Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers▲ | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
24 Oct 2022

Evolutionary responses of energy metabolism, development, and reproduction to artificial selection for increasing heat tolerance in Drosophila subobscuraAndres Mesas, Luis E. Castaneda https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.03.479001The other side of the evolution of heat tolerance: correlated responses in metabolism and life-history traitsRecommended by Inês Fragata and Pedro Simões based on reviews by Marija Savić Veselinović and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Marija Savić Veselinović and 1 anonymous reviewer
Understanding how species respond to environmental changes is becoming increasingly important in order to predict the future of biodiversity and species distributions under current global warming conditions (Rezende 2020; Bennett et al 2021). Two key factors to take into account in these predictions are the tolerance of organisms to heat stress and subsequently how they adapt to increasingly warmer temperatures. Coupled with this, one important factor that is often overlooked when addressing the evolution of thermal tolerance, is the correlated responses in traits that are important to fitness, such as life histories, behavior and the underlying metabolic processes. The rate and intensity of the thermal stress are expected to be major factors in shaping the evolution of heat tolerance and correlated responses in other traits. For instance, lower rates of thermal stress are predicted to select for individuals with a slower metabolism (Santos et al 2012), whereas low metabolism is expected to lead to a lower reproductive rate (Dammhahn et al 2018). To quantify the importance of the rate and intensity of thermal stress on the evolutionary response of heat tolerance and correlated response in behavior, Mesas et al (2021) performed experimental evolution in Drosophila subobscura using selective regimes with slow or fast ramping protocols. Whereas both regimes showed increased heat tolerance with similar evolutionary rates, the correlated responses in thermal performance curves for locomotor behavior differed between selection regimes. These findings suggest that thermal rate and intensity may shape the evolution of correlated responses in other traits, urging the need to understand possible correlated responses at relevant levels such as life history and metabolism. In the present contribution, Mesas and Castañeda (2022) investigate whether the disparity in thermal performance curves observed in the previous experiment (Mesas et al 2021) could be explained by differences in metabolic energy production and consumption, and how this correlated with the reproductive output (fecundity and viability). Overall, the authors show some evidence for lowered enzyme activity and increased performance in life-history traits, particularly for the slow-ramping selected flies. Specifically, the authors observe a reduction in glucose metabolism and increased viability when evolving under slow ramping stress. Interestingly, both regimes show a general increase in fecundity, suggesting that adaptation to these higher temperatures is not costly (for reproduction) in the ancestral environment. The evidence for a somewhat lower metabolism in the slow-ramping lines suggests the evolution of a slow “pace of life”. The “pace of life” concept tries to bridge variation across several levels namely metabolism, physiology, behavior and life history, with low “pace of life” organisms presenting lower metabolic rates, later reproduction and higher longevity than fast “pace of life” organisms (Dammhahn et al 2018, Tuzun & Stocks 2022). As the authors state there is not a clear-cut association with the expectations of the pace of life hypothesis since there was evidence for increased reproductive output under both selection intensity regimes. This suggests that, given sufficient trait genetic variance, positively correlated responses may emerge during some stages of thermal evolution. As fecundity estimates in this study were focussed on early life, the possibility of a decrease in the cumulative reproductive output of the selected flies, even under benign conditions, cannot be excluded. This would help explain the apparent paradox of increased fecundity in selected lines. In this context, it would also be interesting to explore the variation in reproductive output at different temperatures, i.e to obtain thermal performance curves for life histories. Mesas and Castañeda (2022) raise important questions to pursue in the future and contribute to the growing evidence that, in order to predict the distribution of ectothermic species under current global warming conditions, we need to expand beyond determining the physiological thermal limits of each organism (Parratt et al 2021). Ultimately, integrating metabolic, life-history and behavioral changes during evolution under different thermal stresses within a coherent framework is key to developing better predictions of temperature effects on natural populations. Bennett, J.M., Sunday, J., Calosi, P. et al. The evolution of critical thermal limits of life on Earth. Nat Commun 12, 1198 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21263-8 Dammhahn, M., Dingemanse, N.J., Niemelä, P.T. et al. Pace-of-life syndromes: a framework for the adaptive integration of behaviour, physiology and life history. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 72, 62 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-018-2473-y Mesas, A, Jaramillo, A, Castañeda, LE. Experimental evolution on heat tolerance and thermal performance curves under contrasting thermal selection in Drosophila subobscura. J Evol Biol 34, 767– 778 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1111/jeb.13777 Parratt, S.R., Walsh, B.S., Metelmann, S. et al. Temperatures that sterilize males better match global species distributions than lethal temperatures. Nat. Clim. Chang. 11, 481–484 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-021-01047-0 Santos, M, Castañeda, LE, Rezende, EL Keeping pace with climate change: what is wrong with the evolutionary potential of upper thermal limits? Ecology and evolution, 2(11), 2866-2880 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.385 Tüzün, N, Stoks, R. A fast pace-of-life is traded off against a high thermal performance. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 289(1972), 20212414 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2021.2414 Rezende, EL, Bozinovic, F, Szilágyi, A, Santos, M. Predicting temperature mortality and selection in natural Drosophila populations. Science, 369(6508), 1242-1245 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba9287 | Evolutionary responses of energy metabolism, development, and reproduction to artificial selection for increasing heat tolerance in Drosophila subobscura | Andres Mesas, Luis E. Castaneda | <p>Adaptations to warming conditions exhibited by ectotherms include increasing heat tolerance but also metabolic changes to reduce maintenance costs (metabolic depression), which can allow them to redistribute the energy surplus to biological fun... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Ecology, Experimental Evolution, Life History | Inês Fragata | 2022-02-08 01:05:50 | View | |
24 Aug 2022
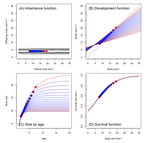
Density dependent environments can select for extremes of body sizeTim Coulson, Anja Felmy, Tomos Potter, Gioele Passoni, Robert A Montgomery, Jean-Michel Gaillard, Peter J Hudson, Joseph Travis, Ronald D Bassar, Shripad D Tuljapurkar, Dustin Marshall, Sonya M Clegg https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.17.480952A population biological modeling approach for life history and body size evolutionRecommended by Wolf Blanckenhorn based on reviews by Frédéric Guillaume and 2 anonymous reviewersBody size evolution is a central theme in evolutionary biology. Particularly the question of when and how smaller body sizes can evolve continues to interest evolutionary ecologists, because most life history models, and the empirical evidence, document that large body size is favoured by natural and sexual selection in most (even small) organisms and environments at most times. How, then, can such a large range of body size and life history syndromes evolve and coexist in nature? The paper by Coulson et al. lifts this question to the level of the population, a relatively novel approach using so-called integral projection (simulation) models (IPMs) (as opposed to individual-based or game theoretical models). As is well outlined by (anonymous) Reviewer 1, and following earlier papers spearheading this approach in other life history contexts, the authors use the well-known carrying capacity (K) of population biology as the ultimate fitness parameter to be maximized or optimized (rather than body size per se), to ultimately identify factors and conditions promoting the evolution of extreme body sizes in nature. They vary (individual or population) size-structured growth trajectories to observe age and size at maturity, surivorship and fecundity/fertility schedules upon evaluating K (see their Fig. 1). Importantly, trade-offs are introduced via density-dependence, either for adult reproduction or for juvenile survival, in two (of several conceivable) basic scenarios (see their Table 2). All other relevant standard life history variables (see their Table 1) are assumed density-independent, held constant or zero (as e.g. the heritability of body size). The authors obtain evidence for disruptive selection on body size in both scenarios, with small size and a fast life history evolving below a threshold size at maturity (at the lowest K) and large size and a slow life history beyond this threshold (see their Fig. 2). Which strategy wins ultimately depends on the fitness benefits of delaying sexual maturity (at larger size and longer lifespan) at the adult stage relative to the preceeding juvenile mortality costs, in agreement with classic life history theory (Roff 1992, Stearns 1992). The modeling approach can be altered and refined to be applied to other key life history parameters and environments. These results can ultimately explain the evolution of smaller body sizes from large body sizes, or vice versa, and their corresponding life history syndromes, depending on the precise environmental circumstances. All reviewers agreed that the approach taken is technically sound (as far as it could be evaluated), and that the results are interesting and worthy of publication. In a first round of reviews various clarifications of the manuscript were suggested by the reviewers. The new version was substantially changed by the authors in response, to the extent that it now is a quite different but much clearer paper with a clear message palatable for the general reader. The writing is now to the point, the paper's focus becomes clear in the Introduction, Methods & Results are much less technical, the Figures illustrative, and the descriptions and interpretations in the Discussion are easy to follow. In general any reader may of course question the choice and realism of the scenarios and underlying assumptions chosen by the authors for simplicity and clarity, for instance no heritability of body size and no cost of reproduction (other than mortality). But this is always the case in modeling work, and the authors acknowledge and in fact suggest concrete extensions and expansions of their approach in the Discussion. References Coulson T., Felmy A., Potter T., Passoni G., Montgomery R.A., Gaillard J.-M., Hudson P.J., Travis J., Bassar R.D., Tuljapurkar S., Marshall D.J., Clegg S.M. (2022) Density-dependent environments can select for extremes of body size. bioRxiv, 2022.02.17.480952, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.17.480952 | Density dependent environments can select for extremes of body size | Tim Coulson, Anja Felmy, Tomos Potter, Gioele Passoni, Robert A Montgomery, Jean-Michel Gaillard, Peter J Hudson, Joseph Travis, Ronald D Bassar, Shripad D Tuljapurkar, Dustin Marshall, Sonya M Clegg | <p>Body size variation is an enigma. We do not understand why species achieve the sizes they do, and this means we also do not understand the circumstances under which gigantism or dwarfism is selected. We develop size-structured integral projecti... |  | Evolutionary Dynamics, Evolutionary Ecology, Evolutionary Theory, Life History | Wolf Blanckenhorn | 2022-02-21 07:59:04 | View | |
15 Sep 2022

Bimodal breeding phenology in the Parsley Frog Pelodytes punctatus as a bet-hedging strategy in an unpredictable environment despite strong priority effectsHelene Jourdan-Pineau, Pierre-Andre Crochet, Patrice David https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.24.481784Spreading the risk of reproductive failure when the environment is unpredictable and ephemeralRecommended by Gabriele Sorci based on reviews by Thomas Haaland and Zoltan RadaiMany species breed in environments that are unpredictable, for instance in terms of the availability of resources needed to raise the offspring. Organisms might respond to such spatial and temporal unpredictability by adopting plastic responses to adjust their reproductive investment according to perceived cues of environmental quality. Some species such as the amphibians might also face the problem of ephemeral habitats, when the ponds where they breed have a chance of drying up before metamorphosis has occurred. In this case, maximizing long-term fitness might involve a strategy of spreading the risk, even though the reproductive success of a single reproductive bout might be lower. Understanding how animals (and plants) get adapted to stochastic environments is particularly crucial in the current context of rapid environmental changes. In this article, Jourdan-Pineau et al. report the results of field surveys of the Parsley Frog (Pelodytes punctatus) in Southern France. This frog has peculiar breeding phenology with females breeding in autumn and spring. The authors provide quite an extensive amount of information on the reproductive success of eggs laid in each season and the possible ecological factors accounting for differences between seasons. Although the presence of interspecific competitors and predators does not seem to account for pond-specific reproductive success, the survival of tadpoles hatching from eggs laid in spring is severely impaired when tadpoles from the autumn cohort have managed to survive. This intraspecific competition takes the form of a “priority” effect where tadpoles from the autumn cohort outcompete the smaller larvae from the spring cohort. Given this strong priority effect, one might tentatively predict that females laying in spring should avoid ponds with tadpoles from the autumn cohort. Surprisingly, however, the authors did not find any evidence for such avoidance, which might indicate strong constraints on the availability of ponds where females might possibly lay. Assuming that each female can indeed lay both in autumn and spring, how is this bimodal phenology maintained? Would not be worthier to allocate all the eggs to the autumn (or the spring) laying season? Eggs laid in autumn and spring have to face different environmental hazards, reducing their hatching success and the probability to produce metamorphs (for instance, tadpoles hatching from eggs laid in autumn have to overwinter which might be a particularly risky phase). Jourdan-Pineau and coworkers addressed this question by adapting a bet-hedging model that was initially developed to investigate the strategy of allocation into seed dormancy of annual plants (Cohen 1966) to the case of the bimodal phenology of the Parsley Frog. By feeding the model with the parameter values obtained from the field surveys, they found that the two breeding strategies (laying in autumn and in spring) can coexist as long as the probability of breeding success in the autumn cohort is between 20% and 80% (the range of values allowing the coexistence of a bimodal phenology shrinking a little bit when considering that frogs can reproduce 5 times during their lifespan instead of three times). This paper provides a very nice illustration of the importance of combining approaches (here field monitoring to gather data that can be used to feed models) to understand the evolution of peculiar breeding strategies. Although future work should attempt to gather individual-based data (in addition to population data), this work shows that spreading the risk can be an adaptive strategy in environments characterized by strong stochastic variation. References Cohen D (1966) Optimizing reproduction in a randomly varying environment. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 12, 119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-5193(66)90188-3 Jourdan-Pineau H., Crochet P.-A., David P. (2022) Bimodal breeding phenology in the Parsley Frog Pelodytes punctatus as a bet-hedging strategy in an unpredictable environment despite strong priority effects. bioRxiv, 2022.02.24.481784, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.24.481784 | Bimodal breeding phenology in the Parsley Frog Pelodytes punctatus as a bet-hedging strategy in an unpredictable environment despite strong priority effects | Helene Jourdan-Pineau, Pierre-Andre Crochet, Patrice David | <p style="text-align: justify;">When environmental conditions are unpredictable, expressing alternative phenotypes spreads the risk of failure, a mixed strategy called bet-hedging. In the southern part of its range, the Parsley Frog <em>Pelodytes ... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Ecology, Life History | Gabriele Sorci | 2022-02-28 11:53:00 | View | |
22 Feb 2023
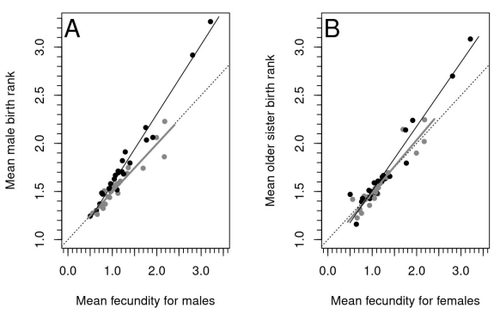
Increased birth rank of homosexual males: disentangling the older brother effect and sexual antagonism hypothesisMichel Raymond, Daniel Turek, Valerie Durand, Sarah Nila, Bambang Suryobroto, Julien Vadez, Julien Barthes, Menelaos Apostolou, Pierre-André Crochet https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.22.481477Evolutionary or proximal explanations for human male homosexual mate preference?Recommended by Jacqui A. Shykoff based on reviews by Ray Blanchard and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Ray Blanchard and 1 anonymous reviewer
Natural populations do not consist of only perfectly adapted individuals. If they did, of course, there would be no fodder for evolution by natural selection. And natural selection is operating all the time, winnowing out less well adapted phenotypes through differential reproduction and survival. Demonstrations of natural selection modifying characters-state distributions to bring phenotypes closer to their optima abound in the evolution literature, with examples of short- and long-term changes in phenotype and allele frequencies. However, evolutionary biologists know that populations cannot reach their adaptive peaks. Natural selection is tracking a moving target, always with some generations of lag time. The adaptive landscape is multidimensional, so the optimal combination of multiple character states may be impossible because of constraints and trade-offs. Natural selection does not operate alone or in isolation – new mutations and migrants that were selected under other conditions will inject locally non-adaptive genetic variation and genetic drift can change allele frequencies in random directions. We understand these processes that generate and maintain less advantageous variants on a continuous gradient from an optimal phenotype in a fitness landscape. More puzzling are heritable polymorphisms with distinct morphologies, physiologies or behaviours maintained in populations despite their measurably lower reproductive success. But a complete model of evolution must also be able to accommodate these Darwinian paradoxes. Raymond et al. (2023) investigate one such Darwinian paradox: In humans, male homosexual mate preference is heritable and is associated with a large reduction in offspring production but nonetheless occurs at relatively high frequencies in most human populations. Furthermore, multiple studies have found that homosexual men come from families that are, on average, larger than those of heterosexual men and that homosexual men have, on average, higher birth rank than do heterosexual men, i.e., having more older siblings and, particularly, more older brothers. Two types of mechanisms consistent with these observations have been proposed: 1) An evolutionary mechanism of sex-antagonistic pleiotropy, whereby highly fecund mothers are more likely to produce homosexual sons, and 2) A mechanistic explanation whereby successive male pregnancies alter the uterine environment by increasing the probability of an immune reaction by the mother to her male fetus, altering development of sexually dimorphic brain structures relevant to sexual orientation. In this article, the authors explore these two mechanisms of sex-antagonistic effects (AE) and fraternal birth order effects (FBOE) and test how well they account for patterns of male homosexuality in population and family data. Clearly, these two effects are somewhat confounded because high birth ranks can only occur in large families. If, indeed, the probability of male homosexuality increases with increasing numbers of (maternal) older brothers, homosexual males will be more common in larger families. Similarly, if high female fecundity leads to a higher probability of male homosexuality via sex-antagonistic effects, homosexual males will, on average, have more older brothers. To disentangle the actions of these two effects the authors modelled the relationship between birth rank and population fecundity and investigated whether AE or FBOE modified this relationship for homosexual men. Simulation results were compared with aggregated population data from 13 countries. Family data on individuals’ sexual preference, birth rank and number of male and female siblings from France, Greece and Indonesia were analysed with generalised linear models and Bayesian approaches to test for a signal of AE or FBOE. These analyses revealed a significant older-brother effect (FBOE) explaining patterns of occurrence of homosexuality in population and family data but no significant independent sex-antagonistic effect (AE). Thus larger family sizes of homosexual men appear due to the older-brother effect, with individuals of high birth rank coming necessarily from large sibships. The simulation approach also revealed that modelling a fraternal birth order effect (FBOE), such that individuals with more older brothers are more likely to be homosexual, generates an artefactual older sister effect simply because homosexual men are overrepresented at higher birth ranks. Older-sister effects reported in the literature may, therefore, be statistical artefacts of an underlying older-brother effect. This paper is interesting for a number of reasons. It does an excellent job of explaining, identifying and dealing with estimation biases and testing for artefactual relationships generated by collinearity. It applies state-of-the art analytical/statistical tools. It breaks down two colinear effects and shows that only one really explains phenotypic variation. This is a great example of how to disentangle correlated variables that may or may not both contribute to trait variation. But most intriguingly, we are left without evidence for an evolutionary mechanism that compensates the large fitness cost associated with male homosexuality in humans. How can we explain high heritability maintained in the face of strong directional selection that should erode heritable genetic variation? The usual suspects include cryptic compensatory mechanisms yet to be discovered or flawed estimates of selection or heritability. For example, data on heritability of male homosexual mate preference in humans come from twin studies and twins share birth rank as well as alleles. Thus it is possible that heritability is over-estimated, including the environmental component associated with birth rank. If, as the authors demonstrate here, birth rank is the strongest predictor of male homosexual mate preference, selection may be acting on a non-heritable plastic component of phenotypic variation. This could explain why heritable variation is not exhausted by selection, rendering the paradox less paradoxical, but fails to provide an adaptive explanation for the maintenance of male homosexual mate preference. References Raymond M., Turek D., Durand V., Nila S., Suryobroto B., Vadez J., Barthes J., Apostolou M. and Crochet P.-A. (2023) Increased birth rank of homosexual males: disentangling the older brother effect and sexual antagonism hypothesis. bioRxiv, 2022.02.22.481477, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.22.481477 | Increased birth rank of homosexual males: disentangling the older brother effect and sexual antagonism hypothesis | Michel Raymond, Daniel Turek, Valerie Durand, Sarah Nila, Bambang Suryobroto, Julien Vadez, Julien Barthes, Menelaos Apostolou, Pierre-André Crochet | <p style="text-align: justify;">Male homosexual orientation remains a Darwinian paradox, as there is no consensus on its evolutionary (ultimate) determinants. One intriguing feature of homosexual men is their higher male birth rank compared to het... |  | Life History, Other, Phenotypic Plasticity, Reproduction and Sex | Jacqui A. Shykoff | 2022-03-03 11:28:44 | View | |
05 Oct 2022
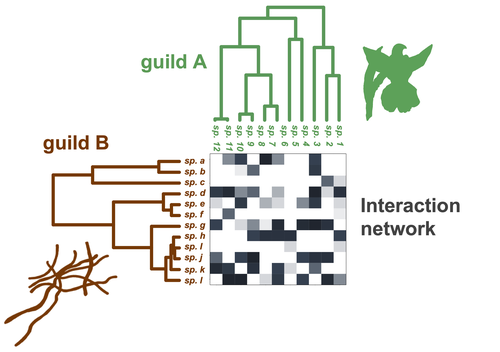
Do closely related species interact with similar partners? Testing for phylogenetic signal in bipartite interaction networksBenoît Perez-Lamarque, Odile Maliet, Benoît Pichon, Marc-André Selosse, Florent Martos, Hélène Morlon https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.30.458192Testing for phylogenetic signal in species interaction networksRecommended by Alejandro Gonzalez Voyer based on reviews by Joaquin Calatayud and Thomas GuillermeSpecies are immersed within communities in which they interact mutualistically, as in pollination or seed dispersal, or nonreciprocally, such as in predation or parasitism, with other species and these interactions play a paramount role in shaping biodiversity (Bascompte and Jordano 2013). Researchers have become increasingly interested in the processes that shape these interactions and how these influence community structure and responses to disturbances. Species interactions are often described using bipartite interaction networks and one important question is how the evolutionary history of the species involved influences the network, including whether there is phylogenetic signal in interactions, in other words whether closely related species interact with other closely related species (Bascompte and Jordano 2013, Perez-Lamarque et al. 2022). To address this question different approaches, correlative and model-based, have been developed to test for phylogenetic signal in interactions, although comparative analyses of the performance of these different metrics are lacking. In their article Perez-Lamarque et al. (2022) set out to test the statistical performance of two widely-used methods, Mantel tests and Phylogenetic Bipartite Linear Models (PBLM; Ives and Godfray 2006) using simulations. Phylogenetic signal is measured as the degree to which distance to the nearest common ancestor predicts the observed similarity in trait values among species. In species interaction networks, the data are actually the between-species dissimilarity among interacting species (Perez-Lamarque et al. 2022), and typical approaches to test for phylogenetic signal cannot be used. However, the Mantel test provides a useful means of analyzing the correlation between two distance matrices, the between-species phylogenetic distance and the between-species dissimilarity in interactions. The PBLM approach, on the other hand, assumes that interactions between species are influenced by unobserved traits that evolve along the phylogenies following a given phenotypic evolution model and the parameters of this model are interpreted in terms of phylogenetic signal (Ives and Godfray 2006). Perez-Lamarque et al (2022) found that the model-based PBLM approach has a high type-I error rate, in other words it often detected phylogenetic signal when there was none. The simple Mantel test was found to present a low type-I error rate and moderate statistical power. However, it tended to overestimate the degree to which species interact with dissimilar partners. In addition to the aforementioned analyses, the authors also tested whether the simple Mantel test was able to detect phylogenetic signal in interactions among species within a given clade in the phylogeny, as phylogenetic signal in species interactions may be localized within specific clades. The article concludes with general guidelines for users wishing to test phylogenetic signal in their interaction networks and illustrates them with an example of an orchid-mycorrhizal fungus network from the oceanic island of La Réunion (Martos et al 2012). This broadly accessible article provides a valuable analysis of the performance of tests of phylogenetic signal in interaction networks enabling users to make informed choices of the analytical methods they wish to employ, and provide useful and detailed guidelines. Therefore, the work should be of broad interest to researchers studying species interactions. References Bascompte J, Jordano P (2013) Mutualistic Networks. Princeton University Press. https://doi.org/10.1515/9781400848720 Ives AR, Godfray HCJ (2006) Phylogenetic Analysis of Trophic Associations. The American Naturalist, 168, E1–E14. https://doi.org/10.1086/505157 Martos F, Munoz F, Pailler T, Kottke I, Gonneau C, Selosse M-A (2012) The role of epiphytism in architecture and evolutionary constraint within mycorrhizal networks of tropical orchids. Molecular Ecology, 21, 5098–5109. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05692.x Perez-Lamarque B, Maliet O, Pichon B, Selosse M-A, Martos F, Morlon H (2022) Do closely related species interact with similar partners? Testing for phylogenetic signal in bipartite interaction networks. bioRxiv, 2021.08.30.458192, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.30.458192 | Do closely related species interact with similar partners? Testing for phylogenetic signal in bipartite interaction networks | Benoît Perez-Lamarque, Odile Maliet, Benoît Pichon, Marc-André Selosse, Florent Martos, Hélène Morlon | <p style="text-align: justify;">Whether interactions between species are conserved on evolutionary time-scales has spurred the development of both correlative and process-based approaches for testing phylogenetic signal in interspecific interactio... |  | Evolutionary Ecology, Species interactions | Alejandro Gonzalez Voyer | 2022-03-10 13:48:15 | View | |
20 Dec 2022
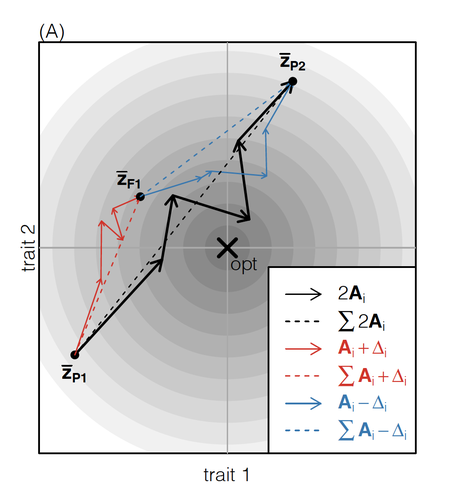
How does the mode of evolutionary divergence affect reproductive isolation?Bianca De Sanctis, Hilde Schneemann, John J. Welch https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.08.483443A general model of fitness effects following hybridisationRecommended by Matthew Hartfield based on reviews by Luis-Miguel Chevin and Juan LiStudying the effects of speciation, hybridisation, and evolutionary outcomes following reproduction from divergent populations is a major research area in evolutionary genetics [1]. There are two phenomena that have been the focus of contemporary research. First, a classic concept is the formation of ‘Bateson-Dobzhansky-Muller’ incompatibilities (BDMi) [2–4] that negatively affect hybrid fitness. Here, two diverging populations accumulate mutations over time that are unique to that subpopulation. If they subsequently meet, then these mutations might negatively interact, leading to a loss in fitness or even a complete lack of reproduction. BDMi formation can be complex, involving multiple genes and the fitness changes can depend on the direction of introgression [5]. Second, such secondary contact can instead lead to heterosis, where offspring are fitter than their parental progenitors [6]. Understanding which outcomes are likely to arise require one to know the potential fitness effects of mutations underlying reproductive isolation, to determine whether they are likely to reduce or enhance fitness when hybrids are formed. This is far from an easy task, as it requires one to track mutations at several loci, along with their effects, across a fitness landscape. The work of De Sanctis et al. [7] neatly fills in this knowledge gap, by creating a general mathematical framework for describing the consequences of a cross from two divergent populations. The derivations are based on Fisher’s Geometric Model, which is widely used to quantify selection acting on a general fitness landscape that is affected by several biological traits [8,9], and has previously been used in theoretical studies of hybridisation [10–12]. By doing so, they are able to decompose how divergence at multiple loci affects offspring fitness through both additive and dominance effects. A key result arising from their analyses is demonstrating how offspring fitness can be captured by two main functions. The first one is the ‘net effect of evolutionary change’ that, broadly defined, measures how phenotypically divergent two populations are. The second is the ‘total amount of evolutionary change’, which reflects how many mutations contribute to divergence and the effect sizes captured by each of them. The authors illustrate these measurements using simulations covering different scenarios, demonstrating how different parental states can lead to similar fitness outcomes. They also propose experimental methods to measure the underlying mutational effects. This study neatly demonstrates how complex genetic phenomena underlying hybridisation can be captured using fairly simple mathematical formulae. This powerful approach will thus open the door for future research to investigate hybridisation in more detail, whether it is by expanding on these theoretical models or using the elegant outcomes to quantify fitness effects in experiments.
References 1. Coyne JA, Orr HA. Speciation. Sunderland, Mass: Sinauer Associates; 2004. | How does the mode of evolutionary divergence affect reproductive isolation? | Bianca De Sanctis, Hilde Schneemann, John J. Welch | <p>When divergent populations interbreed, the outcome will be affected by the genomic and phenotypic differences that they have accumulated. In this way, the mode of evolutionary divergence between populations may have predictable consequences for... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Theory, Hybridization / Introgression, Population Genetics / Genomics, Speciation | Matthew Hartfield | 2022-03-30 14:55:46 | View | |
31 Oct 2022
Genotypic sex shapes maternal care in the African Pygmy mouse, Mus minutoidesLouise D Heitzmann, Marie Challe, Julie Perez, Laia Castell, Evelyne Galibert, Agnes Martin, Emmanuel Valjent, Frederic Veyrunes https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.05.487174Effect of sex chromosomes on mammalian behaviour: a case study in pygmy miceRecommended by Gabriel Marais and Trine Bilde based on reviews by Marion Anne-Lise Picard, Caroline Hu and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Marion Anne-Lise Picard, Caroline Hu and 1 anonymous reviewer
In mammals, it is well documented that sexual dimorphism and in particular sex differences in behaviour are fine-tuned by gonadal hormonal profiles. For example, in lemurs, where female social dominance is common, the level of testosterone in females is unusually high compared to that of other primate females (Petty and Drea 2015). Recent studies however suggest that gonadal hormones might not be the only biological factor involved in establishing sexual dimorphism, sex chromosomes might also play a role. The four core genotype (FCG) model and other similar systems allowing to decouple phenotypic and genotypic sex in mice have provided very convincing evidence of such a role (Gatewood et al. 2006; Arnold and Chen 2009; Arnold 2020a, 2020b). This however is a new field of research and the role of sex chromosomes in establishing sexually dimorphic behaviours has not been studied very much yet. Moreover, the FCG model has some limits. Sry, the male determinant gene on the mammalian Y chromosome might be involved in some sex differences in neuroanatomy, but Sry is always associated with maleness in the FCG model, and this potential role of Sry cannot be studied using this system. Heitzmann et al. have used a natural system to approach these questions. They worked on the African Pygmy mouse, Mus minutoides, in which a modified X chromosome called X* can feminize X*Y individuals, which offers a great opportunity for elegant experiments on the effects of sex chromosomes versus hormones on behaviour. They focused on maternal care and compared pup retrieval, nest quality, and mother-pup interactions in XX, X*X and X*Y females. They found that X*Y females are significantly better at retrieving pups than other females. They are also much more aggressive towards the fathers than other females, preventing paternal care. They build nests of poorer quality but have similar interactions with pups compared to other females. Importantly, no significant differences were found between XX and X*X females for these traits, which points to an effect of the Y chromosome in explaining the differences between X*Y and other females (XX, X*X). Also, another work from the same group showed similar gonadal hormone levels in all the females (Veyrunes et al. 2022). Heitzmann et al. made a number of predictions based on what is known about the neuroanatomy of rodents which might explain such behaviours. Using cytology, they looked for differences in neuron numbers in the hypothalamus involved in the oxytocin, vasopressin and dopaminergic pathways in XX, X*X and X*Y females, but could not find any significant effects. However, this part of their work relied on very small sample sizes and they used virgin females instead of mothers for ethical reasons, which greatly limited the analysis. Interestingly, X*Y females have a higher reproductive performance than XX and X*X ones, which compensate for the cost of producing unviable YY embryos and certainly contribute to maintaining a high frequency of X* in many African pygmy mice populations (Saunders et al. 2014, 2022). X*Y females are probably solitary mothers contrary to other females, and Heitzmann et al. have uncovered a divergent female strategy in this species. Their work points out the role of sex chromosomes in establishing sex differences in behaviours. References Arnold AP (2020a) Sexual differentiation of brain and other tissues: Five questions for the next 50 years. Hormones and Behavior, 120, 104691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2020.104691 Arnold AP (2020b) Four Core Genotypes and XY* mouse models: Update on impact on SABV research. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 119, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.09.021 Arnold AP, Chen X (2009) What does the “four core genotypes” mouse model tell us about sex differences in the brain and other tissues? Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, 30, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2008.11.001 Gatewood JD, Wills A, Shetty S, Xu J, Arnold AP, Burgoyne PS, Rissman EF (2006) Sex Chromosome Complement and Gonadal Sex Influence Aggressive and Parental Behaviors in Mice. Journal of Neuroscience, 26, 2335–2342. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3743-05.2006 Heitzmann LD, Challe M, Perez J, Castell L, Galibert E, Martin A, Valjent E, Veyrunes F (2022) Genotypic sex shapes maternal care in the African Pygmy mouse, Mus minutoides. bioRxiv, 2022.04.05.487174, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.05.487174 Petty JMA, Drea CM (2015) Female rule in lemurs is ancestral and hormonally mediated. Scientific Reports, 5, 9631. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09631 Saunders PA, Perez J, Rahmoun M, Ronce O, Crochet P-A, Veyrunes F (2014) Xy Females Do Better Than the Xx in the African Pygmy Mouse, Mus Minutoides. Evolution, 68, 2119–2127. https://doi.org/10.1111/evo.12387 Saunders PA, Perez J, Ronce O, Veyrunes F (2022) Multiple sex chromosome drivers in a mammal with three sex chromosomes. Current Biology, 32, 2001-2010.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2022.03.029 Veyrunes F, Perez J, Heitzmann L, Saunders PA, Givalois L (2022) Separating the effects of sex hormones and sex chromosomes on behavior in the African pygmy mouse Mus minutoides, a species with XY female sex reversal. bioRxiv, 2022.07.11.499546. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.11.499546 | Genotypic sex shapes maternal care in the African Pygmy mouse, Mus minutoides | Louise D Heitzmann, Marie Challe, Julie Perez, Laia Castell, Evelyne Galibert, Agnes Martin, Emmanuel Valjent, Frederic Veyrunes | <p>Sexually dimorphic behaviours, such as parental care, have long been thought to be driven mostly, if not exclusively, by gonadal hormones. In the past two decades, a few studies have challenged this view, highlighting the direct influence of th... |  | Behavior & Social Evolution, Evolutionary Ecology, Reproduction and Sex | Gabriel Marais | 2022-04-08 20:09:58 | View | |
02 Sep 2022

Introgression between highly divergent sea squirt genomes: an adaptive breakthrough?Christelle Fraïsse, Alan Le Moan, Camille Roux, Guillaume Dubois, Claire Daguin-Thiébaut, Pierre-Alexandre Gagnaire, Frédérique Viard, Nicolas Bierne https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.22.485319A match made in the Anthropocene: human-mediated adaptive introgression across a speciation continuumRecommended by Fernando Racimo based on reviews by Michael Westbury, Andrew Foote and Erin CalfeeThe long-distance transport and introduction of new species by humans is increasingly leading divergent lineages to interact, and sometimes interbreed, even after thousands or millions of years of separation. It is thus of prime importance to understand the consequences of these contemporary admixture events on the evolutionary fitness of interacting organisms, and their ecological implications. Ciona robusta and Ciona intestinalis are two species of sea squirts that diverged between 1.5 and 2 million years ago and recently came into contact again. This occurred through human-mediated introduction of C. robusta (native to the Northwest Pacific) into the range of C. intestinalis (the English channeled Northeast Atlantic). In this study, Fraïsse et al. (2022) follow up on earlier work by Le Moan et al. (2021), who had identified a long genomic hotspot of introgression of C. robusta ancestry segments in chromosome 5 of C. intestinalis. The hotspot bears suggestive evidence of positive selection and the authors aimed to investigate this further using fully phased whole-genome sequences. The authors narrow down on the exact boundaries of the introgressed region, and make a compelling case that it has been the likely target of positive selection after introgression, using various complementary approaches based on patterns of population differentiation, haplotype structure and local levels of diversity in the region. Using extensive demographic modeling, they also show that the introgression event was likely recent (approximately 75 years ago), and distinct from other tracts in the C. intestinalis genome that are likely a product of more ancient episodes of interbreeding in the past 30,000 years. Narrowing down on the potential drivers of selection, the authors show that candidate SNPs in the region overlap with the cytochrome family 2 subfamily U gene - involved in the detoxification of exogenous compounds - potentially reflecting adaptation to chemicals encountered in the sea squirt's environment. There also appears to be copy number variation at the candidate SNPs, which provides clues into the adaptation mechanism in the region. All reviewers agreed that the work carried out by the authors is elegant and the results are robustly supported and well presented. In a round of reviews, various clarifications of the manuscript were suggested by the reviewers, including on the quality of the newly generated sequencing data, and some suggestions for qualifications on the conclusions reached by the authors as well as changes in the figures to increase their clarity. The authors addressed the different concerns of the reviewers, and the new version is much improved. This study into human-mediated introgression and its consequences for adaptation is, in my view, both well thought-out and executed. I therefore provide an enthusiastic recommendation of this manuscript. References Fraïsse C, Le Moan A, Roux C, Dubois G, Daguin-Thiébaut C, Gagnaire P-A, Viard F and Bierne N (2022) Introgression between highly divergent sea squirt genomes: an adaptive breakthrough? bioRxiv, 2022.03.22.485319, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.22.485319 Le Moan A, Roby C, Fraïsse C, Daguin-Thiébaut C, Bierne N, Viard F (2021) An introgression breakthrough left by an anthropogenic contact between two ascidians. Molecular Ecology, 30, 6718–6732. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.16189 | Introgression between highly divergent sea squirt genomes: an adaptive breakthrough? | Christelle Fraïsse, Alan Le Moan, Camille Roux, Guillaume Dubois, Claire Daguin-Thiébaut, Pierre-Alexandre Gagnaire, Frédérique Viard, Nicolas Bierne | <p style="text-align: justify;">Human-mediated introductions are reshuffling species distribution on a global scale. Consequently, an increasing number of allopatric taxa are now brought into contact, promoting introgressive hybridization between ... |  | Adaptation, Hybridization / Introgression, Population Genetics / Genomics | Fernando Racimo | 2022-04-14 15:30:42 | View | |
28 Feb 2023
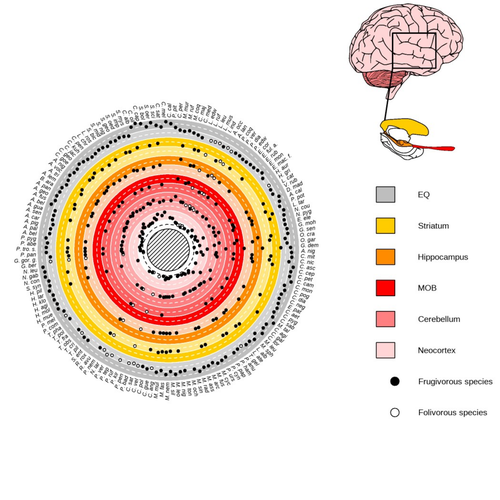
Primate sympatry shapes the evolution of their brain architectureBenjamin Robira, Benoit Perez-Lamarque https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.09.490912Macroevolutionary drivers of brain evolution in primatesRecommended by Fabien Condamine based on reviews by Paula Gonzalez, Orlin Todorov and 3 anonymous reviewersStudying the evolution of animal cognition is challenging because many environmental and species-related factors can be intertwined, which is further complicated when looking at deep-time evolution. Previous knowledge has emphasized the role of intraspecific interactions in affecting the socio-ecological environment shaping cognition. However, much less is known about such an effect at the interspecific level. Yet, the coexistence of different species in the same geographic area at a given time (sympatry) can impact the evolutionary history of species through character displacement due to biotic interactions. Trait evolution has been observed and tested with morphological external traits but more rarely with brain evolution. Compared to most species’ traits, brain evolution is even more delicate to assess since specific brain regions can be involved in different functions, may they be individual-based and social-based information processing. In a very original and thoroughly executed study, Robira & Perez-Lamarque (2023) addressed the question: How does the co-occurrence of congeneric species shape brain evolution and influence species diversification? By considering brain size as a proxy for cognition, they evaluated whether species sympatry impacted the evolution of cognition in frugivorous primates. Fruit resources are hard to find, not continuous through time, heterogeneously distributed across space, but can be predictable. Hence, cognition considerably shapes the foraging strategy and competition for food access can be fierce. Over long timescales, it remains unclear whether brain size and the pace of species diversification are linked in the context of sympatry, and if so how. Recent studies have found that larger brain sizes can be associated with higher diversification rates in birds (Sayol et al. 2019). Similarly, Robira & Perez-Lamarque (2023) thus wondered if the evolution of brain size in primates impacted their dynamic of species diversification, which has been suggested (Melchionna et al. 2020) but not tested. Prior to anything, Robira & Perez-Lamarque (2023) had to retrace the evolutionary history of sympatry between frugivorous primate lineages through time using the primate tree of life, species’ extant distribution, and process-based models to estimate ancestral range evolution. To infer the effect of species sympatry on the evolution of cognition in frugivorous primates, the authors evaluated the support for phylogenetic models of brain size evolution accounting or not for species sympatry and investigated the directionality of the selection induced by sympatry on brain size evolution. Finally, to better understand the impact of cognition and interactions between primates on their evolutionary success, they tested for correlations between brain size or species’ sympatry and species diversification. Robira & Perez-Lamarque (2023) found that the evolution of the whole brain or brain regions used in immediate information processing was best fitted with models not considering sympatry. By contrast, models considering species sympatry best predicted the evolution of brain regions related to long-term memory of interactions with the socio-ecological environment, with a decrease in their size along with stronger sympatry. Specifically, they found that sympatry was associated with a decrease in the relative size of the hippocampus and striatum, but had no significant effect on the neocortex, cerebellum, or overall brain size. The hippocampus is a brain region that plays a crucial role in processing and memorizing spatiotemporal information, which is relevant for frugivorous primates in their foraging behavior. The study suggests that competition between sympatric species for limited food resources may lead to a more complex and unpredictable food distribution, which may in turn render cognitive foraging not advantageous and result in a selection for smaller brain regions involved in foraging. Niche partitioning and dietary specialization in sympatry may also impact cognitive abilities, with more specialized diets requiring lower cognitive abilities and smaller brain region sizes. On the other hand, the absence of an effect of sympatry on brain regions involved in immediate sensory information processing, such as the cerebellum and neocortex, suggests that foragers do not exploit cues left out by sympatric heterospecific species, or they may discard environmental cues in favor of social cues. This is a remarkable study that highlights the importance of considering the impact of ecological factors, such as sympatry, on the evolution of specific brain regions involved in cognitive processes, and the potential trade-offs in brain region size due to niche partitioning and dietary specialization in sympatry. Further research is needed to explore the mechanisms behind these effects and to test for the possible role of social cues in the evolution of brain regions. This study provides insights into the selective pressures that shape brain evolution in primates. References Melchionna M, Mondanaro A, Serio C, Castiglione S, Di Febbraro M, Rook L, Diniz-Filho JAF, Manzi G, Profico A, Sansalone G, Raia P (2020) Macroevolutionary trends of brain mass in Primates. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 129, 14–25. https://doi.org/10.1093/biolinnean/blz161 Robira B, Perez-Lamarque B (2023) Primate sympatry shapes the evolution of their brain architecture. bioRxiv, 2022.05.09.490912, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.09.490912 Sayol F, Lapiedra O, Ducatez S, Sol D (2019) Larger brains spur species diversification in birds. Evolution, 73, 2085–2093. https://doi.org/10.1111/evo.13811 | Primate sympatry shapes the evolution of their brain architecture | Benjamin Robira, Benoit Perez-Lamarque | <p style="text-align: justify;">The main hypotheses on the evolution of animal cognition emphasise the role of conspecifics in affecting the socio-ecological environment shaping cognition. Yet, space is often simultaneously occupied by multiple sp... |  | Behavior & Social Evolution, Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Evolutionary Ecology, Macroevolution, Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics, Phylogeography & Biogeography | Fabien Condamine | 2022-05-10 13:43:02 | View | |
11 Apr 2023
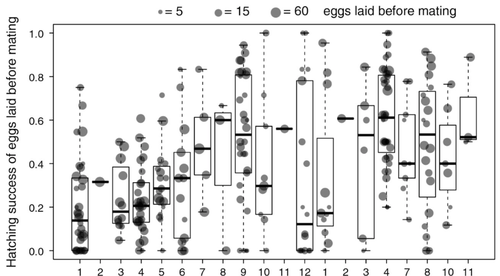
Facultative parthenogenesis: a transient state in transitions between sex and obligate asexuality in stick insects?Chloé Larose, Guillaume Lavanchy, Susana Freitas, Darren J. Parker, Tanja Schwander https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.25.485836Facultative parthenogenesis and transitions from sexual to asexual reproductionRecommended by Trine Bilde based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers
Despite a vast array of ways in which organisms can reproduce (Bell, 1982), most animals engage in sexual reproduction (Otto & Lenormand, 2002). A fascinating alternative to sex is parthenogenesis, where offspring are produced asexually from a gamete, typically the egg, without receiving genetic material from another gamete (Simon, Delmotte, Rispe, & Crease, 2003). One of the long-standing questions in the field is why parthenogenesis is not more widespread, given the costs associated with sex (Otto & Lenormand, 2002). Natural populations of most species appear to be reproducing either sexually or parthenogenetically, even if a species can employ both reproductive modes (Larose et al 2023). Larose et al (2023) highlight the conundrum in this pattern, as organisms that are capable of employing parthenogenesis facultatively would be able to gain the benefits of both modes of reproduction. Why then, is facultative parthenogenesis not more common? Larose et al (2023) propose that constraints on being efficient in both sexual and asexual reproduction could cause a trade-off between reproductive modes that favours an obligate strategy of either sex or no sex. This would provide an explanation for why facultative parthenogenesis is rare. Timema stick insects provide an excellent system to investigate reproductive strategies, as some species have parthenogenetic females, while other species are sexual, and they show repeated transitions from sexual reproduction to obligate parthenogenesis (Schwander & Crespi, 2009). The authors performed comprehensive and complementary studies in a recently discovered species T. douglasi, in which populations show both modes of reproduction, with some populations consisting only of females and others showing equal proportions of males and females. The sex ratio varied significantly, with the proportion of females ranging between 43-100% across 29 populations. These populations form a monophyletic clade with clustering into three genetic lineages and only a few cases of admixture. Females from all populations were capable of producing unfertilized eggs, but the hatching success varied hugely among populations and lineages (3-100%). Parthenogenetically produced offspring were homozygous, showing that parthenogenesis causes a complete loss of heterozygosity in a single generation. After producing eggs as virgins, females were mated to assess the capacity to also reproduce sexually, and fertilization increased the hatching success of eggs in two lineages. In one lineage, in which the hatching success of unfertilized eggs is similar to that of other sexually reproducing Timema species, fertilization reduced egg-hatching success, indicating a trade-off between reproductive modes with parthenogenetic reproduction performing best. Approximately 58% of the offspring produced after mating were fertilized, demonstrating the capacity of females to reproduce parthenogenetically also after mating has occurred, however with huge variation among individuals. This wonderful and meticulously performed study produces strong and complementary evidence for facultative parthenogenesis in T. douglasi populations. The study shows large variation in how reproductive mode is employed, supporting the existence of a trade-off between sexual and parthenogenetic reproduction. This might be an example of an ongoing transition from sexual to asexual reproduction, which indicates that obligate parthenogenesis may derive via transient facultative parthenogenesis. REFERENCES Bell, G. (1982) The Masterpiece of Nature: The Evolution and Genetics of Sexuality. University of California Press. 635 p. Otto, S. P., & Lenormand, T. (2002). Resolving the paradox of sex and recombination. Nature Reviews Genetics, 3(4), 252-261. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg761 Schwander, T., & Crespi, B. J. (2009). Multiple direct transitions from sexual reproduction to apomictic parthenogenesis in Timema stick insects. Evolution, 63(1), 84-103. Simon, J.-C., Delmotte, F., Rispe, C., & Crease, T. (2003). Phylogenetic relationships between parthenogens and their sexual relatives: the possible routes to parthenogenesis in animals. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 79(1), 151-163. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1095-8312.2003.00175.x Larose, C., Lavanchy, G., Freitas, S., Parker, D.J., Schwander, T. (2023) Facultative parthenogenesis: a transient state in transitions between sex and obligate asexuality in stick insects? bioRxiv, 2022.03.25.485836, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.25.485836 | Facultative parthenogenesis: a transient state in transitions between sex and obligate asexuality in stick insects? | Chloé Larose, Guillaume Lavanchy, Susana Freitas, Darren J. Parker, Tanja Schwander | <p>Transitions from obligate sex to obligate parthenogenesis have occurred repeatedly across the tree of life. Whether these transitions occur abruptly or via a transient phase of facultative parthenogenesis is rarely known. We discovered and char... |  | Reproduction and Sex | Trine Bilde | 2022-05-20 10:41:13 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Guillaume Achaz
Juan Arroyo
Trine Bilde
Dustin Brisson
Marianne Elias
Inês Fragata
Matteo Fumagalli
Tatiana Giraud
Frédéric Guillaume
Ruth Hufbauer
Sara Magalhaes
Caroline Nieberding
Michael David Pirie
Tanja Pyhäjärvi
Tanja Schwander
Alejandro Gonzalez Voyer










