Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields▼ | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
26 Sep 2017

Lacking conservation genomics in the giant Galápagos tortoiseEtienne Loire, Nicolas Galtier https://doi.org/10.1101/101980A genomic perspective is needed for the re-evaluation of species boundaries, evolutionary trajectories and conservation strategies for the Galápagos giant tortoisesRecommended by Michael C. Fontaine based on reviews by 4 anonymous reviewersGenome-wide data obtained from even a small number of individuals can provide unprecedented levels of detail about the evolutionary history of populations and species [1], determinants of genetic diversity [2], species boundaries and the process of speciation itself [3]. Loire and Galtier [4] present a clear example, using the emblematic Galápagos giant tortoise (Chelonoidis nigra), of how multi-species comparative population genomic approaches can provide valuable insights about population structure and species delimitation even when sample sizes are limited but the number of loci is large and distributed across the genome. Galápagos giant tortoises are endemic to the Galápagos Islands and are currently recognized as an endangered, multi-species complex including both extant and extinct taxa. Taxonomic definitions are based on morphology, geographic isolation and population genetic evidence based on short DNA sequences of the mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) and/or a dozen or so nuclear microsatellite loci [5-8]. The species complex enjoys maximal protection. Population recoveries have been quite successful and spectacular conservation programs based on mitochondrial genes and microsatellites are ongoing. This includes for example individual translocations, breeding program, “hybrid” sterilization or removal, and resurrection of extinct lineages). In 2013, Loire et al. [9] provided the first population genomic analyses based on genome scale data (~1000 coding loci derived from blood-transcriptomes) from five individuals, encompassing three putative “species”: Chelonnoidis becki, C. porteri and C. vandenburghi. Their results raised doubts about the validity/accuracy of the currently accepted designations of “genetic distinctiveness”. However, the implications for conservation and management have remained unnoticed. In 2017, Loire and Galtier [4] have re-appraised this issue using an original multi-species comparative population genomic analysis of their previous data set [9]. Based on a comparison of 53 animal species, they show that both the level of genome-wide neutral diversity (πS) and level of population structure estimated using the inbreeding coefficient (F) are much lower than would be expected from a sample covering multiple species. The observed values are more comparable to those typically reported at the “among population” level within a single species such as human (Homo sapiens). The authors go to great length to assess the sensitivity of their method to detect population structure (or lack thereof) and show that their results are robust to potential issues, such as contamination and sequencing errors that can occur with Next Generation Sequencing techniques; and biases related to the small sample size and sub-sampling of individuals. They conclude that published mtDNA and microsatellite-based assessment of population structure and species designations may be biased towards over-splitting. This manuscript is a very good read as it shows the potential of the now relatively affordable genome-wide data for helping to both resolve and clarify population and species boundaries, illuminate demographic trends, evolutionary trajectories of isolated groups, patterns of connectivity among them, and test for evidence of local adaptation and even reproductive isolation. The comprehensive information provided by genome-wide data can critically inform and assist the development of the best strategies to preserve endangered populations and species. Loire and Galtier [4] make a strong case for applying genomic data to the Galápagos giant tortoises, which is likely to redirect conservation efforts more effectively and at lower cost. The case of the Galápagos giant tortoises is certainly a very emblematic example, which will find an echo in many other endangered species conservation programs. References [1] Li H and Durbin R. 2011. Inference of human population history from individual whole-genome sequences. Nature, 475: 493–496. doi: 10.1038/nature10231 [2] Romiguier J, Gayral P, Ballenghien M, Bernard A, Cahais V, Chenuil A, Chiari Y, Dernat R, Duret L, Faivre N, Loire E, Lourenco JM, Nabholz B, Roux C, Tsagkogeorga G, Weber AA-T, Weinert LA, Belkhir K, Bierne N, Glémin S and Galtier N. 2014. Comparative population genomics in animals uncovers the determinants of genetic diversity. Nature, 515: 261–263. doi: 10.1038/nature13685 [3] Roux C, Fraïsse C, Romiguier J, Anciaux Y, Galtier N and Bierne N. 2016. Shedding light on the grey zone of speciation along a continuum of genomic divergence. PLoS Biology, 14: e2000234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2000234 [4] Loire E and Galtier N. 2017. Lacking conservation genomics in the giant Galápagos tortoise. bioRxiv 101980, ver. 4 of September 26, 2017. doi: 10.1101/101980 [5] Beheregaray LB, Ciofi C, Caccone A, Gibbs JP and Powell JR. 2003. Genetic divergence, phylogeography and conservation units of giant tortoises from Santa Cruz and Pinzón, Galápagos Islands. Conservation Genetics, 4: 31–46. doi: 10.1023/A:1021864214375 [6] Ciofi C, Milinkovitch MC, Gibbs JP, Caccone A and Powell JR. 2002. Microsatellite analysis of genetic divergence among populations of giant Galápagos tortoises. Molecular Ecology, 11: 2265–2283. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294X.2002.01617.x [7] Garrick RC, Kajdacsi B, Russello MA, Benavides E, Hyseni C, Gibbs JP, Tapia W and Caccone A. 2015. Naturally rare versus newly rare: demographic inferences on two timescales inform conservation of Galápagos giant tortoises. Ecology and Evolution, 5: 676–694. doi: 10.1002/ece3.1388 [8] Poulakakis N, Edwards DL, Chiari Y, Garrick RC, Russello MA, Benavides E, Watkins-Colwell GJ, Glaberman S, Tapia W, Gibbs JP, Cayot LJ and Caccone A. 2015. Description of a new Galápagos giant tortoise species (Chelonoidis; Testudines: Testudinidae) from Cerro Fatal on Santa Cruz island. PLoS ONE, 10: e0138779. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138779 [9] Loire E, Chiari Y, Bernard A, Cahais V, Romiguier J, Nabholz B, Lourenço JM and Galtier N. 2013. Population genomics of the endangered giant Galápagos tortoise. Genome Biology, 14: R136. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-12-r136 | Lacking conservation genomics in the giant Galápagos tortoise | Etienne Loire, Nicolas Galtier | <p>Conservation policy in the giant Galápagos tortoise, an iconic endangered animal, has been assisted by genetic markers for ~15 years: a dozen loci have been used to delineate thirteen (sub)species, between which hybridization is prevented. Here... |  | Evolutionary Applications, Population Genetics / Genomics, Speciation, Systematics / Taxonomy | Michael C. Fontaine | 2017-01-21 15:34:00 | View | |
18 Nov 2022
Fitness costs and benefits in response to artificial artesunate selection in PlasmodiumVilla M, Berthomieu A, Rivero A https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.28.478164The importance of understanding fitness costs associated with drug resistance throughout the life cycle of malaria parasitesRecommended by Silvie Huijben based on reviews by Sarah Reece and Marianna SzucsAntimalarial resistance is a major hurdle to malaria eradication efforts. The spread of drug resistance follows basic evolutionary principles, with competitive interactions between resistant and susceptible malaria strains being central to the fitness of resistant parasites. These competitive interactions can be used to design resistance management strategies, whereby a fitness cost of resistant parasites can be exploited through maintaining competitive suppression of the more fit drug-susceptible parasites. This can potentially be achieved using lower drug dosages or lower frequency of drug treatments. This approach has been demonstrated to work empirically in a rodent malaria model [1,2] and has been demonstrated to have clinical success in cancer treatments [3]. However, these resistance management approaches assume a fitness cost of the resistant pathogen, and, in the case of malaria parasites in general, and for artemisinin resistant parasites in particular, there is limited information on the presence of such fitness cost. The best suggestive evidence for the presence of fitness costs comes from the discontinuation of the use of the drug, which, in the case of chloroquine, was followed by a gradual drop in resistance frequency over the following decade [see e.g. 4,5]. However, with artemisinin derivative drugs still in use, alternative ways to study the presence of fitness costs need to be undertaken. References [1] Huijben S, Bell AS, Sim DG, Tomasello D, Mideo N, Day T, et al. 2013. Aggressive chemotherapy and the selection of drug resistant pathogens. PLoS Pathog. 9(9): e1003578. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003578 [5] Mharakurwa S, Matsena-Zingoni Z, Mudare N, Matimba C, Gara TX, Makuwaza A, et al. 2021. Steep rebound of chloroquine-sensitive Plasmodium falciparum in Zimbabwe. J Infect Dis. 223(2): 306-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa368 | Fitness costs and benefits in response to artificial artesunate selection in Plasmodium | Villa M, Berthomieu A, Rivero A | <p style="text-align: justify;">Drug resistance is a major issue in the control of malaria. Mutations linked to drug resistance often target key metabolic pathways and are therefore expected to be associated with biological costs. The spread of dr... |  | Evolutionary Applications, Life History | Silvie Huijben | 2022-01-31 13:01:16 | View | |
10 Jan 2019
Genomic data provides new insights on the demographic history and the extent of recent material transfers in Norway spruceJun Chen, Lili Li, Pascal Milesi, Gunnar Jansson, Mats Berlin, Bo Karlsson, Jelena Aleksic, Giovanni G Vendramin, Martin Lascoux https://doi.org/10.1101/402016Disentangling the recent and ancient demographic history of European spruce speciesRecommended by Jason Holliday based on reviews by 1 anonymous reviewerGenetic diversity in temperate and boreal forests tree species has been strongly affected by late Pleistocene climate oscillations [2,3,5], but also by anthropogenic forces. Particularly in Europe, where a long history of human intervention has re-distributed species and populations, it can be difficult to know if a given forest arose through natural regeneration and gene flow or through some combination of natural and human-mediated processes. This uncertainty can confound inferences of the causes and consequences of standing genetic variation, which may impact our interpretation of demographic events that shaped species before humans became dominant on the landscape. In their paper entitled "Genomic data provides new insights on the demographic history and the extent of recent material transfers in Norway spruce", Chen et al. [1] used a genome-wide dataset of 400k SNPs to infer the demographic history of Picea abies (Norway spruce), the most widespread and abundant spruce species in Europe, and to understand its evolutionary relationship with two other spruces (Picea obovata [Siberian spruce] and P. omorika [Serbian spruce]). Three major Norway spruce clusters were identified, corresponding to central Europe, Russia and the Baltics, and Scandinavia, which agrees with previous studies. The density of the SNP data in the present paper enabled inference of previously uncharacterized admixture between these groups, which corresponds to the timing of postglacial recolonization following the last glacial maximum (LGM). This suggests that multiple migration routes gave rise to the extant distribution of the species, and may explain why Chen et al.'s estimates of divergence times among these major Norway spruce groups were older (15mya) than those of previous studies (5-6mya) – those previous studies may have unknowingly included admixed material [4]. Treemix analysis also revealed extensive admixture between Norway and Siberian spruce over the last ~100k years, while the geographically-restricted Serbian spruce was both isolated from introgression and had a dramatically smaller effective population size (Ne) than either of the other two species. This small Ne resulted from a bottleneck associated with the onset of the iron age ~3000 years ago, which suggests that anthropogenic depletion of forest resources has severely impacted this species. Finally, ancestry of Norway spruce samples collected in Sweden and Denmark suggest their recent transfer from more southern areas of the species range. This northward movement of genotypes likely occurred because the trees performed well relative to local provenances, which is a common observation when trees from the south are planted in more northern locations (although at the potential cost of frost damage due to inappropriate phenology). While not the reason for the transfer, the incorporation of southern seed sources into the Swedish breeding and reforestation program may lead to more resilient forests under climate change. Taken together, the data and analysis presented in this paper allowed inference of the intra- and interspecific demographic histories of a tree species group at a very high resolution, and suggest caveats regarding sampling and interpretation of data from areas with a long history of occupancy by humans. References [1] Chen, J., Milesi, P., Jansson, G., Berlin, M., Karlsson, B., Aleksić, J. M., Vendramin, G. G., Lascoux, M. (2018). Genomic data provides new insights on the demographic history and the extent of recent material transfers in Norway spruce. BioRxiv, 402016. ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol. doi: 10.1101/402016 | Genomic data provides new insights on the demographic history and the extent of recent material transfers in Norway spruce | Jun Chen, Lili Li, Pascal Milesi, Gunnar Jansson, Mats Berlin, Bo Karlsson, Jelena Aleksic, Giovanni G Vendramin, Martin Lascoux | <p>Primeval forests are today exceedingly rare in Europe and transfer of forest reproductive material for afforestation and improvement have been very common, especially over the last two centuries. This can be a serious impediment when inferring ... | Evolutionary Applications, Hybridization / Introgression, Population Genetics / Genomics | Jason Holliday | Anonymous, Anonymous | 2018-08-29 08:33:15 | View | |
07 Jul 2017

Unmasking the delusive appearance of negative frequency-dependent selectionRecommended by Ignacio Bravo based on reviews by David Baltrus and 2 anonymous reviewersExplaining the processes that maintain polymorphisms in a population has been a fundamental line of research in evolutionary biology. One of the main mechanisms identified that preserves genetic diversity is negative frequency-dependent selection (NFDS), which constitutes a powerful framework for interpreting the presence of persistent polymorphisms. Nevertheless, a number of patterns that are often explained by invoking NFDS may also be compatible with, and possibly more easily explained by, different processes. References [1] Brisson D. 2017. Negative frequency-dependent selection is frequently confounding. bioRxiv 113324, ver. 3 of 20th June 2017. doi: 10.1101/113324 [2] Heino M, Metz JAJ and Kaitala V. 1998. The enigma of frequency-dependent selection. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 13: 367-370. doi: 1016/S0169-5347(98)01380-9 | Negative frequency-dependent selection is frequently confounding | Dustin Brisson | The existence of persistent genetic variation within natural populations presents an evolutionary problem as natural selection and genetic drift tend to erode genetic diversity. Models of balancing selection were developed to account for the high ... |  | Evolutionary Applications, Evolutionary Theory, Population Genetics / Genomics | Ignacio Bravo | 2017-03-03 18:46:42 | View | |
26 Aug 2021
Impact of ploidy and pathogen life cycle on resistance durabilityMéline Saubin, Stephane De Mita, Xujia Zhu, Bruno Sudret, Fabien Halkett https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.28.446112Durability of plant resistance to diploid pathogenRecommended by Hirohisa Kishino based on reviews by Loup Rimbaud and 1 anonymous reviewerDurability of plant resistance to diploid pathogen Hirohisa Kishino Based on the population genetic and epidemiologic model, Saubin et al. (2021) report that the resistant hosts generated by the breeding based on the gene-for-gene interaction is durable much longer against diploid pathogens than haploid pathogens. The avr allele of pathogen that confers the resistance is genetically recessive. The heterozygotes are not recognized by the resistant hosts and only the avr/avr homozygote is adaptive. As a result, the trajectory of avr allele frequency becomes more stochastic due to genetic drift. Although the paper focuses on the evolution of standing polymorphism, it seems obvious that the adaptive mutations in pathogen have much larger probability of being deleted from the population because the individuals own the avr allele mostly in the form of heterozygote at the initial phase after the mutation. Since only few among many models of plant resistance deployment study the case of diploid pathogen and the contribution of the pathogen life cycle, this work will add an important intellect to the literature (Rimbaud et al. 2021). From the study of host-parasite interaction in flax rust Melampsora lini, Flor (1942, 1955) showed that the host resistance is formed by the interaction of a host resistance gene and a corresponding pathogen gene. This gene-for-gene hypothesis has been supported by experimental evidence and has served as a basis of the methods of molecular breeding targeting the dominant R genes. However, modern agriculture provides the pathogen populations with the homogeneous environments and laid strong selection pressure on them. As a result, the newly developed resistant plants face the risk of immediate resistance breakdown (Möller and Stukenbrock 2017). Currently, quantitative resistance is getting attention as characters as a potential target for long-life (mild) resistant breeds (Lannou, 2012). They are polygenic and controlled partly by the same genes that mediate qualitative resistance but mostly by the genes that encode defense-related outputs such as strengthening of the cell wall or defense compound biosynthesis (Corwin and Kliebenstein, 2017). Progress of molecular genetics may overcome the technical difficulty (Bakkeren and Szabo, 2020). Saubin et al. (2021) notes that the pattern of genetic inheritance of the pathogen counterparts that respond to the host traits is crucial regarding with the durability of the resistant hosts. The resistance traits for which avr alleles are predicted to be recessive may be the targets of breeding. References Bakkeren, G., and Szabo, L. J. (2020) Progress on molecular genetics and manipulation of rust fungi. Phytopathology, 110, 532-543. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-07-19-0228-IA Corwin, J. A., and Kliebenstein, D. J. (2017) Quantitative resistance: more than just perception of a pathogen. The Plant Cell, 29, 655-665. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00915 Flor, H. H. (1942) Inheritance of pathogenicity in a cross between physiological races 22 and 24 of Melampsova lini. Phytopathology, 35. Abstract. Flor, H. H. (1955) Host-parasite interactions in flax rust-its genetics and other implications. Phytopathology, 45, 680-685. Lannou, C. (2012) Variation and selection of quantitative traits in plant pathogens. Annual review of phytopathology, 50, 319-338. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-081211-173031 Möller, M. and Stukenbrock, E. H. (2017) Evolution and genome architecture in fungal plant pathogens. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 15, 756–771. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2017.76 Rimbaud, L., Fabre, F., Papaïx, J., Moury, B., Lannou, C., Barrett, L. G., and Thrall, P. H. (2021) Models of Plant Resistance Deployment. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 59. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-020620-122134 Saubin, M., De Mita, S., Zhu, X., Sudret, B. and Halkett, F. (2021) Impact of ploidy and pathogen life cycle on resistance durability. bioRxiv, 2021.05.28.446112, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.28.446112 | Impact of ploidy and pathogen life cycle on resistance durability | Méline Saubin, Stephane De Mita, Xujia Zhu, Bruno Sudret, Fabien Halkett | <p>The breeding of resistant hosts based on the gene-for-gene interaction is crucial to address epidemics of plant pathogens in agroecosystems. Resistant host deployment strategies are developed and studied worldwide to decrease the probability of... |  | Evolutionary Applications, Evolutionary Epidemiology | Hirohisa Kishino | 2021-06-03 07:58:16 | View | |
04 Nov 2020
Treating symptomatic infections and the co-evolution of virulence and drug resistanceSamuel Alizon https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.29.970905More intense symptoms, more treatment, more drug-resistance: coevolution of virulence and drug-resistanceRecommended by Ludek Berec based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewersMathematical models play an essential role in current evolutionary biology, and evolutionary epidemiology is not an exception [1]. While the issues of virulence evolution and drug-resistance evolution resonate in the literature for quite some time [2, 3], the study by Alizon [4] is one of a few that consider co-evolution of both these traits [5]. The idea behind this study is the following: treating individuals with more severe symptoms at a higher rate (which appears to be quite natural) leads to an appearance of virulent drug-resistant strains, via treatment failure. The author then shows that virulence in drug-resistant strains may face different selective pressures than in drug-sensitive strains and hence proceed at different rates. Hence, treatment itself modulates evolution of virulence. As one of the reviewers emphasizes, the present manuscript offers a mathematical view on why the resistant and more virulent strains can be selected in epidemics. Also, we both find important that the author highlights that the topic and results of this study can be attributed to public health policies and development of optimal treatment protocols [6]. References [1] Gandon S, Day T, Metcalf JE, Grenfell BT (2016) Forecasting epidemiological and evolutionary dynamics of infectious diseases. Trends Ecol Evol 31: 776-788. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2016.07.010 | Treating symptomatic infections and the co-evolution of virulence and drug resistance | Samuel Alizon | <p>Antimicrobial therapeutic treatments are by definition applied after the onset of symptoms, which tend to correlate with infection severity. Using mathematical epidemiology models, I explore how this link affects the coevolutionary dynamics bet... |  | Evolutionary Applications, Evolutionary Dynamics, Evolutionary Epidemiology, Evolutionary Theory | Ludek Berec | 2020-03-04 10:18:39 | View | |
16 Dec 2020

Shifts from pulled to pushed range expansions caused by reduction of landscape connectivityMaxime Dahirel, Aline Bertin, Marjorie Haond, Aurélie Blin, Eric Lombaert, Vincent Calcagno, Simon Fellous, Ludovic Mailleret, Thibaut Malausa, Elodie Vercken https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.13.092775The push and pull between theory and data in understanding the dynamics of invasionRecommended by Ben Phillips based on reviews by Laura Naslund and 2 anonymous reviewersExciting times are afoot for those of us interested in the ecology and evolution of invasive populations. Recent years have seen evolutionary process woven firmly into our understanding of invasions (Miller et al. 2020). This integration has inspired a welter of empirical and theoretical work. We have moved from field observations and verbal models to replicate experiments and sophisticated mathematical models. Progress has been rapid, and we have seen science at its best; an intimate discussion between theory and data. References Bîrzu, G., Matin, S., Hallatschek, O., and Korolev, K. S. (2019). Genetic drift in range expansions is very sensitive to density dependence in dispersal and growth. Ecology Letters, 22(11), 1817-1827. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.13364 | Shifts from pulled to pushed range expansions caused by reduction of landscape connectivity | Maxime Dahirel, Aline Bertin, Marjorie Haond, Aurélie Blin, Eric Lombaert, Vincent Calcagno, Simon Fellous, Ludovic Mailleret, Thibaut Malausa, Elodie Vercken | <p>Range expansions are key processes shaping the distribution of species; their ecological and evolutionary dynamics have become especially relevant today, as human influence reshapes ecosystems worldwide. Many attempts to explain and predict ran... |  | Evolutionary Applications, Evolutionary Dynamics, Evolutionary Ecology, Experimental Evolution, Phylogeography & Biogeography | Ben Phillips | 2020-08-04 12:51:56 | View | |
18 Dec 2017
Co-evolution of virulence and immunosuppression in multiple infectionsTsukushi Kamiya, Nicole Mideo, Samuel Alizon 10.1101/149211Two parasites, virulence and immunosuppression: how does the whole thing evolve?Recommended by Sara Magalhaes based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersHow parasite virulence evolves is arguably the most important question in both the applied and fundamental study of host-parasite interactions. Typically, this research area has been progressing through the formalization of the problem via mathematical modelling. This is because the question is a complex one, as virulence is both affected and affects several aspects of the host-parasite interaction. Moreover, the evolution of virulence is a problem in which ecology (epidemiology) and evolution (changes in trait values through time) are tightly intertwined, generating what is now known as eco-evolutionary dynamics. Therefore, intuition is not sufficient to address how virulence may evolve. References [1] Anderson RM and May RM. 1982. Coevolution of hosts and parasites. Parasitology, 1982. 85: 411–426. doi: 10.1017/S0031182000055360 [2] Kamiya T, Mideo N and Alizon S. 2017. Coevolution of virulence and immunosuppression in multiple infections. bioRxiv, ver. 7 peer-reviewed by PCI Evol Biol, 149211. doi: 10.1101/139147 | Co-evolution of virulence and immunosuppression in multiple infections | Tsukushi Kamiya, Nicole Mideo, Samuel Alizon | Many components of the host-parasite interaction have been shown to affect the way virulence, that is parasite induced harm to the host, evolves. However, co-evolution of multiple traits is often neglected. We explore how an immunosuppressive mech... |  | Evolutionary Applications, Evolutionary Dynamics, Evolutionary Ecology, Evolutionary Epidemiology, Evolutionary Theory | Sara Magalhaes | 2017-06-13 16:49:45 | View | |
08 Nov 2021

Dynamics of sex-biased gene expression over development in the stick insect Timema californicumJelisaveta Djordjevic, Zoé Dumas, Marc Robinson-Rechavi, Tanja Schwander, Darren James Parker https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.01.23.427895Sex-biased gene expression in an hemimetabolous insect: pattern during development, extent, functions involved, rate of sequence evolution, and comparison with an holometabolous insectRecommended by Nadia Aubin-Horth based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersAn individual’s sexual phenotype is determined during development. Understanding which pathways are activated or repressed during the developmental stages leading to a sexually mature individual, for example by studying gene expression and how its level is biased between sexes, allows us to understand the functional aspects of dimorphic phenotypes between the sexes. Several studies have quantified the differences in transcription between the sexes in mature individuals, showing the extent of this sex-bias and which functions are affected. There is, however, less data available on what occurs during the different phases of development leading to this phenotype, especially in species with specific developmental strategies, such as hemimetabolous insects. While many well-studied insects such as the honey bee, drosophila, and butterflies, exhibit an holometabolous development ("holo" meaning "complete" in reference to their drastic metamorphosis from the juvenile to the adult stage), hemimetabolous insects have juvenile stages that look similar to the adult stage (the hemi prefix meaning "half", referring to the more tissue-specific changes during development), as seen in crickets, cockroaches, and stick insects. Learning more about what happens during development in terms of the identity of genes that are sex-biased (are they the same genes at different developmental stages? What are their function? Do they exhibit specific sequence evolution rates? Is one sex over-represented in the sex-biased genes?) and their quantity over developmental time (gradual or abrupt increase in number, if any?) would allow us to better understand the evolution of sexual dimorphism at the gene expression level and how it relates to dimorphism at the organismic level. Djordjevic et al (2021) studied the transcriptome during development in an hemimetabolous stick insect, to improve our knowledge of this type of development, where the organismic phenotype is already mostly present in the early life stages. To do this, they quantified whole-genome gene expression levels in whole insects, using RNA-seq at three different developmental stages. One of the interesting results presented by Djordjevic and colleagues is that the increase in the number of genes that were sex-biased in expression is gradual over the three stages of development studied and it is mostly the same genes that stay sex-biased over time, reflecting the gradual change in phenotypes between hatchlings, juveniles and adults. Furthermore, male-biased genes had faster sequence divergence rates than unbiased genes and that female-biased genes. This new information of sex-bias in gene expression in an hemimetabolous insect allowed the authors to do a comparison of sex-biased genes with what has been found in a well-studied holometabolous insect, Drosophila. The gene expression patterns showed that four times more genes were sex-biased in expression in that species than in stick insects. Furthermore, the increase in the number of sex-biased genes during development was quite abrupt and clearly distinct in the adult stage, a pattern that was not seen in stick insects. As pointed out by the authors, this pattern of a "burst" of sex-biased genes at maturity is more common than the gradual increase seen in stick insects. With this study, we now know more about the evolution of sex-biased gene expression in an hemimetabolous insect and how it relates to their phenotypic dimorphism. Clearly, the next step will be to sample more hemimetabolous species at different life stages, to see how this pattern is widespread or not in this mode of development in insects. References Djordjevic J, Dumas Z, Robinson-Rechavi M, Schwander T, Parker DJ (2021) Dynamics of sex-biased gene expression during development in the stick insect Timema californicum. bioRxiv, 2021.01.23.427895, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.01.23.427895 | Dynamics of sex-biased gene expression over development in the stick insect Timema californicum | Jelisaveta Djordjevic, Zoé Dumas, Marc Robinson-Rechavi, Tanja Schwander, Darren James Parker | <p style="text-align: justify;">Sexually dimorphic phenotypes are thought to arise primarily from sex-biased gene expression during development. Major changes in developmental strategies, such as the shift from hemimetabolous to holometabolous dev... |  | Evo-Devo, Evolutionary Dynamics, Evolutionary Ecology, Expression Studies, Genotype-Phenotype, Molecular Evolution, Reproduction and Sex, Sexual Selection | Nadia Aubin-Horth | 2021-04-22 17:36:32 | View | |
04 Mar 2021
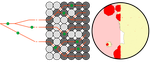
Simulation of bacterial populations with SLiMJean Cury, Benjamin C. Haller, Guillaume Achaz, and Flora Jay https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.28.316869Simulating bacterial evolution forward-in-timeRecommended by Frederic Bertels based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewersJean Cury and colleagues (2021) have developed a protocol to simulate bacterial evolution in SLiM. In contrast to existing methods that depend on the coalescent, SLiM simulates evolution forward in time. SLiM has, up to now, mostly been used to simulate the evolution of eukaryotes (Haller and Messer 2019), but has been adapted here to simulate evolution in bacteria. Forward-in-time simulations are usually computationally very costly. To circumvent this issue, bacterial population sizes are scaled down. One would now expect results to become inaccurate, however, Cury et al. show that scaled-down forwards simulations provide very accurate results (similar to those provided by coalescent simulators) that are consistent with theoretical expectations. Simulations were analyzed and compared to existing methods in simple and slightly more complex scenarios where recombination affects evolution. In all scenarios, simulation results from coalescent methods (fastSimBac (De Maio and Wilson 2017), ms (Hudson 2002)) and scaled-down forwards simulations were very similar, which is very good news indeed. A biologist not aware of the complexities of forwards, backwards simulations and the coalescent, might now naïvely ask why another simulation method is needed if existing methods perform just as well. To address this question the manuscript closes with a very neat example of what exactly is possible with forwards simulations that cannot be achieved using existing methods. The situation modeled is the growth and evolution of a set of 50 bacteria that are randomly distributed on a petri dish. One side of the petri dish is covered in an antibiotic the other is antibiotic-free. Over time, the bacteria grow and acquire antibiotic resistance mutations until the entire artificial petri dish is covered with a bacterial lawn. This simulation demonstrates that it is possible to simulate extremely complex (e.g. real world) scenarios to, for example, assess whether certain phenomena are expected with our current understanding of bacterial evolution, or whether there are additional forces that need to be taken into account. Hence, forwards simulators could significantly help us to understand what current models can and cannot explain in evolutionary biology.
References Cury J, Haller BC, Achaz G, Jay F (2021) Simulation of bacterial populations with SLiM. bioRxiv, 2020.09.28.316869, version 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.28.316869 De Maio N, Wilson DJ (2017) The Bacterial Sequential Markov Coalescent. Genetics, 206, 333–343. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.116.198796 Haller BC, Messer PW (2019) SLiM 3: Forward Genetic Simulations Beyond the Wright–Fisher Model. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 36, 632–637. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy228 Hudson RR (2002) Generating samples under a Wright–Fisher neutral model of genetic variation. Bioinformatics, 18, 337–338. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/18.2.337 | Simulation of bacterial populations with SLiM | Jean Cury, Benjamin C. Haller, Guillaume Achaz, and Flora Jay | <p>Simulation of genomic data is a key tool in population genetics, yet, to date, there is no forward-in-time simulator of bacterial populations that is both computationally efficient and adaptable to a wide range of scenarios. Here we demonstrate... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Population Genetics / Genomics | Frederic Bertels | 2020-10-02 19:03:42 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Guillaume Achaz
Juan Arroyo
Trine Bilde
Dustin Brisson
Marianne Elias
Inês Fragata
Matteo Fumagalli
Tatiana Giraud
Frédéric Guillaume
Ruth Hufbauer
Sara Magalhaes
Caroline Nieberding
Michael David Pirie
Tanja Pyhäjärvi
Tanja Schwander
Alejandro Gonzalez Voyer










