Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors▼ | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
06 Jul 2018

Variation in competitive ability with mating system, ploidy and range expansion in four Capsella speciesXuyue Yang, Martin Lascoux and Sylvain Glémin https://doi.org/10.1101/214866When ecology meets genetics: Towards an integrated understanding of mating system transitions and diversityRecommended by Sylvain Billiard and Henrique Teotonio based on reviews by Yaniv Brandvain, Henrique Teotonio and 1 anonymous reviewerIn the 19th century, C. Darwin and F. Delpino engaged in a debate about the success of species with different reproduction modes, with the later favouring the idea that monoecious plants capable of autonomous selfing could spread more easily than dioecious plants (or self-incompatible hermaphroditic plants) if cross-pollination opportunities were limited [1]. Since then, debate has never faded about how natural selection is responsible for transitions to selfing and can explain the diversity and distribution of reproduction modes we observe in the natural world [2, 3]. References [1] Darwin, C. R. (1876). The effects of cross and self fertilization in the vegetable kingdom. London: Murray.
[2] Stebbins, G. L. (1957). Self fertilization and population variability in the higher plants. The American Naturalist, 91, 337-354. doi: 10.1086/281999 | Variation in competitive ability with mating system, ploidy and range expansion in four Capsella species | Xuyue Yang, Martin Lascoux and Sylvain Glémin | <p>Self-fertilization is often associated with ecological traits corresponding to the ruderal strategy in Grime’s Competitive-Stress-tolerant-Ruderal (CSR) classification of ecological strategies. Consequently, selfers are expected to be less comp... |  | Evolutionary Ecology, Population Genetics / Genomics, Reproduction and Sex, Species interactions | Sylvain Billiard | 2017-11-06 19:54:52 | View | |
10 Nov 2017

POSTPRINT
Rates of Molecular Evolution Suggest Natural History of Life History Traits and a Post-K-Pg Nocturnal Bottleneck of PlacentalsWu J, Yonezawa T, Kishino H. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.08.043A new approach to DNA-aided ancestral trait reconstruction in mammalsRecommended by Nicolas Galtier and Belinda ChangReconstructing ancestral character states is an exciting but difficult problem. The fossil record carries a great deal of information, but it is incomplete and not always easy to connect to data from modern species. Alternatively, ancestral states can be estimated by modelling trait evolution across a phylogeny, and fitting to values observed in extant species. This approach, however, is heavily dependent on the underlying assumptions, and typically results in wide confidence intervals. An alternative approach is to gain information on ancestral character states from DNA sequence data. This can be done directly when the trait of interest is known to be determined by a single, or a small number, of major effect genes. In some of these cases it can even be possible to investigate an ancestral trait of interest by inferring and resurrecting ancestral sequences in the laboratory. Examples where this has been successfully used to address evolutionary questions range from the nocturnality of early mammals [1], to the loss of functional uricases in primates, leading to high rates of gout, obesity and hypertension in present day humans [2]. Another possibility is to rely on correlations between species traits and the genome average substitution rate/process. For instance, it is well established that the ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous substitution rate, dN/dS, is generally higher in large than in small species of mammals, presumably due to a reduced effective population size in the former. By estimating ancestral dN/dS, one can therefore gain information on ancestral body mass (e.g. [3-4]). The interesting paper by Wu et al. [5] further develops this second possibility of incorporating information on rate variation derived from genomic data in the estimation of ancestral traits. The authors analyse a large set of 1185 genes in 89 species of mammals, without any prior information on gene function. The substitution rate is estimated for each gene and each branch of the mammalian tree, and taken as an indicator of the selective constraint applying to a specific gene in a specific lineage – more constraint, slower evolution. Rate variation is modelled as resulting from a gene effect, a branch effect, and a gene X branch interaction effect, which captures lineage-specific peculiarities in the distribution of functional constraint across genes. The interaction term in terminal branches is regressed to observed trait values, and the relationship is used to predict ancestral traits from interaction terms in internal branches. The power and accuracy of the estimates are convincingly assessed via cross validation. Using this method, the authors were also able to use an unbiased approach to determine which genes were the main contributors to the evolution of the life-history traits they reconstructed. The ancestors to current placental mammals are predicted to have been insectivorous - meaning that the estimated distribution of selective constraint across genes in basal branches of the tree resembles that of extant insectivorous taxa - consistent with the mainstream palaeontological hypothesis. Another interesting result is the prediction that only nocturnal lineages have passed the Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary, so that the ancestors of current orders of placentals would all have been nocturnal. This suggests that the so-called "nocturnal bottleneck hypothesis" should probably be amended. Similar reconstructions are achieved for seasonality, sociality and monogamy – with variable levels of uncertainty. The beauty of the approach is to analyse the variance, not only the mean, of substitution rate across genes, and their methods allow for the identification of the genes contributing to trait evolution without relying on functional annotations. This paper only analyses discrete traits, but the framework can probably be extended to continuous traits as well. References [1] Bickelmann C, Morrow JM, Du J, Schott RK, van Hazel I, Lim S, Müller J, Chang BSW, 2015. The molecular origin and evolution of dim-light vision in mammals. Evolution 69: 2995-3003. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/evo.12794 [2] Kratzer, JT, Lanaspa MA, Murphy MN, Cicerchi C, Graves CL, Tipton PA, Ortlund EA, Johnson RJ, Gaucher EA, 2014. Evolutionary history and metabolic insights of ancient mammalian uricases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, USA 111:3763-3768. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1320393111 [3] Lartillot N, Delsuc F. 2012. Joint reconstruction of divergence times and life-history evolution in placental mammals using a phylogenetic covariance model. Evolution 66:1773-1787. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.2011.01558.x [4] Romiguier J, Ranwez V, Douzery EJ, Galtier N. 2013. Genomic evidence for large, long-lived ancestors to placental mammals. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30:5-13. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mss211 [5] Wu J, Yonezawa T, Kishino H. 2016. Rates of Molecular Evolution Suggest Natural History of Life History Traits and a Post-K-Pg Nocturnal Bottleneck of Placentals. Current Biology 27: 3025-3033. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.08.043 | Rates of Molecular Evolution Suggest Natural History of Life History Traits and a Post-K-Pg Nocturnal Bottleneck of Placentals | Wu J, Yonezawa T, Kishino H. | Life history and behavioral traits are often difficult to discern from the fossil record, but evolutionary rates of genes and their changes over time can be inferred from extant genomic data. Under the neutral theory, molecular evolutionary rate i... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Life History, Molecular Evolution, Paleontology, Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics | Nicolas Galtier | 2017-11-10 14:52:26 | View | |
31 Jul 2017

Selection on morphological traits and fluctuating asymmetry by a fungal parasite in the yellow dung flyWolf U. Blanckenhorn 10.1101/136325Parasite-mediated selection promotes small body size in yellow dung fliesRecommended by Rodrigo Medel based on reviews by Rodrigo Medel and 1 anonymous reviewerBody size has long been considered as one of the most important organismic traits influencing demographical processes, population size, and evolution of life history strategies [1, 2]. While many studies have reported a selective advantage of large body size, the forces that determine small-sized organisms are less known, and reports of negative selection coefficients on body size are almost absent at present. This lack of knowledge is unfortunate as climate change and energy demands in stressful environments, among other factors, may produce new selection scenarios and unexpected selection surfaces [3]. In this manuscript, Blanckenhorn [4] reports on a potential explanation for the surprising 10% body size decrease observed in a Swiss population of yellow dung flies during 1993 - 2009. The author took advantage of a fungus outbreak in 2002 to assess the putative role of the fungus Entomopthora scatophagae, a specific parasite of adult yellow dung flies, as selective force acting upon host body size. His findings indicate that, as expected by sexual selection theory, large males experience a mating advantage. However, this positive sexual selection is opposed by a strong negative selection on male and female body size through the viability fitness component. This study provides the first evidence of parasite-mediated disadvantage of large adult body size in the field. While further experimental work is needed to elucidate the exact causes of body size reduction in the population, the author proposes a variation of the trade-off hypothesis raised by Rantala & Roff [5] that large-sized individuals face an immunity cost due to their high absolute energy demands in stressful environments. References [1] Peters RH. 1983. The ecological implications of body size. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. [2] Schmidt-Nielsen K. 1984. Scaling: why is animal size so important? Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. [3] Ohlberger J. 2013. Climate warming and ectotherm body size: from individual physiology to community ecology. Functional Ecology 27: 991-1001. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.12098 [4] Blanckenhorn WU. 2017. Selection on morphological traits and fluctuating asymmetry by a fungal parasite in the yellow dung fly. bioRxiv 136325, ver. 2 of 29th June 2017. doi: 10.1101/136325 [5] Rantala MJ & Roff DA. 2005. An analysis of trade-offs in immune function, body size and development time in the Mediterranean field cricket, Gryllus bimaculatus. Functional Ecology 19: 323-330. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2435.2005.00979.x | Selection on morphological traits and fluctuating asymmetry by a fungal parasite in the yellow dung fly | Wolf U. Blanckenhorn | Evidence for selective disadvantages of large body size remains scarce in general. Previous phenomenological studies of the yellow dung fly *Scathophaga stercoraria* have demonstrated strong positive sexual and fecundity selection on male and fema... |  | Behavior & Social Evolution, Evolutionary Ecology, Life History, Sexual Selection | Rodrigo Medel | Rodrigo Medel | 2017-05-10 11:16:26 | View |
11 Oct 2022
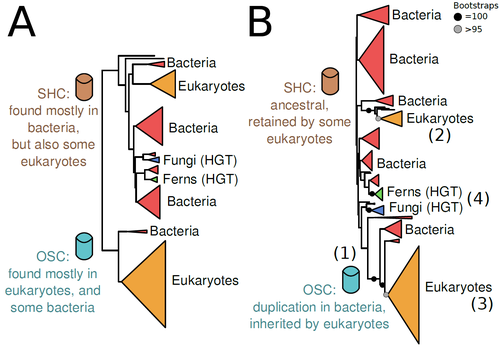
The Eukaryotic Last Common Ancestor Was Bifunctional for Hopanoid and Sterol ProductionWarren R Francis https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202004.0186.v5Gene family analysis suggests new evolutionary scenario for sterol and hopanoid biomarkersRecommended by Iker Irisarri based on reviews by Samuel Abalde, Denis Baurain and Jose Ramon Pardos-BlasSterols and hopanoids are sometimes used as biomarkers to infer the origin of certain groups of organisms. Traditionally, hopanoid-derived products in ancient rocks have been considered to indicate the presence of bacteria, whereas sterol derivatives have been considered to be exclusive to eukaryotes. However, a closer look at the topic reveals a rather complex distribution of either compound in both bacteria and eukaryotes. (1). The known biosynthetic pathways for sterols and hopanoids are similar but diverge at a critical step where two different enzymes are used: squalene-hopene cyclase (SHC) and oxidosqualene cyclase (OSC), the latter requiring oxygen. These two enzymes belong to the same gene family, whose complex evolutionary history is difficult to reconcile with the known species phylogeny. In this study (2), Dr. Warren R. Francis revisits the evolution of this gene family using an extended dataset with a broader taxonomic representation. In contrast to the traditional representation of the tree rooted between SHC and OSC paralogs (i.e., based on function), the author proposes that rooting the tree within bacterial SHCs and assuming a secondary origin of OSC is more parsimonious. This postulates SHC to be the ancestral function –retained in many extant bacteria and some eukaryotes– and OSC to have emerged later within bacteria –currently being mostly present in eukaryotes–. The reconstructed evolutionary history is arguably complex and can only be reconciled with the species' phylogeny by invoking many secondary losses. These losses are considered likely because many extant species acquire sterols and hopanoids by diet and lack one or both enzymes. Some cases of recent horizontal gene transfer are also proposed. In contrast to the dichotomy between bacterial SHCs and eukaryote OSCs, the new proposed scenario suggests that the eukaryote ancestor likely inherited both enzymes from bacteria and thus could be able to synthesize both sterols and hopanoids. Under this hypothesis, not only bacteria but also eukaryotes could be responsible for the hopane found in old rocks. This agrees with eukaryote fossils dating back to more than 1 billion years ago (3). Also, the observed increase of sterane levels in rocks ~600-700 million years old cannot be associated with the origin of eukaryotes, which is a much older event, but could rather reflect changes in atmospheric oxygen levels because oxygen is required for the synthesis of sterols by OSC. References 1. Santana-Molina C, Rivas-Marin E, Rojas AM, Devos DP (2020) Origin and Evolution of Polycyclic Triterpene Synthesis. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 37, 1925–1941. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaa054 2. Francis WR (2022) The Eukaryotic Last Common Ancestor Was Bifunctional for Hopanoid and Sterol Production. Preprints, 2020040186, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202004.0186.v5 3. Butterfield NJ (2000) Bangiomorpha pubescens n. gen., n. sp.: implications for the evolution of sex, multicellularity, and the Mesoproterozoic/Neoproterozoic radiation of eukaryotes. Paleobiology, 26, 386–404. https://doi.org/10.1666/0094-8373(2000)026<0386:BPNGNS>2.0.CO;2 | The Eukaryotic Last Common Ancestor Was Bifunctional for Hopanoid and Sterol Production | Warren R Francis | <p>Steroid and hopanoid biomarkers can be found in ancient rocks and may give a glimpse of what life was present at that time. Sterols and hopanoids are produced by two related enzymes, though the evolutionary history of this protein family is com... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Evolutionary Ecology, Molecular Evolution, Paleontology, Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics | Iker Irisarri | 2021-01-13 16:03:29 | View | |
29 Nov 2022

Joint inference of adaptive and demographic history from temporal population genomic dataVitor A. C. Pavinato, Stéphane De Mita, Jean-Michel Marin, Miguel de Navascués https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.12.435133Inference of genome-wide processes using temporal population genomic dataRecommended by Aurelien Tellier based on reviews by Lawrence Uricchio and 2 anonymous reviewersEvolutionary genomics, and population genetics in particular, aim to decipher the respective influence of neutral and selective forces shaping genetic polymorphism in a species/population. This is a much-needed requirement before scanning genome data for footprints of species adaptation to their biotic and abiotic environment (Johri et al. 2022). In general, we would like to quantify the proportion of the genome evolving neutrally and under selective (positive, balancing and negative) pressures (Kern and Hahn 2018, Johri et al. 2021). We thus need to understand patterns of linked selection along the genome, that is how the distribution of genetic polymorphisms is shaped by selected sites and the recombination landscape. The present contribution by Pavinato et al. (2022) provides an additional method in the population genomics toolbox to quantify the extent of linked positive and negative selection using temporal data. The availability of genomics data for model and non-model species has led to improvement of the modeling framework for demography and selection (Johri et al. 2022), but also new inference methods making use of the full genome data based on the Sequential Markovian Coalescent (SMC, Li and Durbin 2011), Approximate Bayesian Computation (ABC, Jay et al. 2019), ABC and machine learning (Pudlo et al. 2016, Raynal et al. 2019) or Deep Learning (Sanchez et al. 2021). These methods are based on one sample in time and the use of the coalescent theory to reconstruct the past (demographic) history. However, it is also possible to obtain for many species temporal data sampled over several time points. For species with short generation time (in experimental evolution or monitored populations), one can sample a population every couple of generations as exemplified with Drosophila melanogaster (Bergland et al. 2010). For species with longer generation times that cannot be easily regularly sampled in time, it becomes possible to sequence available specimens from museums (e.g. Cridland et al. 2018) or ancient DNA samples. Methods using temporal data are based on the classical population genomics assumption that demography (migration, population subdivision, population size changes) leaves a genome-wide signal, while selection leaves a localized signal in the close vicinity of the causal mutation. Several methods do assess the demography of a population (change in effective population size, Ne, in time) using temporal data (e.g. Jorde and Ryman 2007) which can be used to calibrate the detection of loci under strong positive selection (Foll et al. 2014). Recently Buffalo and Coop (2020) used genome-wide covariance between allele frequency changes across time samples (and across replicates) to quantify the effects of linked selection over short timescales. In the present contribution, Pavinato et al. (2022) make use of temporal data to draw the joint estimation of demographic and selective parameters using a simulation-based method (ABC-Random Forests). This study by Pavinato et al. (2022) builds a framework allowing to infer the census size of the population in time (N) separately from the effect of genetic drift, which is determined by change in effective population size (Ne) in time, as well estimates of genome-wide parameters of selection. In a nutshell, the authors use a forward simulator and summarize genome data by genomic windows using classic statistics (nucleotide diversity, Tajima’s D, FST, heterozygosity) between time samples and for each sample. They specifically use the distributions (higher moments) of these statistics among all windows. The authors combine as input for the ABC-RF, vectors of summary statistics, model parameters and five latent variables: Ne, the ratio Ne/N, the number of beneficial mutations under strong selection, the average selection coefficient of strongly selected mutations, and the average substitution load. Indeed, the authors are interested in three different types of selection components: 1) the adaptive potential of a population which is estimated as the population mutation rate of beneficial mutations (θb), 2) the number of mutations under strong selection (irrespective of whether they reached fixation or not), and 3) the overall population fitness which is a function of the genetic load. In other words, the novelty of this method is not to focus on the detection of loci under selection, but to infer key parameters/distributions summarizing the genome-wide signal of demography and (positive and negative) selection. As a proof of principle, the authors then apply their method to a dataset of feral populations of honey bees (Apis mellifera) collected in California across many years and recovered from Museum samples (Cridland et al. 2018). The approach yields estimates of Ne which are on the same order of magnitude of previous estimates in hymenopterans, and the authors discuss why the different populations show various values of Ne and N which can be explained by different history of admixture with wild but also domesticated lineages of bees. This study focuses on quantifying the genome-wide joint footprints of demography, and strong positive and negative selection to determine which proportion of the genome evolves neutrally or not. Further application of this method can be anticipated, for example, to study species with ecological and life-history traits which generate discrepancies between census size and Ne, for example for plants with selfing or seed banking (Sellinger et al. 2020), and for which the genome-wide effect of linked selection is not fully understood. References Johri P, Aquadro CF, Beaumont M, Charlesworth B, Excoffier L, Eyre-Walker A, Keightley PD, Lynch M, McVean G, Payseur BA, Pfeifer SP, Stephan W, Jensen JD (2022) Recommendations for improving statistical inference in population genomics. PLOS Biology, 20, e3001669. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3001669 Kern AD, Hahn MW (2018) The Neutral Theory in Light of Natural Selection. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35, 1366–1371. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy092 Johri P, Riall K, Becher H, Excoffier L, Charlesworth B, Jensen JD (2021) The Impact of Purifying and Background Selection on the Inference of Population History: Problems and Prospects. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 38, 2986–3003. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab050 Pavinato VAC, Mita SD, Marin J-M, Navascués M de (2022) Joint inference of adaptive and demographic history from temporal population genomic data. bioRxiv, 2021.03.12.435133, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.12.435133 Li H, Durbin R (2011) Inference of human population history from individual whole-genome sequences. Nature, 475, 493–496. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10231 Jay F, Boitard S, Austerlitz F (2019) An ABC Method for Whole-Genome Sequence Data: Inferring Paleolithic and Neolithic Human Expansions. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 36, 1565–1579. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msz038 Pudlo P, Marin J-M, Estoup A, Cornuet J-M, Gautier M, Robert CP (2016) Reliable ABC model choice via random forests. Bioinformatics, 32, 859–866. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv684 Raynal L, Marin J-M, Pudlo P, Ribatet M, Robert CP, Estoup A (2019) ABC random forests for Bayesian parameter inference. Bioinformatics, 35, 1720–1728. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty867 Sanchez T, Cury J, Charpiat G, Jay F (2021) Deep learning for population size history inference: Design, comparison and combination with approximate Bayesian computation. Molecular Ecology Resources, 21, 2645–2660. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13224 Bergland AO, Behrman EL, O’Brien KR, Schmidt PS, Petrov DA (2014) Genomic Evidence of Rapid and Stable Adaptive Oscillations over Seasonal Time Scales in Drosophila. PLOS Genetics, 10, e1004775. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004775 Cridland JM, Ramirez SR, Dean CA, Sciligo A, Tsutsui ND (2018) Genome Sequencing of Museum Specimens Reveals Rapid Changes in the Genetic Composition of Honey Bees in California. Genome Biology and Evolution, 10, 458–472. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evy007 Jorde PE, Ryman N (2007) Unbiased Estimator for Genetic Drift and Effective Population Size. Genetics, 177, 927–935. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.107.075481 Foll M, Shim H, Jensen JD (2015) WFABC: a Wright–Fisher ABC-based approach for inferring effective population sizes and selection coefficients from time-sampled data. Molecular Ecology Resources, 15, 87–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12280 Buffalo V, Coop G (2020) Estimating the genome-wide contribution of selection to temporal allele frequency change. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117, 20672–20680. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1919039117 Sellinger TPP, Awad DA, Moest M, Tellier A (2020) Inference of past demography, dormancy and self-fertilization rates from whole genome sequence data. PLOS Genetics, 16, e1008698. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008698 | Joint inference of adaptive and demographic history from temporal population genomic data | Vitor A. C. Pavinato, Stéphane De Mita, Jean-Michel Marin, Miguel de Navascués | <p style="text-align: justify;">Disentangling the effects of selection and drift is a long-standing problem in population genetics. Simulations show that pervasive selection may bias the inference of demography. Ideally, models for the inference o... |  | Adaptation, Population Genetics / Genomics | Aurelien Tellier | 2021-10-20 09:41:26 | View | |
18 Nov 2022
Fitness costs and benefits in response to artificial artesunate selection in PlasmodiumVilla M, Berthomieu A, Rivero A https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.28.478164The importance of understanding fitness costs associated with drug resistance throughout the life cycle of malaria parasitesRecommended by Silvie Huijben based on reviews by Sarah Reece and Marianna SzucsAntimalarial resistance is a major hurdle to malaria eradication efforts. The spread of drug resistance follows basic evolutionary principles, with competitive interactions between resistant and susceptible malaria strains being central to the fitness of resistant parasites. These competitive interactions can be used to design resistance management strategies, whereby a fitness cost of resistant parasites can be exploited through maintaining competitive suppression of the more fit drug-susceptible parasites. This can potentially be achieved using lower drug dosages or lower frequency of drug treatments. This approach has been demonstrated to work empirically in a rodent malaria model [1,2] and has been demonstrated to have clinical success in cancer treatments [3]. However, these resistance management approaches assume a fitness cost of the resistant pathogen, and, in the case of malaria parasites in general, and for artemisinin resistant parasites in particular, there is limited information on the presence of such fitness cost. The best suggestive evidence for the presence of fitness costs comes from the discontinuation of the use of the drug, which, in the case of chloroquine, was followed by a gradual drop in resistance frequency over the following decade [see e.g. 4,5]. However, with artemisinin derivative drugs still in use, alternative ways to study the presence of fitness costs need to be undertaken. References [1] Huijben S, Bell AS, Sim DG, Tomasello D, Mideo N, Day T, et al. 2013. Aggressive chemotherapy and the selection of drug resistant pathogens. PLoS Pathog. 9(9): e1003578. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003578 [5] Mharakurwa S, Matsena-Zingoni Z, Mudare N, Matimba C, Gara TX, Makuwaza A, et al. 2021. Steep rebound of chloroquine-sensitive Plasmodium falciparum in Zimbabwe. J Infect Dis. 223(2): 306-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa368 | Fitness costs and benefits in response to artificial artesunate selection in Plasmodium | Villa M, Berthomieu A, Rivero A | <p style="text-align: justify;">Drug resistance is a major issue in the control of malaria. Mutations linked to drug resistance often target key metabolic pathways and are therefore expected to be associated with biological costs. The spread of dr... |  | Evolutionary Applications, Life History | Silvie Huijben | 2022-01-31 13:01:16 | View | |
22 Mar 2022
Substantial genetic mixing among sexual and androgenetic lineages within the clam genus CorbiculaVastrade M., Etoundi E., Bournonville T., Colinet M., Debortoli N., Hedtke S.M., Nicolas E., Pigneur L.-M., Virgo J., Flot J.-F., Marescaux J. and Van Doninck K. https://doi.org/10.1101/590836Strange reproductive modes and population geneticsRecommended by Chris Jiggins based on reviews by Arnaud Estoup, Simon Henry Martin and 2 anonymous reviewersThere are many organisms that are asexual or have unusual modes of reproduction. One such quasi-sexual reproductive mode is androgenesis, in which the offspring, after fertilization, inherits only the entire paternal nuclear genome. The maternal genome is ditched along the way. One group of organisms which shows this mode of reproduction are clams in the genus Corbicula, some of which are androecious, while others are dioecious and sexual. The study by Vastrade et al. (2022) describes population genetic patterns in these clams, using both nuclear and mitochondrial sequence markers. In contrast to what might be expected for an asexual lineage, there is evidence for significant genetic mixing between populations. In addition, there is high heterozygosity and evidence for polyploidy in some lineages. Overall, the picture is complicated! However, what is clear is that there is far more genetic mixing than expected. One possible mechanism by which this could occur is 'nuclear capture' where there is a mixing of maternal and paternal lineages after fertilization. This can sometimes occur as a result of hybridization between 'species', leading to further mixing of divergent lineages. Thus the group is clearly far from an ancient asexual lineage - recombination and mixing occur with some regularity. The study also analyzed recent invasive populations in Europe and America. These had reduced genetic diversity, but also showed complex patterns of allele sharing suggesting a complex origin of the invasive lineages. In the future, it will be exciting to apply whole genome sequencing approaches to systems such as this. There are challenges in interpreting a handful of sequenced markers especially in a system with polyploidy and considerable complexity, and whole-genome sequencing could clarify some of the outstanding questions, Overall, this paper highlights the complex genetic patterns that can result through unusual reproductive modes, which provides a challenge for the field of population genetics and for the recognition of species boundaries. References Vastrade M, Etoundi E, Bournonville T, Colinet M, Debortoli N, Hedtke SM, Nicolas E, Pigneur L-M, Virgo J, Flot J-F, Marescaux J, Doninck KV (2022) Substantial genetic mixing among sexual and androgenetic lineages within the clam genus Corbicula. bioRxiv, 590836, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/590836 | Substantial genetic mixing among sexual and androgenetic lineages within the clam genus Corbicula | Vastrade M., Etoundi E., Bournonville T., Colinet M., Debortoli N., Hedtke S.M., Nicolas E., Pigneur L.-M., Virgo J., Flot J.-F., Marescaux J. and Van Doninck K. | <p style="text-align: justify;">“Occasional” sexuality occurs when a species combines clonal reproduction and genetic mixing. This strategy is predicted to combine the advantages of both asexuality and sexuality, but its actual consequences on the... |  | Evolutionary Ecology, Hybridization / Introgression, Phylogeography & Biogeography | Chris Jiggins | 2019-03-29 15:42:56 | View | |
31 Mar 2017
POSTPRINT
Human adaptation of Ebola virus during the West African outbreakUrbanowicz, R.A., McClure, C.P., Sakuntabhai, A., Sall, A.A., Kobinger, G., Müller, M.A., Holmes, E.C., Rey, F.A., Simon-Loriere, E., and Ball, J.K. 10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.013Ebola evolution during the 2013-2016 outbreakRecommended by Sylvain Gandon and Sébastien LionThe Ebola virus (EBOV) epidemic that started in December 2013 resulted in around 28,000 cases and more than 11,000 deaths. Since the emergence of the disease in Zaire in 1976 the virus had produced a number of outbreaks in Africa but until 2013 the reported numbers of human cases had never risen above 500. Could this exceptional epidemic size be due to the spread of a human-adapted form of the virus? The large mutation rate of the virus [1-2] may indeed introduce massive amounts of genetic variation upon which selection may act. Several earlier studies based on the accumulation of genome sequences sampled during the epidemic led to contrasting conclusions. A few studies discussed evidence of positive selection on the glycoprotein that may be linked to phenotypic variations on infectivity and/or immune evasion [3-4]. But the heterogeneity in the transmission of some lineages could also be due to environmental heterogeneity and/or stochasticity. Most studies could not rule out the null hypothesis of the absence of positive selection and human adaptation [1-2 and 5]. In a recent experimental study, Urbanowicz et al. [6] chose a different method to tackle this question. A phylogenetic analysis of genome sequences from viruses sampled in West Africa revealed the existence of two main lineages (one with a narrow geographic distribution in Guinea, and the other with a wider geographic distribution) distinguished by a single amino acid substitution in the glycoprotein of the virus (A82V), and of several sub-lineages characterised by additional substitutions. The authors used this phylogenetic data to generate a panel of mutant pseudoviruses and to test their ability to infect human and fruit bat cells. These experiments revealed that specific amino acid substitutions led to higher infectivity of human cells, including A82V. This increased infectivity on human cells was associated with a decreased infectivity in fruit bat cell cultures. Since fruit bats are likely to be the reservoir of the virus, this paper indicates that human adaptation may have led to a specialization of the virus to a new host. An accompanying paper in the same issue of Cell by Diehl et al. [7] reports results that confirm the trend identified by Urbanowicz et al. [6] and further indicate that the increased infectivity of A82V is specific for primate cells. Diehl et al. [7] also report some evidence for higher virulence of A82V in humans. In other words, the evolution of the virus may have led to higher abilities to infect and to kill its novel host. This work thus confirms the adaptive potential of RNA virus and the ability of Ebola to specialize to a novel host. In this context, the availability of an effective vaccine against the disease is particularly welcome [8]. The study of Urbanowicz et al. [6] is also remarkable because it illustrates the need of experimental approaches for the study of phenotypic variation when inference methods based on phylodynamics fail to extract a clear biological message. The analysis of genomic evolution is still in its infancy and there is a need for new theoretical developments to help detect more rapidly candidate mutations involved in adaptations to new environmental conditions. References [1] Gire, S.K., Goba, A., Andersen, K.G., Sealfon, R.S.G., Park, D.J., Kanneh, L., Jalloh, S., Momoh, M., Fullah, M., Dudas, G., et al. (2014). Genomic surveillance elucidates Ebola virus origin and transmission during the 2014 outbreak. Science 345, 1369–1372. doi: 10.1126/science.1259657 | Human adaptation of Ebola virus during the West African outbreak | Urbanowicz, R.A., McClure, C.P., Sakuntabhai, A., Sall, A.A., Kobinger, G., Müller, M.A., Holmes, E.C., Rey, F.A., Simon-Loriere, E., and Ball, J.K. | The 2013–2016 outbreak of Ebola virus (EBOV) in West Africa was the largest recorded. It began following the cross-species transmission of EBOV from an animal reservoir, most likely bats, into humans, with phylogenetic analysis revealing the co-ci... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Epidemiology, Genome Evolution, Genotype-Phenotype, Molecular Evolution, Species interactions | Sylvain Gandon | 2017-03-31 14:20:38 | View | |
18 Dec 2017
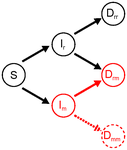
Co-evolution of virulence and immunosuppression in multiple infectionsTsukushi Kamiya, Nicole Mideo, Samuel Alizon 10.1101/149211Two parasites, virulence and immunosuppression: how does the whole thing evolve?Recommended by Sara Magalhaes based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersHow parasite virulence evolves is arguably the most important question in both the applied and fundamental study of host-parasite interactions. Typically, this research area has been progressing through the formalization of the problem via mathematical modelling. This is because the question is a complex one, as virulence is both affected and affects several aspects of the host-parasite interaction. Moreover, the evolution of virulence is a problem in which ecology (epidemiology) and evolution (changes in trait values through time) are tightly intertwined, generating what is now known as eco-evolutionary dynamics. Therefore, intuition is not sufficient to address how virulence may evolve. References [1] Anderson RM and May RM. 1982. Coevolution of hosts and parasites. Parasitology, 1982. 85: 411–426. doi: 10.1017/S0031182000055360 [2] Kamiya T, Mideo N and Alizon S. 2017. Coevolution of virulence and immunosuppression in multiple infections. bioRxiv, ver. 7 peer-reviewed by PCI Evol Biol, 149211. doi: 10.1101/139147 | Co-evolution of virulence and immunosuppression in multiple infections | Tsukushi Kamiya, Nicole Mideo, Samuel Alizon | Many components of the host-parasite interaction have been shown to affect the way virulence, that is parasite induced harm to the host, evolves. However, co-evolution of multiple traits is often neglected. We explore how an immunosuppressive mech... |  | Evolutionary Applications, Evolutionary Dynamics, Evolutionary Ecology, Evolutionary Epidemiology, Evolutionary Theory | Sara Magalhaes | 2017-06-13 16:49:45 | View | |
11 Sep 2017

POSTPRINT
Less effective selection leads to larger genomesTristan Lefébure, Claire Morvan, Florian Malard, Clémentine François, Lara Konecny-Dupré, Laurent Guéguen, Michèle Weiss-Gayet, Andaine Seguin-Orlando, Luca Ermini, Clio Der Sarkissian, N. Pierre Charrier, David Eme, Florian Mermillod-Blondin, Laurent Duret, Cristina Vieira, Ludovic Orlando and Christophe Douady 10.1101/gr.212589.116Colonisation of subterranean ecosystems leads to larger genome in waterlouse (Aselloidea)Recommended by Benoit Nabholz and Jochen B. W. WolfThe total amount of DNA utilized to store hereditary information varies immensely among eukaryotic organisms. Single copy genome sizes – disregarding differences due to ploidy - differ by more than three orders of magnitude ranging from a few million nucleotides (Mb) to hundreds of billions (Gb). With the ever-increasing availability of fully sequenced genomes we now know that most of the difference is due either to whole genome duplication or to variation in the abundance of repetitive elements. Regarding repetitive elements, the evolutionary forces underlying the large variation 'allowing' more or less elements in a genome remain largely elusive. A tentative correlation between an organism's complexity (however this may be adequately measured) and genome size, the so called C-value paradox [1], has long been dismissed. Studies testing for selection on secondary phenotypic effects associated with genome size (cell size, metabolic rates, nutrient availability) have yielded mixed results. Nonadaptive theories capitalizing on a role of deleterious insertion-deletion mutations and genetic drift as the main drivers have likewise received mixed support [2-3]. Overall, most evidence was derived from analyses across broad taxonomical scales [4-6]. Lefébure and colleagues [7] take a different approach. They confine their considerations to a homogeneous, restricted taxonomical group, isopod crustaceans of the superfamily Aselloidea. This taxonomic focus allows the authors to circumvent many of the confounding factors such as phylogenetic inertia, life history divergence and mutation rate variation that tend to trouble analyses across broad taxonomic timescales. Another important feature of the chosen system is the evolutionary independent transition of habitat use that has occurred at least 11 times. One group of species inhabits subterranean ecosystems (groundwater), another group thrives on surface water. Populations of the former live in low-energy habitats and are expected to be outnumbered by their surface dwelling relatives. Interestingly – and a precondition for the study - the groundwater species have significantly larger genomes (up to 137%). With this unique set-up, the authors are able to investigate the link between genome size and evolutionary forces related to a proxy of long-term population size by removing many of the confounding factors a priori. Upfront, we learn that the dN/dS ratio is higher in the groundwater species. This may either suggest prevalent positive selection or lower efficacy of purifying selection (relaxed constraint) in the group of species in which population sizes are expected to be low. Using a series of population genetic analyses the authors provide compelling evidence for the latter. Analyses are carefully conducted and include models for estimating the intensity and frequency of purifying and positive selection, the DoS (direction of selection) and α statistic. Next the authors also exclude the possibility that increased dN/dS of the subterranean groundwater species may be due to nonfunctionalization, which may result from the subterranean lifestyle. Overall, these analyses suggest relaxed constraint in smaller populations as the most plausible alternative to explain increased dN/dS ratios. In addition to the efficacy of selection, the authors estimate the timing of the ecological transition under the rationale that the amount of time a species may have been exposed to the subterranean habitat may reflect long term population sizes. To calibrate the 'colonization clock' they apply a neat trick based on the degree of degeneration of the opsin gene (as vision tends to get lost in these habitats). When finally testing which parameters may explain differences in genome size all factors – ecological status, selection efficiency as measured by dN/dS and colonization time - turned out to be significant predictors. Direct estimates of the short term effective population size Ne from polymorphism data, however, did not correlate with genome size. Ruling out the effect of other co-variates such as body size and growth rate the authors conclude that genome size was overall best predicted by long-term population size change upon habitat shift. In that the authors provide convincing evidence that the increase in genome size is linked to a decrease in long-term reduction of selection efficiency of subterranean species. Assuming a bias for insertion mutations over deletion mutations (which is usually the case in eukaryotes) this result is in agreement with the theory of mutational hazard [4-6]. This theory proposed by Michael Lynch postulates that the accumulation of non-functional DNA has a weak deleterious effect that can only be efficiently opposed by natural selection in species with high Ne. In conclusion, Lefébure and colleagues provide novel and welcome evidence supporting a 'neutralist' hypothesis of genome size evolution without the need to invoke an adaptive component. Methodologically, the study cautions against the common use of polymorphism-based estimates of Ne which are often obfuscated by transitory demographic change. Instead, alternative measures of selection efficacy linked to long-term population size may serve as better predictors of genome size. We hope that this study will stimulate additional work testing the link between Ne and genome size variation in other taxonomical groups [8-9]. Using genome sequences instead of the transcriptome approach applied here may concomitantly further our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying genome size change. References [1] Thomas, CA Jr. 1971. The genetic organization of chromosomes. Annual Review of Genetics 5: 237–256. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.05.120171.001321 [2] Ågren JA, Greiner S, Johnson MTJ, Wright SI. 2015. No evidence that sex and transposable elements drive genome size variation in evening primroses. Evolution 69: 1053–1062. doi: 10.1111/evo.12627 [3] Bast J, Schaefer I, Schwander T, Maraun M, Scheu S, Kraaijeveld K. 2016. No accumulation of transposable elements in asexual arthropods. Molecular Biology and Evolution 33: 697–706. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv261 [4] Lynch M. 2007. The Origins of Genome Architecture. Sinauer Associates. [5] Lynch M, Bobay LM, Catania F, Gout JF, Rho M. 2011. The repatterning of eukaryotic genomes by random genetic drift. Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics 12: 347–366. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-082410-101412 [6] Lynch M, Conery JS. 2003. The origins of genome complexity. Science 302: 1401–1404. doi: 10.1126/science.1089370 [7] Lefébure T, Morvan C, Malard F, François C, Konecny-Dupré L, Guéguen L, Weiss-Gayet M, Seguin-Orlando A, Ermini L, Der Sarkissian C, Charrier NP, Eme D, Mermillod-Blondin F, Duret L, Vieira C, Orlando L, and Douady CJ. 2017. Less effective selection leads to larger genomes. Genome Research 27: 1016-1028. doi: 10.1101/gr.212589.116 [8] Lower SS, Johnston JS, Stanger-Hall KF, Hjelmen CE, Hanrahan SJ, Korunes K, Hall D. 2017. Genome size in North American fireflies: Substantial variation likely driven by neutral processes. Genome Biolology and Evolution 9: 1499–1512. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx097 [9] Sessegolo C, Burlet N, Haudry A. 2016. Strong phylogenetic inertia on genome size and transposable element content among 26 species of flies. Biology Letters 12: 20160407. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2016.0407 | Less effective selection leads to larger genomes | Tristan Lefébure, Claire Morvan, Florian Malard, Clémentine François, Lara Konecny-Dupré, Laurent Guéguen, Michèle Weiss-Gayet, Andaine Seguin-Orlando, Luca Ermini, Clio Der Sarkissian, N. Pierre Charrier, David Eme, Florian Mermillod-Blondin, Lau... | The evolutionary origin of the striking genome size variations found in eukaryotes remains enigmatic. The effective size of populations, by controlling selection efficacy, is expected to be a key parameter underlying genome size evolution. However... |  | Evolutionary Theory, Genome Evolution, Molecular Evolution, Population Genetics / Genomics | Benoit Nabholz | 2017-09-08 09:39:23 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Guillaume Achaz
Juan Arroyo
Trine Bilde
Dustin Brisson
Marianne Elias
Inês Fragata
Matteo Fumagalli
Tatiana Giraud
Frédéric Guillaume
Ruth Hufbauer
Sara Magalhaes
Caroline Nieberding
Michael David Pirie
Tanja Pyhäjärvi
Tanja Schwander
Alejandro Gonzalez Voyer










