Separate the wheat from the chaff: genomic analysis of local adaptation in the red coral Corallium rubrum
Pratlong M, Haguenauer A, Brener K, Mitta G, Toulza E, Garrabou J, Bensoussan N, Pontarotti P, Aurelle D
https://doi.org/10.1101/306456
Pros and Cons of local adaptation scans
Recommended by Guillaume Achaz based on reviews by Lucas Gonçalves da Silva and 1 anonymous reviewer
The preprint by Pratlong et al. [1] is a well thought quest for genomic regions involved in local adaptation to depth in a species a red coral living the Mediterranean Sea. It first describes a pattern of structuration and then attempts to find candidate genes involved in local adaptation by contrasting deep with shallow populations. Although the pattern of structuration is clear and meaningful, the candidate genomic regions involved in local adaptation remain to be confirmed. Two external reviewers and myself found this preprint particularly interesting regarding the right-mindedness of the authors in front of the difficulties they encounter during their experiments. The discussions on the pros and cons of the approach are very sound and can be easily exported to a large number of studies that hunt for local adaptation. In this sense, the lessons one can learn by reading this well documented manuscript are certainly valuable for a wide range of evolutionary biologists.
More precisely, the authors RAD-sequenced 6 pairs of 'shallow vs deep' samples located in 3 geographical sea areas (Banyuls, Corsica and Marseilles). They were hoping to detect genes involved in the adaptation to depth, if there were any. They start by assessing the patterns of structuration of the 6 samples using PCA and AMOVA [2] and also applied the STRUCTURE [3] assignment software. They show clearly that the samples were mostly differentiated between geographical areas and that only 1 out the 3 areas shows a pattern of isolation by depth (i.e. Marseille). They nevertheless went on and scanned for variants that are highly differentiated in the deep samples when compared to the shallow paired samples in Marseilles, using an Fst outliers approach [4] implemented in the BayeScEnv software [5]. No clear functional signal was in the end detected among the highly differentiated SNPs, leaving a list of candidates begging for complementary data.
The scan for local adaptation using signatures of highly divergent regions is a classical problem of population genetics. It has been applied on many species with various degrees of success. This study is a beautiful example of a well-designed study that did not give full satisfactory answers. Readers will especially appreciate the honesty and the in-depth discussions of the authors while exposing their results and their conclusions step by step.
References
[1] Pratlong, M., Haguenauer, A., Brener, K., Mitta, G., Toulza, E., Garrabou, J., Bensoussan, N., Pontarotti P., & Aurelle, D. (2018). Separate the wheat from the chaff: genomic scan for local adaptation in the red coral Corallium rubrum. bioRxiv, 306456, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol. doi: 10.1101/306456
[2] Excoffier, L., Smouse, P. E. & Quattro, J. M. (1992). Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics, 131(2), 479-491.
[3] Pritchard, J. K., Stephens, M., & Donnelly, P. (2000). Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics, 155(2), 945-959.
[4] Lewontin, R. C., & Krakauer, J. (1973). Distribution of gene frequency as a test of the theory of the selective neutrality of polymorphisms. Genetics, 74(1), 175-195.
[5] de Villemereuil, P., & Gaggiotti, O. E. (2015). A new FST‐based method to uncover local adaptation using environmental variables. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 6(11), 1248-1258. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.12418
| Separate the wheat from the chaff: genomic analysis of local adaptation in the red coral Corallium rubrum | Pratlong M, Haguenauer A, Brener K, Mitta G, Toulza E, Garrabou J, Bensoussan N, Pontarotti P, Aurelle D | <p>Genomic data allow an in-depth and renewed study of local adaptation. The red coral (Corallium rubrum, Cnidaria) is a highly genetically structured species and a promising model for the study of adaptive processes along an environmental gradien... |  | Adaptation, Population Genetics / Genomics | Guillaume Achaz | | 2018-04-24 11:27:40 | View |
Leaps and bounds: geographical and ecological distance constrained the colonisation of the Afrotemperate by Erica
Michael D. Pirie, Martha Kandziora, Nicolai M. Nuerk, Nicholas C. Le Maitre, Ana Laura Mugrabi de Kuppler, Berit Gehrke, Edward G.H. Oliver, and Dirk U. Bellstedt
https://doi.org/10.1101/290791
The colonization history of largely isolated habitats
Recommended by Andrea S. Meseguer based on reviews by Simon Joly, Florian Boucher and 2 anonymous reviewers
The build-up of biodiversity is the result of in situ speciation and immigration, with the interplay between geographical distance and ecological suitability determining the probability of an organism to establish in a new area. The relative contribution of these factors have long interested biogeographers, in particular to explain the distribution of organisms adapted to habitats that remained largely isolated, such as the colonization of oceanic islands or land waters. The focus of this study is the formation of the afrotemperate flora; patches of temperate vegetation separated by thousands of kilometers in Africa, with high levels of endemism described in the Cape region, the Drakensberg range and the high mountains of tropical east Africa [1]. The floristic affinities between these centers of endemism have frequently been explored but the origin of many afrotemperate lineages remains enigmatic [2].
To identify the biogeographic history and drivers of biogeographic movements of the large afrotemperate genus Erica, the study of Pirie and colleagues [3] develops a robust hypothesis-testing approach relying on historical biogeographic models, phylogenetic and species occurrence data. Specifically, the authors test the directionality of migrations through Africa and address the general question on whether geographic proximity or climatic niche similarity constrained the colonization of the Afrotemperate by Erica. They found that the distribution of Erica species in Africa is the result of infrequent colonization events and that both geographic proximity and niche similarity limited geographic movements (with the model that incorporates both factors fitting the data better than null models). Unfortunately, the correlation between geographic and environmental distances found in this study limited the potential evaluation of their roles individually. They also found that species of Erica have dispersed from Europe to African regions, with the Drakensberg Mountains representing a colonization sink, rather than acting as a “stepping stone” between the Cape and Tropical African regions.
Advances in historical biogeography have been recently questioned by the difficulty to compare biogeographic models emphasizing long distance dispersal (DEC+J) versus vicariance (DEC) using statistical methods, such as AIC, as well as by questioning the own performance of DEC+J models [4]. Behind Pirie et al. main conclusions prevails the assumption that patterns of concerted long distance dispersal are more realistic than vicariance scenarios, such that a widespread afrotemperate flora that receded with climatic changes never existed. Pirie et al. do not explicitly test for this scenario based on the idea that these habitats remained largely isolated over time and our current knowledge on African paleoclimates and vegetation, emphasizing the value of arguments based on empirical (biological, geographic) considerations in model comparisons. I, however, appreciate from this study that the results of the biogeographic models emphasizing long distance dispersal, vicariance, and the unconstrained models are congruent with each other and presented together.
Pirie and colleagues [3] bring a nice study on the importance of long distance dispersal and biome shift in structuring the regional floras of Africa. They evidence outstanding examples of radiations in Erica resulting from single dispersal events over long distances and between ecologically dissimilar areas, which highlight the importance of niche evolution and biome shifts in the assembly of diversity. Although we still face important limitations in data availability and model realism, the last decade has witnessed an improvement of our understanding of how historical and environmental triggers are intertwined on shaping biological diversity. I found Pirie et al.’s approach (and analytical framework) very stimulating and hope that will help movement in that direction, providing interesting perspectives for future investigations of other regions.
References
[1] Linder, H.P. 1990. On the relationship between the vegetation and floras of the Afromontane and the Cape regions of Africa. Mitteilungen aus dem Institut für Allgemeine Botanik Hamburg 23b:777–790.
[2] Galley, C., Bytebier, B., Bellstedt, D. U., & Peter Linder, H. (2006). The Cape element in the Afrotemperate flora: from Cape to Cairo?. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 274(1609), 535-543. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2006.0046
[3] Pirie, M. D., Kandziora, M., Nuerk, N. M., Le Maitre, N. C., de Kuppler, A. L. M., Gehrke, B., Oliver, E. G. H., & Bellstedt, D. U. (2018). Leaps and bounds: geographical and ecological distance constrained the colonisation of the Afrotemperate by Erica. bioRxiv, 290791. ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol. doi: 10.1101/290791
[4] Ree, R. H., & Sanmartín, I. (2018). Conceptual and statistical problems with the DEC+ J model of founder‐event speciation and its comparison with DEC via model selection. Journal of Biogeography, 45(4), 741-749. doi: 10.1111/jbi.13173
| Leaps and bounds: geographical and ecological distance constrained the colonisation of the Afrotemperate by Erica | Michael D. Pirie, Martha Kandziora, Nicolai M. Nuerk, Nicholas C. Le Maitre, Ana Laura Mugrabi de Kuppler, Berit Gehrke, Edward G.H. Oliver, and Dirk U. Bellstedt | <p>The coincidence of long distance dispersal and biome shift is assumed to be the result of a multifaceted interplay between geographical distance and ecological suitability of source and sink areas. Here, we test the influence of these factors o... | 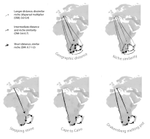 | Phylogeography & Biogeography | Andrea S. Meseguer | | 2018-04-09 10:10:04 | View |
Let’s move beyond costs of resistance!
Recommended by Inês Fragata and Claudia Bank based on reviews by Danna Gifford, Helen Alexander and 1 anonymous reviewer
The increase in the prevalence of (antibiotic) resistance has become a major global health concern and is an excellent example of the impact of real-time evolution on human society. This has led to a boom of studies that investigate the mechanisms and factors involved in the evolution of resistance, and to the spread of the concept of "costs of resistance". This concept refers to the relative fitness disadvantage of a drug-resistant genotype compared to a non-resistant reference genotype in the ancestral (untreated) environment.
In their paper, Lenormand et al. [1] discuss the history of this concept and highlight its caveats and limitations. The authors address both practical and theoretical problems that arise from the simplistic view of "costly resistance" and argue that they can be prejudicial for antibiotic resistance studies. For a better understanding, they visualize their points of critique by means of Fisher's Geometric model.
The authors give an interesting historical overview of how the concept arose and speculate that it emerged (during the 1980s) in an attempt by ecologists to spread awareness that fitness can be environment-dependent, and because of the concept's parallels to trade-offs in life-history evolution. They then identify several problems that arise from the concept, which, besides the conceptual misunderstandings that they can cause, are important to keep in mind when designing experimental studies.
The authors highlight and explain the following points:
1. Costs of resistance do not necessarily imply pleiotropic effects of a resistance mutation, and pleiotropy is not necessarily the cause of fitness trade-offs.
2. Any non-treated environment and any treatment dose can result in a different cost.
3. Different reference genotypes may result in different costs. Specifically, the reference genotype has to be "optimally" adapted to the reference environment to provide an accurate measurement of costs.
Lenormand et al.'s paper [1] is a timely perspective piece in light of the ever-increasing efforts to understand and tackle resistance evolution [2]. Although some readers may shy away from the rather theoretical presentation of the different points of concern, it will be useful for both theoretical and empirical readers by illustrating the misconceptions that can arise from the concept of the cost of resistance. Ultimately, the main lesson to be learned from this paper may not be to ban the term "cost of resistance" from one's vocabulary, but rather to realize that the successful fight against drug resistance requires more differential information than the measurement of fitness effects in a drug-treated vs. non-treated environment in the lab [3-4]. Specifically, a better integration of the ecological aspects of drug resistance evolution and maintenance is needed [5], and we are far from a general understanding of how environmental factors interact and influence an organism's (absolute and relative) fitness and the effect of resistance mutations.
References
[1] Lenormand T, Harmand N, Gallet R. 2018. Cost of resistance: an unreasonably expensive concept. bioRxiv 276675, ver. 3 peer-reviewed by Peer Community In Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/276675
[2] Andersson DI and Hughes D. Persistence of antibiotic resistance in bacterial populations. 2011. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 35: 901-911. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00289.x
[3] Chevereau G, Dravecká M, Batur T, Guvenek A, Ayhan DH, Toprak E, Bollenbach T. 2015. Quantifying the determinants of evolutionary dynamics leading to drug resistance. PLoS biology 13, e1002299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002299
[4] Bengtsson-Palme J, Kristiansson E, Larsson DGJ. 2018. Environmental factors influencing the development and spread of antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 42: 68–80. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fux053
[5] Hiltunen T, Virta M, Laine AL. 2017. Antibiotic resistance in the wild: an eco-evolutionary perspective. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 372: 20160039. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0039
| Cost of resistance: an unreasonably expensive concept | Thomas Lenormand, Noemie Harmand, Romain Gallet | <p>The cost of resistance, or the fitness effect of resistance mutation in absence of the drug, is a very widepsread concept in evolutionary genetics and beyond. It has represented an important addition to the simplistic view that resistance mutat... | 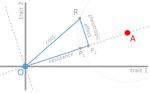 | Adaptation, Evolutionary Applications, Evolutionary Ecology, Evolutionary Theory, Experimental Evolution, Genotype-Phenotype, Population Genetics / Genomics | Inês Fragata | | 2018-03-09 02:22:07 | View |
Sexual selection and inbreeding: two efficient ways to limit the accumulation of deleterious mutations
E. Noël, E. Fruitet, D. Lelaurin, N. Bonel, A. Ségard, V. Sarda, P. Jarne and P. David
https://doi.org//273367
Inbreeding compensates for reduced sexual selection in purging deleterious mutations
Recommended by Charles Baer based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Two evolutionary processes have been shown in theory to enhance the effects of natural selection in purging deleterious mutations from a population (here ""natural"" selection is defined as ""selection other than sexual selection""). First, inbreeding, especially self-fertilization, facilitates the removal of deleterious recessive alleles, the effects of which are largely hidden from selection in heterozygotes when mating is random. Second, sexual selection can facilitate the removal of deleterious alleles of arbitrary dominance, with little or no demographic cost, provided that deleterious effects are greater in males than in females (""genic capture""). Inbreeding (especially selfing) and sexual selection are often negatively correlated in nature. Empirical tests of the role of sexual selection in purging deleterious mutations have been inconsistent, potentially due to the positive relationship between sexual selection and intersexual genetic conflict.
In their preprint, Noël et al. [1] report a cleverly designed, and impressively long-term, experimental evolution study designed to tease apart the relative contributions of selfing and sexual selection in purging deleterious mutations, using the self-compatible hermaphroditic snail Physa acuta. Hermaphroditism relieves at least some of the potential conflict between males and females because each individual expresses traits of each sex. The authors report a 50-generation (ten years!) evolution experiment with four experimental treatments: Control (C), in which snails reproduced by mass mating (allowing sexual selection) and the next generation was sampled randomly from offspring in proportion to maternal family size; Male-selection (M) in which snails reproduced by mass mating but maternal family size was held constant, removing the opportunity for fertility selection; Female fertility selection (F) in which snails mated monogamously but fertility selection was imposed, and selfing (S), in which snails reproduced by selfing every other generation, alternating with monogamy + fertility selection. Juvenile survival was taken as the proxy for fitness and was measured for offspring of self-fertilization and of outcross matings. Each line type (C, M, F, S) was replicated twice.
The results are enviably clear-cut: after 50 generations of evolution, outcross fitness dropped precipitously in the F treatment (monogamy+female fertility selection) and remained at ancestral levels in the other three treatments. Clearly, sexual selection in males is more efficient at purging deleterious alleles than is female fertility selection. Similarly, inbreeding depression was reduced in the S lines relative to the other treatments, indicating that, unsurprisingly, deleterious recessive mutations of large effect are purged under strong inbreeding. Outcross fitness in the S lines did not decline, in contrast to the F lines, which indicates that deleterious mutations are on average slightly recessive.
Taken as a whole, this study by Noël et al. [1] provides a compelling empirical demonstration of the efficacy of both sexual selection and strong inbreeding as mechanisms of purging, and implicates sexual conflict as a potentially important factor in studies in which relaxation of sexual selection fails to result in purging.
References
[1] Noël, E., Fruitet, E., Lelaurin, D., Bonel, N., Segard, A., Sarda, V., Jarne, P., & David P. (2018). Sexual selection and inbreeding: two efficient ways to limit the accumulation of deleterious mutations. bioRxiv, 273367, ver. 3 recommended and peer-reviewed by PCI Evol Biol. doi: 10.1101/273367
| Sexual selection and inbreeding: two efficient ways to limit the accumulation of deleterious mutations | E. Noël, E. Fruitet, D. Lelaurin, N. Bonel, A. Ségard, V. Sarda, P. Jarne and P. David | <p>This preprint has been reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Evolutionary Biology (https://dx.doi.org/10.24072/pci.evolbiol.100055). Theory and empirical data showed that two processes can boost selection against deleterious mutations, ... |  | Adaptation, Experimental Evolution, Reproduction and Sex, Sexual Selection | Charles Baer | Anonymous | 2018-03-01 08:12:37 | View |
Field evidence for manipulation of mosquito host selection by the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum
Amelie Vantaux, Franck Yao, Domonbabele FdS Hien, Edwige Guissou, Bienvenue K Yameogo, Louis-Clement Gouagna, Didier Fontenille, Francois Renaud, Frederic Simard, Carlo Constantini, Frederic Thomas, Karine Mouline, Benjamin Roche, Anna Cohuet, Kounbobr R Dabire, Thierry Lefevre
https://doi.org/10.1101/207183
Malaria host manipulation increases probability of mosquitoes feeding on humans
Recommended by Alison Duncan based on reviews by Olivier Restif, Ricardo S. Ramiro and 1 anonymous reviewer
Parasites can manipulate their host’s behaviour to ensure their own transmission. These manipulated behaviours may be outside the range of ordinary host activities [1], or alter the crucial timing and/or location of a host’s regular activity. Vantaux et al show that the latter is true for the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum [2]. They demonstrate that three species of Anopheles mosquito were 24% more likely to choose human hosts, rather than other vertebrates, for their blood feed when they harboured transmissible stages (sporozoites) compared to when they were uninfected, or infected with non-transmissible malaria parasites [2]. Host choice is crucial for the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum to complete its life-cycle, as their host range is much narrower than the mosquito’s for feeding; P. falciparum can only develop in hominids, or closely related apes [3].
The study only shows this stage-dependent parasite manipulation retrospectively (by identifying host type and parasite stage in mosquitoes after their blood feed [2]). There was no difference in the preferences of infectious (with sporozoites) or un-infectious (infected without sporozoites, or uninfected) mosquitoes between human versus cow hosts in a choice test [2]. This suggests that the final decision about whether to feed occurs when the mosquito is in close range of the host.
This, coupled with previous findings, shows that vector manipulation is a fine-tuned business, that can act at multiple stages of the parasite life-cycle and on many behaviours [4]. Indeed, mosquitoes with non-transmissible Plasmodium stages (oocysts) are more reluctant to feed than sporozoite-infected mosquitoes [5] as vectors can be killed by their host whilst feeding, doing so before they are ready to transmit is risky for the malaria parasite. Thus, it seems that Plasmodium is, to some extent, master of its vector; commanding it not to feed when it cannot be transmitted, to feed when it is ready to be transmitted and to feed on the right type of host. What does this mean for our understanding of malaria transmission and epidemics?
Vantaux et al use a mathematical model, parameterised using data from this experiment, to highlight the consequences of this 24% increase in feeding on humans for P. falciparum transmission. They show that this increase raises the number of infectious bites humans receive from 4 (if sporozoite-infected mosquitoes had the same probability as uninfected mosquitoes) to 14 (an increase in 250%), for mosquitoes with a 15-day life-span, at ratios of 1:1 mosquitoes to humans. Longer mosquito life-spans and higher ratios of mosquitoes to humans further increases the number of infectious bites.
These results [2] have important implications for epidemiological forecasting and disease management. Public health strategies could focus on possible ways to trap sporozoite-infected mosquitoes, mimicking cues they use to locate their human hosts, or identify the behaviour of mosquitoes harbouring non-yet infectious Plasmodium, and trap them before they bite. Moreover, the results of the model show that failing to take into account the preference for humans of sporozoite-infected mosquitoes could underestimate the size of pending epidemics.
An important question previously raised is whether Plasmodium-induced alteration in host behaviour really is manipulation, or just a side-effect of being infected [4,5]. The fact that Vantaux et al show that these altered feeding behaviours increases the likelihood of transmission, in that a sporozoite-infected mosquito is more likely to feed on a human, strongly suggests that it is adaptive for the parasite [2]. Ultimately, to show that it is manipulation would require the identification of molecular factors released by Plasmodium that are responsible for physiological changes in the mosquito [6].
References
[1] Thomas, F., Schmidt-Rhaesa, A., Martin, G., Manu, C., Durand, P., & Renaud, F. (2002). Do hairworms (Nematomorpha) manipulate the water seeking behaviour of their terrestrial hosts? Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 15(3), 356–361. doi: 10.1046/j.1420-9101.2002.00410.x
[2] Vantaux, A., Yao, F., Hien, D. F., Guissou, E., Yameogo, B. K., Gouagna, L.-C., … Lefevre, T. (2018). Field evidence for manipulation of mosquito host selection by the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. BioRxiv, 207183 ver 6. doi: 10.1101/207183
[3] Prugnolle, F., Durand, P., Ollomo, B., Duval, L., Ariey, F., Arnathau, C., … Renaud, F. (2011). A Fresh Look at the Origin of Plasmodium falciparum, the Most Malignant Malaria Agent. PLOS Pathogens, 7(2), e1001283. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001283
[4] Cator, L. J., Lynch, P. A., Read, A. F., & Thomas, M. B. (2012). Do malaria parasites manipulate mosquitoes? Trends in Parasitology, 28(11), 466–470. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2012.08.004
[5] Cator, L. J., George, J., Blanford, S., Murdock, C. C., Baker, T. C., Read, A. F., & Thomas, M. B. (2013). “Manipulation” without the parasite: altered feeding behaviour of mosquitoes is not dependent on infection with malaria parasites. Proceedings. Biological Sciences, 280(1763), 20130711. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.0711
[6] Herbison, R., Lagrue, C., & Poulin, R. (2018). The missing link in parasite manipulation of host behaviour. Parasites & Vectors, 11. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-2805-9
| Field evidence for manipulation of mosquito host selection by the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum | Amelie Vantaux, Franck Yao, Domonbabele FdS Hien, Edwige Guissou, Bienvenue K Yameogo, Louis-Clement Gouagna, Didier Fontenille, Francois Renaud, Frederic Simard, Carlo Constantini, Frederic Thomas, Karine Mouline, Benjamin Roche, Anna Cohuet, Kou... | <p>Whether the malaria parasite *Plasmodium falciparum* can manipulate mosquito host choice in ways that enhance parasite transmission toward human is unknown. We assessed the influence of *P. falciparum* on the blood-feeding behaviour of three of... |  | Evolutionary Ecology | Alison Duncan | | 2018-02-28 09:12:14 | View |
Range size dynamics can explain why evolutionarily age and diversification rate correlate with contemporary extinction risk in plants
Andrew J. Tanentzap, Javier Igea, Matthew G. Johnston, Matthew J. Larcombe
https://doi.org/10.1101/152215
Are both very young and the very old plant lineages at heightened risk of extinction?
Recommended by Arne Mooers based on reviews by Dan Greenberg and 1 anonymous reviewer
Human economic activity is responsible for the vast majority of ongoing extinction, but that does not mean lineages are being affected willy-nilly. For amphibians [1] and South African flowering plants [2], young species have a somewhat higher than expected chance of being threatened with extinction. In contrast, older Australian marsupial lineages seem to be more at risk [3]. Both of the former studies suggested that situations leading to peripheral isolation might simultaneously increase ongoing speciation and current threat via small geographic range, while the authors of the latter study suggested that older species might have evolved increasingly narrow niches. Here, Andrew Tanentzap and colleagues [4] dig deeper into the putative links between species age, niche breadth and threat status. Across 500-some plant genera worldwide, they find that, indeed, ""younger"" species (i.e. from younger and faster-diversifying genera) were more likely to be listed as imperiled by the IUCN, consistent with patterns for amphibians and African plants. Given this, results from their finer-level analyses of conifers are initially bemusing: here, ""older"" (i.e., on longer terminal branches) species were at higher risk. This would make conifers more like Australian marsupials, with the rest of the plants being more like amphibians. However, here where the data were more finely grained, the authors detected a second interesting pattern: using an intriguing matched-pair design, they detect a signal of conifer species niches seemingly shrinking as a function of age. The authors interpret this as consistent with increasing specialization, or loss of ancestral warm wet habitat, over paleontological time. It is true that conifers in general are older than plants more generally, with some species on branches that extend back many 10s of millions of years, and so a general loss of suitable habitat makes some sense. If so, both the pattern for all plants (small initial ranges heightening extinction) and the pattern for conifers (eventual increasing specialization or habitat contraction heightening extinction) could occur, each on a different time scale. As a coda, the authors detected no effect of age on threat status in palms; however, this may be both because palms have already lost species to climate-change induced extinction, and because they are thought to speciate more via long-distance dispersal and adaptive divergence then via peripheral isolation.
Given how quickly ranges can change, how hard it is to measure niche breadth, and the qualitatively different time scales governing past diversification and present-day extinction drivers, this is surely not the last word on the subject, even for plants. However, even the hint of a link between drivers of extinction in the Anthropocene and drivers of diversification through the ages is intellectually exciting and, perhaps, even, somehow, of practical importance.
References
[1] Greenberg, D. A., & Mooers, A. Ø. (2017). Linking speciation to extinction: Diversification raises contemporary extinction risk in amphibians. Evolution Letters, 1, 40–48. doi: 10.1002/evl3.4
[2] Davies, T. J., Smith, G. F., Bellstedt, D. U., Boatwright, J. S., Bytebier, B., Cowling, R. M., Forest, F., et al. (2011). Extinction risk and diversification are linked in a plant biodiversity hotspot. PLoS Biology, 9:e1000620. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000620
[3] Johnson, C. N., Delean S., & Balmford, A. (2002). Phylogeny and the selectivity of extinction in Australian marsupials. Animal Conservation, 5, 135–142. doi: 10.1017/S1367943002002196
[4] Tanentzap, A. J., Igea, J., Johnston, M. G., & Larcombe, M. G. (2018). Range size dynamics can explain why evolutionarily age and diversification rate correlate with contemporary extinction risk in plants. bioRxiv, 152215, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol. doi: 10.1101/152215
| Range size dynamics can explain why evolutionarily age and diversification rate correlate with contemporary extinction risk in plants | Andrew J. Tanentzap, Javier Igea, Matthew G. Johnston, Matthew J. Larcombe | <p>Extinction threatens many species, yet few factors predict this risk across the plant Tree of Life (ToL). Taxon age is one factor that may associate with extinction if occupancy of geographic and adaptive zones varies with time, but evidence fo... | 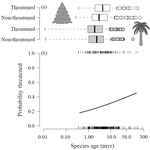 | Macroevolution, Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics, Phylogeography & Biogeography | Arne Mooers | | 2018-02-01 21:01:19 | View |
Transgenerational cues about local mate competition affect offspring sex ratios in the spider mite Tetranychus urticae
Alison B. Duncan, Cassandra Marinosci, Céline Devaux, Sophie Lefèvre, Sara Magalhães, Joanne Griffin, Adeline Valente, Ophélie Ronce, Isabelle Olivieri
https://doi.org/10.1101/240127
Maternal effects in sex-ratio adjustment
Recommended by Dries Bonte based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Optimal sex ratios have been topic of extensive studies so far. Fisherian 1:1 proportions of males and females are known to be optimal in most (diploid) organisms, but many deviations from this golden rule are observed. These deviations not only attract a lot of attention from evolutionary biologists but also from population ecologists as they eventually determine long-term population growth. Because sex ratios are tightly linked to fitness, they can be under strong selection or plastic in response to changing demographic conditions. Hamilton [1] pointed out that an equality of the sex ratio breaks down when there is local competition for mates. Competition for mates can be considered as a special case of local resource competition. In short, this theory predicts females to adjust their offspring sex ratio conditional on cues indicating the level of local mate competition that their sons will experience. When cues indicate high levels of LMC mothers should invest more resources in the production of daughters to maximise their fitness, while offspring sex ratios should be closer to 50:50 when cues indicate low levels of LMC.
In isolated populations, Macke et al. [2] found sex ratio to evolve fast in response to changes in population sex-structure in the spider mite Tetranychus urticae. Spider mites are becoming top-models in evolutionary biology because of their easy housekeeping, fast generation times and well-studied genome [3]. The species is known to respond fast to changes in relatedness and kin-structure by changing its mating strategy [4], but also dispersal [5]. Sex ratio adjustments are likely mediated by differential investments in egg size, with small eggs possibly experiencing lower chances of fertilization, and thus to develop in haploid males [4].
Alison Duncan and colleagues [6] asked the question whether sex ratios change plastically in response to changes in the local population structure. They additionally questioned whether maternal effects could drive changes in sex-allocation of spider mite mothers. Indeed, theory predicts that if environmental changes are predictable across generations, intergenerational plasticity might be more adaptive than intragenerational plasticity [7]. Especially in spatially structured and highly dynamics populations, female spider mites may experience highly variable demographic conditions from one generation to another. During range expansions, spatial variation in local relatedness and inbreeding are documented to change and to impact eco-evolutionary trajectories as well (e.g. [8]).
Duncan et al. [6] specifically investigate whether the offspring sex ratio of T. urticae females changes in response to 1) the current number of females in the same patch, 2) the number of females in the patches of their mothers and 3) their relatedness to their mate. They surprisingly find the maternal environment to be more important than the actual experienced sex-ratio conditions. These insights thus show the maternal environment to be a reliable predictor of LMC experienced by grand-children. Maternal effects have been found to impact many traits, but this study is the first to convincingly demonstrate maternal effects in sex allocation. It therefore provides an alternative explanation of the apparent fast evolved responses under constant demographic conditions [2], and adds evidence to the importance of non-genetic trait changes for adaptation towards changing demographic and environmental conditions.
References
[1] Hamilton, W. D. (1967). Extraordinary Sex Ratios. Science, 156(3774), 477–488. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3774.477
[2] Macke, E., Magalhães, S., Bach, F., & Olivieri, I. (2011). Experimental evolution of reduced sex ratio adjustment under local mate competition. Science, 334(6059), 1127–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.1212177
[3] Grbić, M., Van Leeuwen, T., Clark, R. M., et al. (2011). The genome of Tetranychus urticae reveals herbivorous pest adaptations. Nature, 479(7374), 487–492. doi: 10.1038/nature10640
[4] Macke, E., Magalhães, S., Bach, F., & Olivieri, I. (2012). Sex-ratio adjustment in response to local mate competition is achieved through an alteration of egg size in a haplodiploid spider mite. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 279(1747), 4634–4642. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2012.1598
[5] Bitume, E. V., Bonte, D., Ronce, O., Bach, F., Flaven, E., Olivieri, I., & Nieberding, C. M. (2013). Density and genetic relatedness increase dispersal distance in a subsocial organism. Ecology Letters, 16(4), 430–437. doi: 10.1111/ele.12057
[6] Duncan, A., Marinosci, C., Devaux, C., Lefèvre, S., Magalhães, S., Griffin, J., Valente, A., Ronce, O., Olivieri, I. (2018). Transgenerational cues about local mate competition affect offspring sex ratios in the spider mite Tetranychus urticae. BioRxiv, 240127, ver. 3. doi: 10.1101/240127
[7] Petegem, K. V., Moerman, F., Dahirel, M., Fronhofer, E. A., Vandegehuchte, M. L., Leeuwen, T. V., Wybouw, N., Stoks, R., Bonte, D. (2018). Kin competition accelerates experimental range expansion in an arthropod herbivore. Ecology Letters, 21(2), 225–234. doi: 10.1111/ele.12887
[8] Marshall, D. J., & Uller, T. (2007). When is a maternal effect adaptive? Oikos, 116(12), 1957–1963. doi: 10.1111/j.2007.0030-1299.16203.x
| Transgenerational cues about local mate competition affect offspring sex ratios in the spider mite Tetranychus urticae | Alison B. Duncan, Cassandra Marinosci, Céline Devaux, Sophie Lefèvre, Sara Magalhães, Joanne Griffin, Adeline Valente, Ophélie Ronce, Isabelle Olivieri | <p style="text-align: justify;">In structured populations, competition between closely related males for mates, termed Local Mate Competition (LMC), is expected to select for female-biased offspring sex ratios. However, the cues underlying sex all... |  | Evolutionary Ecology, Life History | Dries Bonte | | 2017-12-29 16:10:32 | View |
Fine-grained habitat-associated genetic connectivity in an admixed population of mussels in the small isolated Kerguelen Islands
Christelle Fraïsse, Anne Haguenauer, Karin Gerard, Alexandra Anh-Thu Weber, Nicolas Bierne, Anne Chenuil
https://doi.org/10.1101/239244
Introgression from related species reveals fine-scale structure in an isolated population of mussels and causes patterns of genetic-environment associations
Recommended by Marianne Elias based on reviews by Thomas Broquet and Tatiana Giraud
Assessing population connectivity is central to understanding population dynamics, and is therefore of great importance in evolutionary biology and conservation biology. In the marine realm, the apparent absence of physical barriers, large population sizes and high dispersal capacities of most organisms often result in no detectable structure, thereby hindering inferences of population connectivity. In a review paper, Gagnaire et al. [1] propose several ideas to improve detection of population connectivity. Notably, using simulations they show that under certain circumstances introgression from one species into another may reveal cryptic population structure within that second species.
The isolated Kerguelen archipelago in the south of Indian Ocean represents a typical situation where the structure of coastal marine organisms is expected to be difficult to detect. In an elegant genomic study, Fraïsse et al. [2] take advantage of introgression from foreign lineages to infer fine-grained population structure in a population of mussels around the Kerguelen archipelago, and investigate its association with environmental variables. Using a large panel of genome-wide markers (GBS) and applying a range of methods that unravel patterns of divergence and gene flow among lineages, they first find that the Kerguelen population is highly admixed, with a major genetic background corresponding to the southern mussel lineage Mytilus platensis introgressed by three northern lineages. By selecting a panel of loci enriched in ancestry-informative SNPs (ie, SNPs highly differentiated among northern lineages) they then detect a fine-scale genetic structure around the Kerguelen archipelago, and identify a major connectivity break. They further show an associating between the genetic structure and environmental variables, particularly the presence of Macrocystis kelp, a marker of habitat exposure to waves (a feature repeatedly evidenced to be important for mussels). While such association pattern could lead to the interpretation that differentiated SNPs correspond to loci directly under selection or linked with such loci, and even be considered as support for adaptive introgression, Fraïsse et al. [2] convincingly show by performing simulations that the genetic-environment association detected can be entirely explained by dispersal barriers associated with environmental variables (habitat-associated connectivity). They also explain why the association is better detected by ancestry-informative SNPs as predicted by Gagnaire et al. [1]. In addition, intrinsic genetic incompatibilities, which reduce gene flow, tend to become trapped at ecotones due to ecological selection, even when loci causing genetic incompatibilities are unlinked with loci involved in adaption to local ecological conditions (Bierne et al. [3]’s coupling hypothesis), leading to correlations between environmental variables and loci not involved in local adaptation. Notably, in Fraïsse et al. [2]’s study, the association between the kelp and ancestry-informative alleles is not consistent throughout the archipelago, casting further doubt on the implication of these alleles in local adaptation.
The study of Fraïsse et al. [2] is therefore an important contribution to evolutionary biology because 1) it provides an empirical demonstration that alleles of foreign origin can be pivotal to detect fine-scale connectivity patterns and 2) it represents a test case of Bierne et al. [3]’s coupling hypothesis, whereby introgressed alleles also enhance patterns of genetic-environment associations. Since genomic scan or GWAS approaches fail to clearly reveal loci involved in local adaptation, how can we disentangle environment-driven selection from intrinsic reproductive barriers and habitat-associated connectivity? A related question is whether we can reliably identify cases of adaptive introgression, which have increasingly been put forward as a mechanism involved in adaptation [4]. Unfortunately, there is no easy answer, and the safest way to go is to rely – where possible – on independent information [5], in particular functional studies of the detected loci, as is for example the case in the mimetic butterfly Heliconius literature (e. g., [6]) where several loci controlling colour pattern variation are well characterized.
References
[1] Gagnaire, P.-A., Broquet, T., Aurelle, D., Viard, F., Souissi, A., Bonhomme, F., Arnaud-Haond, S., & Bierne, N. (2015). Using neutral, selected, and hitchhiker loci to assess connectivity of marine populations in the genomic era. Evolutionary Applications, 8, 769–786. doi: 10.1111/eva.12288
[2] Fraïsse, C., Haguenauer, A., Gerard, K., Weber, A. A.-T., Bierne, N., & Chenuil, A. (2018). Fine-grained habitat-associated genetic connectivity in an admixed population of mussels in the small isolated Kerguelen Islands. bioRxiv, 239244, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol. doi: 10.1101/239244
[3] Bierne, N., Welch, J., Loire, E., Bonhomme, F., & David, P. (2011). The coupling hypothesis: why genome scans may fail to map local adaptation genes. Molecular Ecology, 20, 2044–2072. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05080.x
[4] Hedrick, P. W. (2013). Adaptive introgression in animals: examples and comparison to new mutation and standing variation as sources of adaptive variation. Molecular Ecology, 22, 4606–4618. doi: 10.1111/mec.12415
[5] Ravinet, M., Faria, R., Butlin, R. K., Galindo, J., Bierne, N., Rafajlović, M., Noor, M. A. F., Mehlig, B., & Westram, A. M. (2017). Interpreting the genomic landscape of speciation: a road map for finding barriers to gene flow. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 30, 1450–1477. doi: 10.1111/jeb.13047.
[6] Jay, P., Whibley, A., Frézal, L., Rodríguez de Cara, M. A., Nowell, R. W., Mallet, J., Dasmahapatra, K. K., & Joron, M. (2018). Supergene evolution triggered by the introgression of a chromosomal inversion. Current Biology, 28, 1839–1845.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.04.072
| Fine-grained habitat-associated genetic connectivity in an admixed population of mussels in the small isolated Kerguelen Islands | Christelle Fraïsse, Anne Haguenauer, Karin Gerard, Alexandra Anh-Thu Weber, Nicolas Bierne, Anne Chenuil | <p>Reticulated evolution -i.e. secondary introgression / admixture between sister taxa- is increasingly recognized as playing a key role in structuring infra-specific genetic variation and revealing cryptic genetic connectivity patterns. When admi... |  | Hybridization / Introgression, Phylogeography & Biogeography, Population Genetics / Genomics | Marianne Elias | | 2017-12-28 14:16:16 | View |
One (more) step towards a dynamic view of the Latitudinal Diversity Gradient
Recommended by Joaquín Hortal and Juan Arroyo based on reviews by Juan Arroyo, Joaquín Hortal, Arne Mooers, Joaquin Calatayud and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Juan Arroyo, Joaquín Hortal, Arne Mooers, Joaquin Calatayud and 2 anonymous reviewers
The Latitudinal Diversity Gradient (LDG) has fascinated natural historians, ecologists and evolutionary biologists ever since [1] described it about 200 years ago [2]. Despite such interest, agreement on the origin and nature of this gradient has been elusive. Several tens of hypotheses and models have been put forward as explanations for the LDG [2-3], that can be grouped in ecological, evolutionary and historical explanations [4] (see also [5]). These explanations can be reduced to no less than 26 hypotheses, which account for variations in ecological limits for the establishment of progressively larger assemblages, diversification rates, and time for species accumulation [5]. Besides that, although in general the tropics hold more species, different taxa show different shapes and rates of spatial variation [6], and a considerable number of groups show reverse patterns, with richer assemblages in cold temperate regions (see e.g. [7-9]).
Understanding such complexity needs integrating ecological and evolutionary research into the wide temporal and spatial perspectives provided by the burgeoning field of biogeography. This integrative discipline ¬–that traces back to Humboldt himself (e.g. [10])– seeks to put together historical and functional explanations to explain the complex dynamics of Earth’s biodiversity. Different to quantum physicists, biogeographers cannot pursue the ultimate principle behind the patterns we observe in nature due to the interplay of causes and effects, which in fact tell us that there is not such a single principle. Rather, they need to identify an array of basic principles coming from different perspectives, to then integrate them into models that provide realistic –but never simple– explanations to biodiversity gradients such as LDG (see, e.g., [5; 11]). That is, rather than searching for a sole explanation, research on the LDG must aim to identify as many signals hidden in the pattern as possible, and provide hypotheses or models that account for these signals. To later integrate them and, whenever possible, to validate them with empirical data on the organisms’ distribution, ecology and traits, phylogenies, fossils, etc.
Within this context, Meseguer & Condamine [12] provide a novel perspective to LDG research using phylogenetic and fossil evidence on the origin and extinction of taxa within the turtle, crocodile and lizard (i.e. squamate) lineages. By digging into deep time down to the Triassic (about 250 Myr ago) they are able to identify several episodes of flattening and steepening of the LDG for these three clades. Strikingly, their results show similar diversification rates in the northern hemisphere and in the equator during the over 100 Myr long global greenhouse period that extends from the late Jurassic to the Cretaceous and early Neogene. During this period, the LDG for these three groups would have appeared quite even across a mainly tropical Globe, although the equatorial regions were apparently much more evolutionarily dynamic. The equator shows much higher rates of origination and extinction of branches throughout the Cretaceous, but they counteract each other so net diversification is similar to that of the northern hemisphere in all three groups. The transition to a progressively colder Earth in the Paleogene (starting around 50 Myr ago) provokes a mass extinction in the three clades, which is compensated in the equator by the dispersal of many taxa from the areas that currently pertain to the Holarctic biogeographical realm. Finally, during the coldhouse Earth’s climatic conditions of the Neogene only squamates show significant positive diversification rates in extratropical areas, while the diversity of testudines remains, and crocodiles continue declining progressively towards oblivion in the whole world.
Meseguer & Condamine [12] attribute these temporal patterns to the so-called asymmetric gradient of extinction and dispersal (AGED) framework. Here, the dynamics of extinction-at and dispersal-from high latitudes during colder periods increase the steepness of the LDG. Whereas the gradient flattens when Earth warms up as a result of dispersal from the equator followed by increased diversification in extratropical regions. This idea in itself is not new, for the influence of climatic oscillations on diversification rates is well known, at least for the Pleistocene Ice Ages [13], as is the effect of niche conservatism on the LDG [14]. Nevertheless, Meseguer & Condamine’s AGED provides a synthetic verbal model that could allow integrating the three main types of processes behind the LDG into a single framework. To do this it would be necessary to combine AGED’s cycles of dispersal and diversification with realistic models of: (1) the ecological limits to host rich assemblages in the colder and less productive temperate climatic domains; (2) the variations in diversification rates with shifts in temperature and/or energy regimes; and (3) the geographical patterns of climatic oscillation through time that determine the time for species accumulation in each region.
Integrating these models may allow transposing Meseguer & Condamine’s [12] framework into the more mechanistic macroecological models advocated by Pontarp et al. [5]. This type of mechanistic models has been already used to understand the development of biodiversity gradients through the climatic oscillations of the Pleistocene and the Quaternary (e.g. [11]). So the challenge in this case would be to generate a realistic scenario of geographical dynamics that accounts for plate tectonics and long-term climatic oscillations. This is still a major gap and we would benefit from the integrated work by historical geologists and climatologists here. For instance, there is little doubt about the progressive cooling through the Cenozoic based in isotope recording in sea floor sediments [15]. Meseguer & Condamine [12] use this evidence for separating greenhouse, transition and coldhouse world scenarios, which should not be a problem for these rough classes. However, a detailed study of the evolutionary correlation of true climate variables across the tree of life is still pending, as temperature is inferred only for sea water in an ice-free ocean, say earlier half of the Cenozoic [15]. Precipitation regime is even less known. Such scenario would provide a scaffold upon which the temporal dynamics of several aspects of the generation and loss of biodiversity can be modelled. Additionally, one of the great advantages of selecting key clades to study the LDG would be to determine the functional basis of diversification. There are species traits that are well known to affect speciation and extinction probabilities, such as reproductive strategies or life histories (e.g. [16]). Whereas these traits might also be a somewhat redundant effect of climatic causes, they might foster (i.e. “extended reinforcement”, [17]) or slow diversification. Even so, it is unlikely that such a model would account for all the latitudinal variation in species richness. But it will at least provide a baseline for the main latitudinal variations in the diversity of the regional communities (sensu [18]) worldwide. Within this context the effects of recent ecological, evolutionary and historical processes, such as environmental heterogeneity, current diversification rates or glacial cycles, will only modify the general LDG pattern resulting from the main processes contained in Meseguer & Condamine’s AGED, thereby providing a more comprehensive understanding of the geographical gradients of diversity.
References
[1] Humboldt, A. v. (1808). Ansichten der Natur, mit wissenschaftlichen Erläuterungen. J. G. Cotta, Tübingen.
[2] Hawkins, B. A. (2001). Ecology's oldest pattern? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 16, 470. doi: 10.1016/S0169-5347(01)02197-8
[3] Lomolino, M. V., Riddle, B. R. & Whittaker, R. J. (2017). Biogeography. Fifth Edition. Sinauer Associates, Inc., Sunderland, Massachussets.
[4] Mittelbach, G. G., Schemske, D. W., Cornell, H. V., Allen, A. P., Brown, J. M., Bush, M. B., Harrison, S. P., Hurlbert, A. H., Knowlton, N., Lessios, H. A., McCain, C. M., McCune, A. R., McDade, L. A., McPeek, M. A., Near, T. J., Price, T. D., Ricklefs, R. E., Roy, K., Sax, D. F., Schluter, D., Sobel, J. M. & Turelli, M. (2007). Evolution and the latitudinal diversity gradient: speciation, extinction and biogeography. Ecology Letters, 10, 315-331. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01020.x
[5] Pontarp, M., Bunnefeld L., Cabral, J. S., Etienne, R. S., Fritz, S. A., Gillespie, R. Graham, C. H., Hagen, O., Hartig, F., Huang, S., Jansson, R., Maliet, O., Münkemüller, T., Pellissier, L., Rangel, T. F., Storch, D., Wiegand, T. & Hurlbert, A. H. (2019). The latitudinal diversity gradient: novel understanding through mechanistic eco-evolutionary models. Trends in ecology & evolution, 34, 211-223. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2018.11.009
[6] Hillebrand, H. (2004). On the generality of the latitudinal diversity gradient. The American Naturalist, 163, 192-211. doi: 10.1086/381004
[7] Santos, A. M. C. & Quicke, D. L. J. (2011). Large-scale diversity patterns of parasitoid insects. Entomological Science, 14, 371-382. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-8298.2011.00481.x
[8] Morinière, J., Van Dam, M. H., Hawlitschek, O., Bergsten, J., Michat, M. C., Hendrich, L., Ribera, I., Toussaint, E. F. A. & Balke, M. (2016). Phylogenetic niche conservatism explains an inverse latitudinal diversity gradient in freshwater arthropods. Scientific Reports, 6, 26340. doi: 10.1038/srep26340
[9] Weiser, M. D., Swenson, N. G., Enquist, B. J., Michaletz, S. T., Waide, R. B., Zhou, J. & Kaspari, M. (2018). Taxonomic decomposition of the latitudinal gradient in species diversity of North American floras. Journal of Biogeography, 45, 418-428. doi: 10.1111/jbi.13131
[10] Humboldt, A. v. (1805). Essai sur la geographie des plantes; accompagné d'un tableau physique des régions equinoxiales. Levrault, Paris.
[11] Rangel, T. F., Edwards, N. R., Holden, P. B., Diniz-Filho, J. A. F., Gosling, W. D., Coelho, M. T. P., Cassemiro, F. A. S., Rahbek, C. & Colwell, R. K. (2018). Modeling the ecology and evolution of biodiversity: Biogeographical cradles, museums, and graves. Science, 361, eaar5452. doi: 10.1126/science.aar5452
[12] Meseguer, A. S. & Condamine, F. L. (2019). Ancient tropical extinctions contributed to the latitudinal diversity gradient. bioRxiv, 236646, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol. doi: 10.1101/236646
[13] Jansson, R., & Dynesius, M. (2002). The fate of clades in a world of recurrent climatic change: Milankovitch oscillations and evolution. Annual review of ecology and systematics, 33(1), 741-777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.33.010802.150520
[14] Wiens, J. J., & Donoghue, M. J. (2004). Historical biogeography, ecology and species richness. Trends in ecology & evolution, 19, 639-644. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2004.09.011
[15] Zachos, J. C., Dickens, G. R., & Zeebe, R. E. (2008). An early Cenozoic perspective on greenhouse warming and carbon-cycle dynamics. Nature, 451, 279-283. doi: 10.1038/nature06588
[16] Zúñiga-Vega, J. J., Fuentes-G, J. A., Ossip-Drahos, A. G., & Martins, E. P. (2016). Repeated evolution of viviparity in phrynosomatid lizards constrained interspecific diversification in some life-history traits. Biology letters, 12, 20160653. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2016.0653
[17] Butlin, R. K., & Smadja, C. M. (2018). Coupling, reinforcement, and speciation. The American Naturalist, 191, 155-172. doi: 10.1086/695136
[18] Ricklefs, R. E. (2015). Intrinsic dynamics of the regional community. Ecology letters, 18, 497-503. doi: 10.1111/ele.12431
| Ancient tropical extinctions contributed to the latitudinal diversity gradient | Andrea S. Meseguer, Fabien Condamine | <p>Biodiversity currently peaks at the equator, decreasing toward the poles. Growing fossil evidence suggest that this hump-shaped latitudinal diversity gradient (LDG) has not been persistent through time, with similar species diversity across lat... | 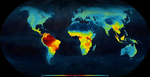 | Evolutionary Dynamics, Evolutionary Ecology, Macroevolution, Paleontology, Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics, Phylogeography & Biogeography | Joaquín Hortal | | 2017-12-20 14:58:01 | View |
A new approach to DNA-aided ancestral trait reconstruction in mammals
Recommended by Nicolas Galtier and Belinda Chang
Reconstructing ancestral character states is an exciting but difficult problem. The fossil record carries a great deal of information, but it is incomplete and not always easy to connect to data from modern species. Alternatively, ancestral states can be estimated by modelling trait evolution across a phylogeny, and fitting to values observed in extant species. This approach, however, is heavily dependent on the underlying assumptions, and typically results in wide confidence intervals.
An alternative approach is to gain information on ancestral character states from DNA sequence data. This can be done directly when the trait of interest is known to be determined by a single, or a small number, of major effect genes. In some of these cases it can even be possible to investigate an ancestral trait of interest by inferring and resurrecting ancestral sequences in the laboratory. Examples where this has been successfully used to address evolutionary questions range from the nocturnality of early mammals [1], to the loss of functional uricases in primates, leading to high rates of gout, obesity and hypertension in present day humans [2]. Another possibility is to rely on correlations between species traits and the genome average substitution rate/process. For instance, it is well established that the ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous substitution rate, dN/dS, is generally higher in large than in small species of mammals, presumably due to a reduced effective population size in the former. By estimating ancestral dN/dS, one can therefore gain information on ancestral body mass (e.g. [3-4]).
The interesting paper by Wu et al. [5] further develops this second possibility of incorporating information on rate variation derived from genomic data in the estimation of ancestral traits. The authors analyse a large set of 1185 genes in 89 species of mammals, without any prior information on gene function. The substitution rate is estimated for each gene and each branch of the mammalian tree, and taken as an indicator of the selective constraint applying to a specific gene in a specific lineage – more constraint, slower evolution. Rate variation is modelled as resulting from a gene effect, a branch effect, and a gene X branch interaction effect, which captures lineage-specific peculiarities in the distribution of functional constraint across genes. The interaction term in terminal branches is regressed to observed trait values, and the relationship is used to predict ancestral traits from interaction terms in internal branches. The power and accuracy of the estimates are convincingly assessed via cross validation. Using this method, the authors were also able to use an unbiased approach to determine which genes were the main contributors to the evolution of the life-history traits they reconstructed.
The ancestors to current placental mammals are predicted to have been insectivorous - meaning that the estimated distribution of selective constraint across genes in basal branches of the tree resembles that of extant insectivorous taxa - consistent with the mainstream palaeontological hypothesis. Another interesting result is the prediction that only nocturnal lineages have passed the Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary, so that the ancestors of current orders of placentals would all have been nocturnal. This suggests that the so-called "nocturnal bottleneck hypothesis" should probably be amended. Similar reconstructions are achieved for seasonality, sociality and monogamy – with variable levels of uncertainty.
The beauty of the approach is to analyse the variance, not only the mean, of substitution rate across genes, and their methods allow for the identification of the genes contributing to trait evolution without relying on functional annotations. This paper only analyses discrete traits, but the framework can probably be extended to continuous traits as well.
References
[1] Bickelmann C, Morrow JM, Du J, Schott RK, van Hazel I, Lim S, Müller J, Chang BSW, 2015. The molecular origin and evolution of dim-light vision in mammals. Evolution 69: 2995-3003. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/evo.12794
[2] Kratzer, JT, Lanaspa MA, Murphy MN, Cicerchi C, Graves CL, Tipton PA, Ortlund EA, Johnson RJ, Gaucher EA, 2014. Evolutionary history and metabolic insights of ancient mammalian uricases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, USA 111:3763-3768. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1320393111
[3] Lartillot N, Delsuc F. 2012. Joint reconstruction of divergence times and life-history evolution in placental mammals using a phylogenetic covariance model. Evolution 66:1773-1787. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.2011.01558.x
[4] Romiguier J, Ranwez V, Douzery EJ, Galtier N. 2013. Genomic evidence for large, long-lived ancestors to placental mammals. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30:5-13. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mss211
[5] Wu J, Yonezawa T, Kishino H. 2016. Rates of Molecular Evolution Suggest Natural History of Life History Traits and a Post-K-Pg Nocturnal Bottleneck of Placentals. Current Biology 27: 3025-3033. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.08.043
| Rates of Molecular Evolution Suggest Natural History of Life History Traits and a Post-K-Pg Nocturnal Bottleneck of Placentals | Wu J, Yonezawa T, Kishino H. | Life history and behavioral traits are often difficult to discern from the fossil record, but evolutionary rates of genes and their changes over time can be inferred from extant genomic data. Under the neutral theory, molecular evolutionary rate i... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Life History, Molecular Evolution, Paleontology, Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics | Nicolas Galtier | | 2017-11-10 14:52:26 | View |



















 based on reviews by Juan Arroyo, Joaquín Hortal, Arne Mooers, Joaquin Calatayud and 2 anonymous reviewers
based on reviews by Juan Arroyo, Joaquín Hortal, Arne Mooers, Joaquin Calatayud and 2 anonymous reviewers













