal transfer of Wolbachia bacterial symbiont genomeSébastien Leclercq, Julien Thézé, Mohamed Amine Chebbi, Isabelle Giraud, Bouziane Moumen, Lise Ernenwein, Pierre Grève, Clément Gilbert, and Richard Cordaux 10.1073/pnas.1608979113A newly evolved W(olbachia) sex chromosome in pillbug!Recommended by Gabriel Marais and Sylvain CharlatIn some taxa such as fish and arthropods, closely related species can have different mechanisms of sex determination and in particular different sex chromosomes, which implies that new sex chromosomes are constantly evolving [1]. Several models have been developed to explain this pattern but empirical data are lacking and the causes of the fast sex chromosome turn over remain mysterious [2-4]. Leclerq et al. [5] in a paper that just came out in PNAS have focused on one possible explanation: Wolbachia. This widespread intracellular symbiont of arthropods can manipulate its host reproduction in a number of ways, often by biasing the allocation of resources toward females, the transmitting sex. Perhaps the most spectacular example is seen in pillbugs, where Wolbachia commonly turns infected males into females, thus doubling its effective transmission to grandchildren. Extensive investigations on this phenomenon were initiated 30 years ago in the host species Armadillidium vulgare. The recent paper by Leclerq et al. beautifully validates an hypothesis formulated in these pioneer studies [6], namely, that a nuclear insertion of the Wolbachia genome caused the emergence of new female determining chromosome, that is, a new sex chromosome. Many populations of A. vulgare are infected by the feminising Wolbachia strain wVulC, where the spread of the bacterium has also induced the loss of the ancestral female determining W chromosome (because feminized ZZ individuals produce females without transmitting any W). In these populations, all individuals carry two Z chromosomes, so that the bacterium is effectively the new sex-determining factor: specimens that received Wolbachia from their mother become females, while the occasional loss of Wolbachia from mothers to eggs allows the production of males. Intriguingly, studies from natural populations also report that some females are devoid both of Wolbachia and the ancestral W chromosome, suggesting the existence of new female determining nuclear factor, the hypothetical “f element”. Leclerq et al. [5] found the f element and decrypted its origin. By sequencing the genome of a strain carrying the putative f element, they found that a nearly complete wVulC genome got inserted in the nuclear genome and that the chromosome carrying the insertion has effectively become a new W chromosome. The insertion is indeed found only in females, PCRs and pedigree analysis tell. Although the Wolbachia-derived gene(s) that became sex-determining gene(s) remain to be identified among many possible candidates, the genomic and genetic evidence are clear that this Wolbachia insertion is determining sex in this pillbug strain. Leclerq et al. [5] also found that although this insertion is quite recent, many structural changes (rearrangements, duplications) have occurred compared to the wVulC genome, which study will probably help understand which bacterial gene(s) have retained a function in the nucleus of the pillbug. Also, in the future, it will be interesting to understand how and why exactly the nuclear inserted Wolbachia rose in frequency in the pillbug population and how the cytoplasmic Wolbachia was lost, and to tease apart the roles of selection and drift in this event. We highly recommend this paper, which provides clear evidence that Wolbachia has caused sex chromosome turn over in one species, opening the conjecture that it might have done so in many others. References [1] Bachtrog D, Mank JE, Peichel CL, Kirkpatrick M, Otto SP, Ashman TL, Hahn MW, Kitano J, Mayrose I, Ming R, Perrin N, Ross L, Valenzuela N, Vamosi JC. 2014. Tree of Sex Consortium. Sex determination: why so many ways of doing it? PLoS Biology 12: e1001899. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001899 [2] van Doorn GS, Kirkpatrick M. 2007. Turnover of sex chromosomes induced by sexual conflict. Nature 449: 909-912. doi: 10.1038/nature06178 [3] Cordaux R, Bouchon D, Grève P. 2011. The impact of endosymbionts on the evolution of host sex-determination mechanisms. Trends in Genetics 27: 332-341. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2011.05.002 [4] Blaser O, Neuenschwander S, Perrin N. 2014. Sex-chromosome turnovers: the hot-potato model. American Naturalist 183: 140-146. doi: 10.1086/674026 [5] Leclercq S, Thézé J, Chebbi MA, Giraud I, Moumen B, Ernenwein L, Grève P, Gilbert C, Cordaux R. 2016. Birth of a W sex chromosome by horizontal transfer of Wolbachia bacterial symbiont genome. Proceeding of the National Academy of Science USA 113: 15036-15041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1608979113 [6] Legrand JJ, Juchault P. 1984. Nouvelles données sur le déterminisme génétique et épigénétique de la monogénie chez le crustacé isopode terrestre Armadillidium vulgare Latr. Génétique Sélection Evolution 16: 57–84. doi: 10.1186/1297-9686-16-1-57 | Birth of a W sex chromosome by horizontal transfer of Wolbachia bacterial symbiont genome | Sébastien Leclercq, Julien Thézé, Mohamed Amine Chebbi, Isabelle Giraud, Bouziane Moumen, Lise Ernenwein, Pierre Grève, Clément Gilbert, and Richard Cordaux | Sex determination is an evolutionarily ancient, key developmental pathway governing sexual differentiation in animals. Sex determination systems are remarkably variable between species or groups of species, however, and the evolutionary forces und... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Genome Evolution, Molecular Evolution, Reproduction and Sex, Species interactions | Gabriel Marais | 2017-01-13 15:15:51 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Guillaume Achaz
Juan Arroyo
Trine Bilde
Dustin Brisson
Marianne Elias
Inês Fragata
Matteo Fumagalli
Tatiana Giraud
Frédéric Guillaume
Ruth Hufbauer
Sara Magalhaes
Caroline Nieberding
Michael David Pirie
Tanja Pyhäjärvi
Tanja Schwander
Alejandro Gonzalez Voyer










