Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
14 May 2025
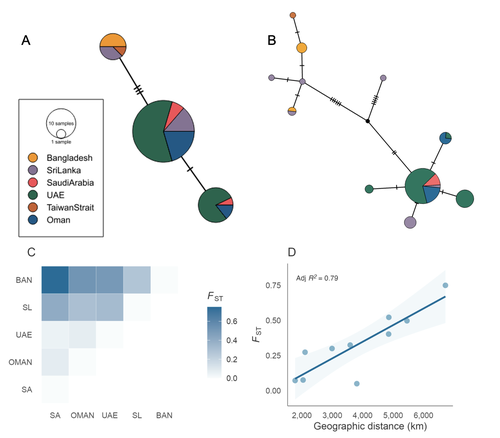
Population structure and genetic diversity of the Critically Endangered bowmouth guitarfish (Rhina ancylostomus) in the Northwest Indian OceanMarja J. Kipperman, Rima W. Jabado, Alifa Bintha Haque, Daniel Fernando, P A D L Anjani, Julia LY Spaet, Emily Humble https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.15.585225The Bowmouth Guitarfish Doesn’t Travel Far: Genomic Evidence for Low Connectivity and Regional Differentiation in Rhina ancylostomusRecommended by Benoit Nabholz based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewersChondrichthyan fishes (sharks, rays, and chimaeras) are among the most endangered taxa on Earth. Most species exhibit life-history traits that make them particularly sensitive to both direct and indirect human impacts, especially fisheries (Jabado et al. 2024). In this context, genomic data can provide crucial insights into population structure and historical and current connectivity among populations, thereby informing conservation strategies. Increasing genomic research would also enhance our understanding of shark, ray, and chimaera diversity, including the identification of cryptic species and or subspecies. In this study, Kipperman et al. (2025) investigate the population structure of the bowmouth guitarfish (Rhina ancylostomus), an endangered species in the understudied family Rhinobatidae. This represents the first analysis of population structure in this species. The authors combine over 3,000 nuclear SNPs, obtained using a restriction enzyme reduction-based DNA sequencing strategy, with mitochondrial data from 70 samples across six populations in the Northwest Indian Ocean. Their results reveal significant population structure driven by isolation-by-distance between eastern and western populations across most of the species' range, from Saudi Arabia to Taiwan. These findings highlight limited connectivity among populations and demonstrate the species' low dispersal capacity. Further analyses of genetic diversity show that populations in eastern Saudi Arabia and Oman have significantly lower genetic diversity than those in the eastern part of the species’ range. The authors hypothesize that this pattern results from a westward colonization of the species from the Indo-Malayan archipelago. The study has a few minor limitations, including unbalanced and incomplete sampling across the species’ range and a lack of detailed description of the SNP sequencing and bioinformatics pipeline, which is based on proprietary protocols. The absence of a reference genome is also a drawback. However, all these limitations are transparently acknowledged and discussed in the manuscript. Moreover, they do not undermine the robust analyses in the manuscript. Kipperman and collaborators’ study provides important insights into the genetic structure of a critically endangered guitarfish species. Well-designed analyses such as this are essential for improving our knowledge of chondrichthyan population structures. References Jabado, R.W., Morata, A.Z.A., Bennett, R.H., Finucci, B., Ellis, J.R., Fowler, S.L., Grant, M.I., Barbosa Martins, A.P., & Sinclair, S.L. (eds.) (2024). The global status of sharks, rays, and chimaeras. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN https://doi.org/10.59216/ssg.gsrsrc.2024 Marja J. Kipperman, Rima W. Jabado, Alifa Bintha Haque, Daniel Fernando, P A D L Anjani, Julia LY Spaet, Emily Humble (2025) Population structure and genetic diversity of the Critically Endangered bowmouth guitarfish (Rhina ancylostomus) in the Northwest Indian Ocean. bioRxiv, ver.2 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evolutionary Biology https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.15.585225 | Population structure and genetic diversity of the Critically Endangered bowmouth guitarfish (*Rhina ancylostomus*) in the Northwest Indian Ocean | Marja J. Kipperman, Rima W. Jabado, Alifa Bintha Haque, Daniel Fernando, P A D L Anjani, Julia LY Spaet, Emily Humble | <p>The bowmouth guitarfish (<em>Rhina ancylostomus</em>) is a unique and relatively understudied species of wedgefish with a distribution spanning the Indo-Pacific Oceans. Due to targeted and bycatch fisheries, this species is experiencing serious... |  | Population Genetics / Genomics | Benoit Nabholz | Anonymous | 2024-04-12 11:38:42 | View |
02 May 2025
Experimental evidence for short term directional selection of epigenetic trait variationBenoit Pujol, Mathieu Latutrie, Pierick Mouginot, Nelia Luviano- Aparicio, Jésaëlle Piquet, Sara Marin, and Stéphane Maury https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15227609Transgenerationally-transmitted epigenetic variation responds to phenotypic selection – results from a novel selection methodologyRecommended by Pim Edelaar based on reviews by Leandro Quadrana and Sophie Brunel Muguet based on reviews by Leandro Quadrana and Sophie Brunel Muguet
The breeder’s equation is a classical equation in evolutionary theory, and basically states that the response of a trait to selection is equal to the strength of selection on this trait multiplied by the heritability of the trait. There can be several reasons why reality does not conform to a narrow interpretation of this equation, but in spite of that, let us actually indulge in a broad interpretation of the equation. Typically, the heritability of a trait is interpreted to refer to the genetic basis of a trait (the additive genetic variance). However, a broad interpretation of the breeder’s equation would be that if selection acts on a trait and that trait is somehow heritable, we should expect to observe an evolutionary change in that trait. In other words, the source and mechanism of inheritance does not matter for the breeder’s equation to have applicability. In this paper, Pujol et al. (2025) follow this rationale for epigenetic variation, and more specifically for differentially methylated regions in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. They used 120 lines which vary across 126 differentially methylated regions of the genome, but are genetically identical, thereby eliminating additive genetic variance from the heritability component of the breeder’s equation. Previous studies have already shown that these differentially methylated regions are associated with different phenotypes, suggesting they somehow functionally affect the development of the plants. Previous studies have also shown that these differentially methylated regions are stably transmitted across generation, i.e., that they are heritable. This predicts that if one selects for different phenotypes, there should be an evolutionary response in the phenotypes, and an associated shift in the differentially methylated regions that are responsible for the phenotypic variation. By and large, this is what Pujol et al. (2025) found. They selected divergently on four different plants traits (biomass, rosette size, flowering time, and height at first fruit), in two different populations, and with two different selection strengths. For most traits they found a phenotypic shift, and this largely corresponded with associated shifts in the differentially methylated regions. The patterns were very congruent between the different selection strengths, and very similar for the two different populations. We can therefore confidently conclude that epigenetic variation has effects on fitness-relevant phenotypic traits, that therefore natural selection can act on this epigenetic variation, and if so that this would cause an evolutionary change in the phenotypes under selection and in the differentially methylated regions causing this phenotypic variation. I.e., the breeder’s equation can indeed by applied to more than just genetically heritable variation, it can also be applied to non-genetically heritable variation. While this seems like a very obvious result, there are still very few studies that show how selection on non-genetic heritable variation results in a between-generation shift in this non-genetic heritable variation. In that sense, this study can function as a case in favour of a broader interpretation of evolution; to refer to a heritable between-generation change in the composition of a population, independent of whether the heredity is genetic or non-genetic. Critics might say that this study has only limited validity, since the epigenetic variation has been artificially increased in the used plant lines, and may not reflect naturally occurring variation. Indeed, more studies on natural selection on epigenetic variation are called for, but these will have the added complication that they need to correct for genetic variation, which is often correlated to epigenetic variation. Here, the authors could exclude genetic variation by working with epigenetically different lines that were genetically identical. The study stands out in yet another respect – it uses a highly unusual and apparently novel selection design (although the authors do not know for sure if their idea is actually novel). Typically, in a selection study only a subset of parents is allowed to reproduce out of the total set of potential parents. If one wants to select for different traits separately, or with different selection strengths, separate selection studies need to be undertaken. Here the authors took a different approach. They let all their parents reproduce (3 offspring per plant), and phenotyped all offspring. They then, virtually, selected for different traits or for different selection strengths in the parents by excluding from their dataset the offspring of parents that are selected not to reproduce – after they had actually already reproduced! It is almost as if selection acts with a time delay, destroying not only the selected parents but also their offspring. This has the benefit that a single dataset is generated (all phenotyped offspring of all parents), and then selection can be exerted as often as one wants, for example for distinct types of selection, or on different (combinations) of traits. While the initial effort to phenotype offspring of all potential parents is large, and exponentially so if multiple generations are selected, the subsequent evaluation of distinct types of selection on any of the phenotyped traits is virtually effortless. For example, the authors applied divergent selection, but could reuse their dataset to apply stabilising selection. This novel selection design may therefore be a very attractive approach for many other researchers. References Benoit Pujol, Mathieu Latutrie, Pierick Mouginot, Nelia Luviano- Aparicio, Jésaëlle Piquet, Sara Marin, and Stéphane Maury (2025) Experimental evidence for short term directional selection of epigenetic trait variation. Zenodo, ver.2 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evolutionary Biology https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15227609 | Experimental evidence for short term directional selection of epigenetic trait variation | Benoit Pujol, Mathieu Latutrie, Pierick Mouginot, Nelia Luviano- Aparicio, Jésaëlle Piquet, Sara Marin, and Stéphane Maury | <p>Evolution by natural selection can occur when organisms harbor genetically inherited phenotypic variation, and phenotypic variants have differential fitness. Stable transgenerational epigenetic variation also exists for fitness-related traits a... | Morphological Evolution, Non Genetic Inheritance | Pim Edelaar | 2024-07-17 16:07:37 | View | ||
10 Apr 2025
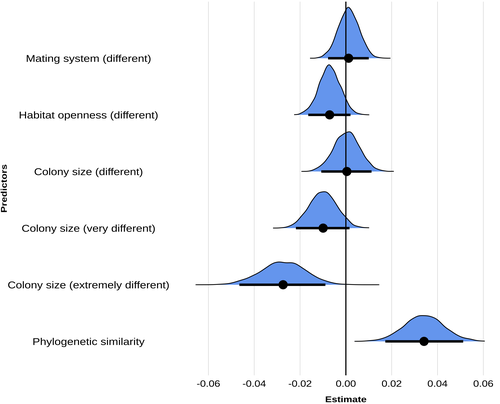
Colony size as the main driver of the evolution of song diversity and composition in weaverbirdsE. Harscouet-Commecy, N. Adenot, A. Thetiot, N. Bresciani, D. Oschadleus, R. Covas, F. Rybak, C. Doutrelant https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/z5bgy_v2Inequality among the lexiconsRecommended by Michael D Greenfield based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersIt has now been over a century since the American linguist Edward Sapir observed that there are no ‘primitive’ languages, stating ‘When it comes to linguistic form, Plato walks with the Macedonian swineherd, Confucius with the head-hunting savage of Assam’ (Sapir 1921, p. 104). Nothing has been found among human groups since that would refute Sapir’s insight. However, in interspecific comparisons among non-human animals, such equality is most definitely not the case, and scientists have asked what might account for some species being blessed with rich and complex communication while others seem to make do with a relatively undeveloped repertoire of signals. Many of the investigations have focused on acoustic communications, as these are more easily identified as signals, measured, and demarcated than substrate vibrations, odors and optical displays. But no consensus has emerged explaining the ‘inequality among the lexicons’. In the article ‘Colony size as the main driver of the evolution of song diversity and composition in weaverbirds’, Erwan Harscouet-Commecy and coauthors aimed to find definitive answers to the issue of interspecific differences in communication complexity. The article considers two aspects of communication complexity, basic diversity – essentially the number of different sounds made by a species – and ‘composition’, a higher level measure centered on acoustically recognizable ‘types’ of sounds. Sexual selection, social complexity, habitat and phylogeny are then examined as potential influences on communication. Weaverbirds, the monophyletic family Ploceidae, including 122 species in 15 genera in sub-Saharan Africa and tropical Asia, was an eminently appropriate choice for the study. The birds have diverse nesting and mating behavior and songs, and many have been investigated intensively. For their analyses, the authors were quite rigorous in evaluating the species’ songs and in assessing the potential influences on song complexity. Unexpectedly, they did not find that heightened sexual selection led to complex songs, but they note that the proxy used for sexual selection – a polygynous as opposed to a monogamous mating system – may be inaccurate. Additionally, the strong pair bonding in monogamy may have actually selected for song complexity. What the authors did find was a very clear influence of social complexity, measured by colony size, and a secondary influence of phylogeny. Questions do remain, such as the specific pathway – common genetic or common cultural heritage – along which phylogeny influences song complexity. Another question one might raise is whether low song complexity in some species reflects reliance on other modalities of communication, e.g. plumage or movement displays. But at present, the article appears as a gold standard for investigating the complexity of communication among animal species. References Sapir, E. 1921. Language: An Introduction to the Study of Speech. New York: Harcourt, Brace. ISBN 978-1-108-06378-4 E. Harscouet-Commecy, N. Adenot, A. Thetiot, N. Bresciani, D. Oschadleus, R. Covas, F. Rybak, C. Doutrelant (2024) Colony size as the main driver of the evolution of song diversity and composition in weaverbirds. OSF, ver.2 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/z5bgy_v2 | Colony size as the main driver of the evolution of song diversity and composition in weaverbirds | E. Harscouet-Commecy, N. Adenot, A. Thetiot, N. Bresciani, D. Oschadleus, R. Covas, F. Rybak, C. Doutrelant | <p>Birdsong is a complex signal shaped by multiple factors and has been explored most<br>widely through the lens of sexual selection, but with mixed results. Here, we focus on<br>the evolution of two song parameters, diversity, which is widely stu... |  | Behavior & Social Evolution, Evolutionary Ecology | Michael D Greenfield | 2024-06-26 13:43:32 | View | |
24 Mar 2025

On the potential for GWAS with phenotypic population means and allele-frequency data (popGWAS)Markus Pfenninger https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.12.598621popGWAS: Data-efficient trait mapping in natural populations for biodiversity researchRecommended by Frédéric Guillaume based on reviews by Petri Kemppainen and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Petri Kemppainen and 1 anonymous reviewer
The study by Pfenninger (2025) addresses the critical need to understand the genomic basis of ecologically important traits to better predict and respond to the impacts of global change on biodiversity (Gienapp et al. 2017). It introduces the popGWAS, a novel GWAS approach, which utilizes phenotypic population means and genome-wide allele frequency data, obtainable through methods like Pool-sequencing (Pool-Seq), to identify the genetic loci underlying quantitative polygenic traits in natural populations and predict their mean. The core idea is that trait-increasing alleles should exhibit higher frequencies in populations with higher mean trait values. popGWAS then maps mean allele frequencies across populations to their trait means. Working with as many allele frequency values as populations sampled, popGWAS potentially has more power to find significant associations at genomic loci than individual-based GWAS working with three genotypes at a locus. This new method addresses some of the problems faced by traditional genome-wide association studies (GWAS), which require extensive resources and large sample sizes, posing challenges for biodiversity research on non-model species in natural populations. To evaluate the effectiveness of popGWAS, Pfenninger (2025) conducted extensive population genetic forward simulations, examining scenarios with varying numbers of populations, ranging from 12 to 60. The results indicated that popGWAS performance improved with increasing sample size, showing a diminishing return above 36 populations. In a direct comparison across all simulation scenarios, popGWAS consistently outperformed individual-based GWAS (iGWAS). On average, popGWAS identified more true positive loci than iGWAS. In addition, when combined with minimum entropy feature selection (MEFS), popGWAS achieved large predictive accuracy of population means of 0.8 or better in over 97% of simulations with 36 or more populations, regardless of other parameters. In contrast, iGWAS failed to generate valid phenotypic predictions in over 70% of the simulations. Also, unlike iGWAS, popGWAS did not suffer from p-value inflation. Yet, population structure or varying levels of relatedness among individuals were not fully accounted for in the simulations. The extent to which popGWAS would be sensitive to such individual covariates remains to be shown. Finally, popGWAS was relatively insensitive to low trait heritability because random individual variation gets averaged out when calculating the population mean trait value. The study demonstrates that popGWAS is a promising approach, particularly for oligogenic and moderately polygenic traits. The method performs more poorly for polygenic traits with large genetic redundancy, where different alleles contribute to the same trait mean in different populations. The method thus performs better when large-effect loci contribute to genetic differentiation in parallel across populations, as expected when gene flow is moderate to high (Yeaman & Whitlock 2011). Low genomic predictability is reached when drift dominates or when genetic architectures are highly polygenic. The popGWAS method proved effective with a moderate number of sampled populations and, when combined with machine learning for genomic prediction, exhibited strong performance in predicting population means, even for low-heritability traits. Notably, popGWAS consistently outperformed iGWAS in terms of identifying true positive loci and prediction accuracy. This suggests that popGWAS can make GWAS studies more accessible for biodiversity genomics research, providing a valuable tool for dissecting the genetic basis of complex traits in natural populations. A key aspect contributing to the efficiency of popGWAS is its compatibility with pooled sequencing (Pool-Seq). Pool-Seq provides estimates of allele frequencies within a population by sequencing a mixed DNA sample representing multiple individuals from that population (Futschik & Schlötterer 2010). This approach is significantly more cost-effective than sequencing each individual separately, allowing researchers to obtain genome-wide allele frequency data across multiple populations with a substantially reduced budget. This data efficiency makes GWAS more accessible to a wider range of researchers, particularly those working in biodiversity genomics where financial resources may be limited. Furthermore, popGWAS can be coupled with bulk phenotyping methods, such as automatic video recording, remote sensing, metabolomics/transcriptomics, etc., to efficiently obtain population-level phenotypic data, further streamlining the research process. Ultimately, popGWAS represents a valuable addition to the geneticist's toolkit, offering a complementary approach to iGWAS that can be particularly advantageous in specific research contexts where predicting trait mean is more important than resolving the precise genetic basis of a trait.
References Futschik, A. and Schlötterer, C. 2010. The Next Generation of Molecular Markers From Massively Parallel Sequencing of Pooled DNA Samples. Genetics 186(1): 207-218. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.110.114397 Gienapp, P., Fior, S., Guillaume, F., Lasky, J. R., Sork, V. L. and Csilléry, K. 2017. Genomic Quantitative Genetics to Study Evolution in the Wild. Trends Ecol. Evol. 32(12): 897-908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2017.09.004 Markus Pfenninger (2025) On the potential for GWAS with phenotypic population means and allele-frequency data (popGWAS). bioRxiv, ver.3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.12.598621 Yeaman, S. and Whitlock, M. C. 2011. The genetic architecture of adaptation under migration-selection balance. Evolution 65(7): 1897-1911. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.2011.01269.x
| On the potential for GWAS with phenotypic population means and allele-frequency data (popGWAS) | Markus Pfenninger | <p>It is vital to understand the genomic basis of differences in ecologically important traits if we are to understand the impact of global change on biodiversity and enhance our ability for targeted intervention. This study explores the potential... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Evolutionary Applications, Genotype-Phenotype, Population Genetics / Genomics | Frédéric Guillaume | 2024-06-15 08:41:14 | View | |
18 Mar 2025
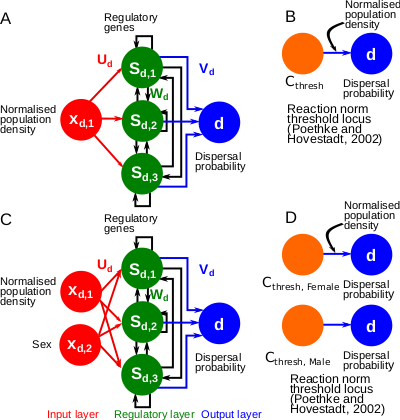
A gene-regulatory network model for density-dependent and sex-biased dispersal evolution during range expansionsJhelam N. Deshpande, Emanuel A. Fronhofer https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.18.549508Evolved gene-regulatory networks underlying dispersal plasticity can accelerate range expansionsRecommended by Charles Mullon based on reviews by Arnaud Le Rouzic and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Arnaud Le Rouzic and 2 anonymous reviewers
Natural populations rarely experience a uniform environment. Local density, resource availability, and mating opportunities often vary considerably across a population range. Theory has shown that such heterogeneity favours the evolution of density-dependent dispersal in the form of dispersal reaction norms. These models typically assume a simple genetic basis, with dispersal reaction norms encoded by a single Mendelian locus. Yet, dispersal plasticity is presumably controlled by more complex genetic architectures. Early work by Ezoe and Iwasa (1997) illustrated how evolved neural networks could generate dispersal reaction norms very similar to those predicted by Mendelian genetics.
In their manuscript, Deshpande and Fronhofer (2023) build on this work by examining how different genetic architectures influence the evolution of dispersal plasticity and its ecological consequences. They compare dispersal plasticity encoded either by a classical reaction norm controlled by a single Mendelian locus or by a gene-regulatory network following the Wagner model, where several interacting regulatory genes respond to local density cues and the individual's sex to determine dispersal probability.
Under stable conditions, both architectures successfully reproduce classical patterns of density- and sex-dependent dispersal. However, a clear difference emerges once populations expand into new, empty territories. Evolved gene-regulatory networks harbour substantially more cryptic genetic variation, which is revealed under these changing conditions. Previously hidden variation becomes exposed to selection at the expanding front, where low-density conditions create novel selective pressures. As a result, dispersal increases significantly, accelerating range expansions compared to the simpler, single-locus architectures.
These findings highlight how the genetic architecture of ecologically relevant traits, such as dispersal, not only shapes range dynamics but can also influence how populations respond to the demographic and environmental shifts encountered during expansion. By demonstrating that gene-regulatory networks facilitate faster range expansions due to their ability to store and later reveal cryptic genetic variation, Deshpande and Fronhofer take a useful step toward integrating genetic complexity into eco-evolutionary models.
References
Ezoe, H. and Iwasa, Y. (1997), Evolution of condition-dependent dispersal: A genetic-algorithm search for the ESS reaction norm. Popul Ecol, 39: 127-137. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02765258
Jhelam N. Deshpande, Emanuel A. Fronhofer (2023) A gene-regulatory network model for density-dependent and sex-biased dispersal evolution during range expansions. bioRxiv, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol
| A gene-regulatory network model for density-dependent and sex-biased dispersal evolution during range expansions | Jhelam N. Deshpande, Emanuel A. Fronhofer | <p>Dispersal is key to understanding ecological and evolutionary dynamics. Dispersal may itself evolve and exhibit phenotypic plasticity. Specifically, organisms may modulate their dispersal rates in response to the density of their conspecifics (... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Ecology, Evolutionary Theory, Genotype-Phenotype, Phenotypic Plasticity | Charles Mullon | 2023-12-17 20:54:44 | View | |
15 Mar 2025
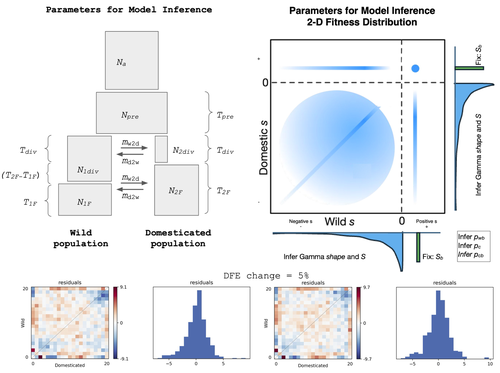
Detection of Domestication Signals through the Analysis of the Full Distribution of Fitness EffectsDavid Castellano, Ioanna-Theoni Vourlaki, Ryan N Gutenkunst, Sebastian E Ramos-Onsins https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.24.505198How the analysis of the distribution of fitness effects can reveal novel insights onto the genetics of domesticationRecommended by Matteo Fumagalli based on reviews by Miguel de Navascués and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Miguel de Navascués and 1 anonymous reviewer
The joint full distribution of fitness effects (DEF) is an important indicator in population genetic studies, and its inference has been the subject of intense research [1]. However, we still lack a solid framework to estimate DFE under certain demographic conditions. In this study, Castellano and colleagues propose to estimate the DFE by analysing the site frequency spectrum (SFS), and specifically develop a new approach for the joint DFE model inference [2]. The latter is based on the proportion of variants with divergent selection coefficients. Authors performed extensive simulations under models of domestication which is arguably one of the most crucial series of events in human evolution [3]. Domestication is associated with significant genetic costs in animals [4]. While DFE is typically estimated by contrasting SFS of silent and functional mutations [5], it has been recently suggested to use the joint SFS between domesticated and wild populations to estimate the DFE [6]. Authors build on this model and expand its parameterisation. Authors were able to dissect the impact of linked selection on inferred demographic history of wild and domesticated populations, with a robust estimation of the deleterious DFE. There are still several limitations in the interpretation of DFE as, for instance, some selective sweeps can bias their estimates and some demographic scenarios are challenging to infer. Also, classic quantitative trait models should be evaluated as a complementary approach. Finally, the in silico predictions presented in this study could be validated by empirical scans on existing genomic data sets. Nevertheless, this study is an important contribution to our understanding on how demography, and domestication in particular, can affect variants under selection in recent evolutionary histories. References [1] Eyre-Walker A, Keightley PD. The distribution of fitness effects of new mutations. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8(8):610-618. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2146 [2] Castellano D, Vourlaki IT, Gutenkunst RN, Ramos-Onsins SE. Detection of Domestication Signals through the Analysis of the Full Distribution of Fitness Effects. BioRxiv 2025, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.24.505198 [3] Frantz LAF, Bradley DG, Larson G, Orlando L. Animal domestication in the era of ancient genomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2020;21(8):449-460. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-020-0225-0 [4] Schubert M, Jónsson H, Chang D, et al. Prehistoric genomes reveal the genetic foundation and cost of horse domestication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(52):E5661-E5669. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1416991111 [5] Kousathanas A, Keightley PD. A comparison of models to infer the distribution of fitness effects of new mutations. Genetics. 2013;193(4):1197-1208. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.112.148023 [6] Huang X, Fortier AL, Coffman AJ, et al. Inferring Genome-Wide Correlations of Mutation Fitness Effects between Populations. Mol Biol Evol. 2021;38(10):4588-4602. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab162 | Detection of Domestication Signals through the Analysis of the Full Distribution of Fitness Effects | David Castellano, Ioanna-Theoni Vourlaki, Ryan N Gutenkunst, Sebastian E Ramos-Onsins | <p> Domestication is a process marked by complex interactions between demographic changes and selective pressures, which together shape genetic diversity. While the phenotypic outcomes of domestication are well documented, its genetic basis—p... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Dynamics, Genome Evolution, Molecular Evolution, Population Genetics / Genomics | Matteo Fumagalli | Parul Johri, Miguel de Navascués | 2024-05-10 15:17:06 | View |
13 Mar 2025

Unraveling genetic load dynamics during biological invasion: insights from two invasive insect speciesEric Lombaert, Aurelie Blin, Barbara Porro, Thomas Guillemaud, Julio S Bernal, Gary Chang, Natalia Kirichenko, Thomas W Sappington, Stefan Toepfer, Emeline Deleury https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.09.02.610743The genetic load of invasive population: how little do we know ?Recommended by Quentin Rougemont based on reviews by Sylvain Glémin and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Sylvain Glémin and 2 anonymous reviewers
We live both in a worrying and fascinating time. Worrying because human-induced global change has dramatic consequences on biodiversity around the world. Fascinating because these changes enable us to witness evolutionary processes unfolding on relatively short time scales. One such process is biological invasion. An intriguing evolutionary question is to understand which factor facilitates the success of an invasive species. In particular, serial bottlenecks at the expanding front should reduce the effective population size and decrease genetic diversity. Theoretically, this will increase the fixation of deleterious mutations due to the effect of genetic drift and overall affect the evolutionary potential of the invading species. In the short term, reduced genetic diversity and inbreeding in small populations increases the number of recessive deleterious variants exposed in a homozygous state. This may generate a reduction in mean fitness of the population. However, in the long term and under specific demographic scenarios recessive deleterious alleles may be more efficiently removed by purifying selection. Such purging may explain the success of invasion by reducing inbreeding depression and minimizing loss of fitness. Here, Lombaert et al. estimate the genetic load in two invasive insect species, a predator species, the harlequin ladybird (Harmonia axyridis) and a crop pest species, the western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera). The authors smartly took advantage of a pool-seq transcriptome-based exome capture method to estimate genetic load and assess the purge hypothesis using standard population genetic statistics, such as the ratio of nonsynonymous over synonymous expected heterozygosity, the frequency of derived alleles, and their excess or deficit. The results revealed different patterns in the two species: In the western corn rootworm, the authors find a clear signal of reduced genetic diversity in invasive populations. This was associated with a slightly reduced genetic load. However, there was only marginal evidence of purging regarding the most deleterious mutations, and in a single population, with moderately deleterious variants being weakly purged, as theoretically expected. In the harlequin ladybird, in contrast, the reduction of genetic diversity in invasive populations has been small, a result related to the mild severity of the bottlenecks. In this species, the authors found a tendency toward fixation of the genetic load and no signal of purging. Such results are intriguing, showing that different species seem to exhibit contrasted fate of genetic load. Differences in the invasion history and ecology of the species may explain these patterns. This is one of the first studies to use a population genomics approach to study the genetic load associated with biological invasion. Future studies based on whole genome data collected at the individual level across multiple species are needed to better understand the dynamics of genetic load during biological invasion and to draw more general conclusions. Advances in forward simulations may also be used to shed light on the evolution of the genetic load at different stages of the invasion process and under different strengths of bottlenecks.
References Eric Lombaert, Aurelie Blin, Barbara Porro, Thomas Guillemaud, Julio S Bernal, Gary Chang, Natalia Kirichenko, Thomas W Sappington, Stefan Toepfer, Emeline Deleury (2025) Unraveling genetic load dynamics during biological invasion: insights from two invasive insect species. bioRxiv, ver.3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.09.02.610743 | Unraveling genetic load dynamics during biological invasion: insights from two invasive insect species | Eric Lombaert, Aurelie Blin, Barbara Porro, Thomas Guillemaud, Julio S Bernal, Gary Chang, Natalia Kirichenko, Thomas W Sappington, Stefan Toepfer, Emeline Deleury | <p>Many invasive species undergo a significant reduction in genetic diversity, i.e. a genetic bottleneck, in the early stages of invasion. However, this reduction does not necessarily prevent them from achieving considerable ecological success and... |  | Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Population Genetics / Genomics | Quentin Rougemont | 2024-09-04 10:35:53 | View | |
07 Feb 2025
Discordant population structure inferred from male- and female-type mtDNAs from Macoma balthica, a bivalve species characterized by doubly uniparental inheritance of mitochondriaSabrina Le Cam, Brémaud Julie, Vanessa Becquet, Valerie Huet, Pascale Garcia, Amélia Viricel, Sophie Breton, Eric Pante https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.28.479517Unraveling the Complexities of Mitochondrial Inheritance in Macoma balthica: Insights from Doubly Uniparental InheritanceRecommended by Rita Castilho based on reviews by Risto Väinölä and John WaresThe study by Le Cam and colleagues, entitled “Discordant population structure inferred from male- and female-type mtDNAs from Macoma balthica, a bivalve species characterized by doubly uniparental inheritance of mitochondria”, provides a fascinating exploration of the genetic structure and evolutionary dynamics of the Baltic tellin, Macoma balthica, a bivalve species exhibiting doubly uniparental inheritance (DUI) of mitochondria. This work is a significant contribution to the field of evolutionary biology, particularly in understanding how sex-specific mitochondrial inheritance can shape population structure and genetic diversity in marine organisms. DUI is a remarkable exception to the typical maternal inheritance of mitochondria in metazoans, where both males and females can transmit their mitochondria, but through different routes. In species with DUI, females pass on their mitochondria to all offspring, while males transmit their mitochondria exclusively to their sons. This system results in males being heteroplasmic, carrying both maternal (F-type) and paternal (M-type) mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). The study leverages this unique inheritance pattern to investigate the genetic diversity, divergence, and population structure of M. balthica across its distribution range, from the North Sea to the Gironde Estuary in Southern France. One of the most striking findings of this study is the discordant population structure inferred from the male- and female-type mtDNAs. The authors sequenced the cox1 gene from both F-type and M-type mtDNA in 302 male individuals across 14 sampling sites. They found that the genetic differentiation between northern and southern populations was nearly three times higher for the M-type mtDNA compared to the F-type mtDNA. This discrepancy was further highlighted by the geographic localization of the strongest genetic break, which differed significantly between the two markers. For the F-type mtDNA, the break was located at the Finistère Peninsula, while for the M-type mtDNA, it was found at the Cotentin Peninsula, approximately 250 km apart. The authors propose several explanations for these differences, including a higher mutation rate, relaxed negative selection, and variations in effective population sizes for the M-type mtDNA. These factors could contribute to the observed divergence in genetic structure between the two mitochondrial types. Additionally, the study suggests that mito-nuclear genetic incompatibilities, arising from the interaction between mitochondrial and nuclear genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production, could play a role in maintaining these genetic barriers. The study also provides valuable insights into the phylogeographic history of M. balthica. The divergence times estimated for the F-type and M-type mtDNA clades suggest that the split between the northern and southern populations occurred before the last glacial maximum (LGM). This finding supports a scenario of pre-LGM vicariance rather than post-glacial primary intergradation. The authors' use of net divergence to estimate the timing of cladogenesis events within the Macoma species complex adds a robust temporal dimension to their phylogeographic analysis. Another intriguing aspect of the study is the evidence of asymmetric introgression and hybrid zone dynamics. The authors observed that the genetic clines for the F-type and M-type mtDNAs were not only discordant in their geographic locations but also in their widths. The cline for the M-type mtDNA was significantly narrower than that for the F-type mtDNA, suggesting different selective pressures or migration balances acting on the two mitochondrial types. This finding raises important questions about the role of sex-specific selection and gene flow in shaping the genetic structure of populations with DUI. The study also highlights the importance of considering sex-specific genetic markers in population genetic studies. One of the most intriguing aspects is the implication that M-type mtDNA may be evolving under different constraints than its female counterpart. The authors found higher nucleotide diversity and net divergence in M-type sequences suggestive of a relaxed selective regime or an increased mutation rate, which aligns with previous studies on DUI species. Given that M-type mitochondria function predominantly in sperm cells, the potential for oxidative damage, reduced purifying selection, and a higher mutation rate could explain these patterns. More broadly, this finding reinforces the idea that mitochondrial genomes, though typically constrained by purifying selection, can evolve along sex-specific trajectories when their inheritance is decoupled from maternal transmission.
References Sabrina Le Cam, Brémaud Julie, Vanessa Becquet, Valerie Huet, Pascale Garcia, Amélia Viricel, Sophie Breton, Eric Pante (2025) Discordant population structure inferred from male- and female-type mtDNAs from Macoma balthica, a bivalve species characterized by doubly uniparental inheritance of mitochondria. bioRxiv, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.28.479517 | Discordant population structure inferred from male- and female-type mtDNAs from Macoma balthica, a bivalve species characterized by doubly uniparental inheritance of mitochondria | Sabrina Le Cam, Brémaud Julie, Vanessa Becquet, Valerie Huet, Pascale Garcia, Amélia Viricel, Sophie Breton, Eric Pante | <p> Doubly Uniparental Inheritance (DUI) of mitochondria is a remarkable exception to the Strictly Maternal Inheritance (SMI) in metazoans. In species characterized by DUI --almost exclusively gonochoric bivalve mollusks-- females (F) transmi... | Phylogeography & Biogeography, Population Genetics / Genomics | Rita Castilho | 2022-03-03 10:22:01 | View | ||
31 Jan 2025
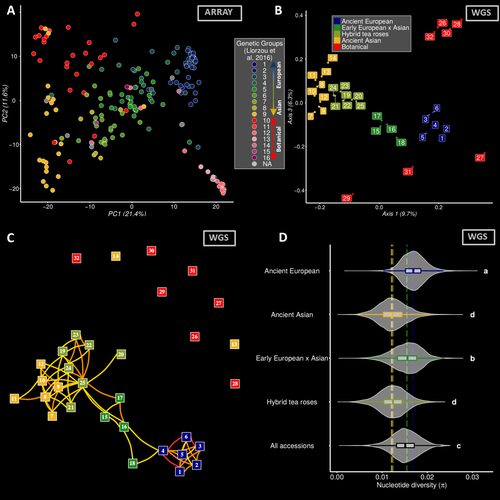
Dark side of the honeymoon: reconstructing the Asian x European rose breeding history through the lens of genomicsThibault Leroy, Elise Albert, Tatiana Thouroude, Sylvie Baudino, Jean-Claude Caissard, Annie Chastellier, Jerome Chameau, Julien Jeauffre, Therese Loubert, Saretta Nindya Paramita, Alix Pernet, Vanessa Soufflet-Freslon, Cristiana Oghina-Pavie, Fabrice Foucher, Laurence Hibrand-Saint Oyant, Jeremy Clotault https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.22.546162A genomic view on the history of rose garden breeding in EuropeRecommended by mathieu gautier based on reviews by Pierre Nouhaud, Vincent Segura and 1 anonymous reviewerRoses, a symbol of love and beauty, have a rich history of cultivation that spans millennia. While their aesthetic appeal has remained a constant, the genetic changes underlying their domestication and breeding remain intriguing. The manuscript titled "Dark side of the honeymoon: reconstructing the Asian x European rose breeding history through the lens of genomics" by Leroy et al. provides an unprecedented insight into the genomic shifts that accompanied the breeding history of roses in Europe during the 19th century. By leveraging on genotyping and whole-genome sequencing data from more than 200 accessions, this study reconstructs the genetic journey of roses from their European origins to their integration with Asian varieties. This work is particularly fascinating for evolutionary biologists, geneticists, and horticulturists alike, as it sheds light on several critical aspects of plant breeding history. The study provides compelling evidence of a rapid transition from predominantly European to a near-Asian genetic background within a few generations. This shift highlights the strong influence of Asian roses in shaping modern cultivated varieties, particularly through the introduction of recurrent blooming traits, novel colors, and scents. A striking finding is the reduction in genetic diversity that occurred during this transition, likely due to selective breeding practices that prioritized a narrow set of desirable traits. This discovery underscores the potential risks of genetic bottlenecks in cultivated plants and raises concerns about the long-term sustainability of modern rose breeding programs. The study also features a robust methodological framework applied to a unique data set which includes 204 rose accessions, covering both botanically and historically significant varieties. Whole genome sequencing of 32 accessions provides high-resolution insights into genomic evolution. Comprehensive phenotypic characterization over multiple years further allows in-depth investigation of the genetic architecture of key horticultural traits such as petal number, flowering time, disease resistance, and scent composition, with the building of the largest GWAS catalog for roses to date. Finally, the findings emphasize the need for sustainable breeding practices that balance genetic innovation with the preservation of historical diversity, by maintaining rose collections. Integrating ancient genetic resources into modern breeding programs could enhance resilience against diseases and environmental changes, while maintaining the aesthetic qualities that make roses so beloved. Overall, the manuscript by Leroy et al. is a landmark contribution to our understanding of the genomic history of rose breeding. By merging historical records with cutting-edge genomic analysis, the study not only reconstructs a critical phase of horticultural evolution but also provides invaluable insights for future breeding strategies. References Thibault Leroy, Elise Albert, Tatiana Thouroude, Sylvie Baudino, Jean-Claude Caissard, Annie Chastellier, Jerome Chameau, Julien Jeauffre, Therese Loubert, Saretta Nindya Paramita, Alix Pernet, Vanessa Soufflet-Freslon, Cristiana Oghina-Pavie, Fabrice Foucher, Laurence Hibrand-Saint Oyant, Jeremy Clotault (2024) Dark side of the honeymoon: reconstructing the Asian x European rose breeding history through the lens of genomics. bioRxiv, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.22.546162 | Dark side of the honeymoon: reconstructing the Asian x European rose breeding history through the lens of genomics | Thibault Leroy, Elise Albert, Tatiana Thouroude, Sylvie Baudino, Jean-Claude Caissard, Annie Chastellier, Jerome Chameau, Julien Jeauffre, Therese Loubert, Saretta Nindya Paramita, Alix Pernet, Vanessa Soufflet-Freslon, Cristiana Oghina-Pavie, Fab... | <p>Roses hold significant symbolic value in Western cultural heritage, often serving as a symbol of love and romance. Despite their ancient cultivation, the appreciation for the phenotypic diversity of roses emerged relatively recently, notably du... |  | Genotype-Phenotype, Hybridization / Introgression, Population Genetics / Genomics | mathieu gautier | Vincent Segura, Anonymous, Pierre Nouhaud | 2024-04-18 12:28:31 | View |
14 Jan 2025
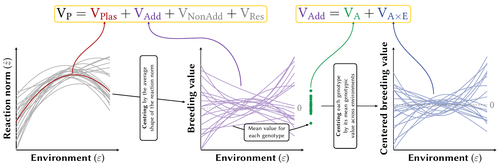
Partitioning the phenotypic and genetic variances of reaction normsPierre de Villemereuil, Luis-Miguel Chevin https://doi.org/10.32942/X2NC8BPhenotypic plasticity across traits, organisms and environments: decomposing the components of phenotypic varianceRecommended by Staffan Jacob based on reviews by Jarrod Hadfield and Thibaut Morel JournelPhenotypic plasticity can lead to rapid and important changes of trait distributions depending on environmental conditions, with important consequences for population dynamics, species interactions and adaptation. To better understand the evolution and importance of plasticity, we need to improve our ability to quantify and compare phenotypic plasticity among organisms, and estimate the evolutionary potential of plastic capacity. Plasticity is classically quantified through regression slopes, with units of traits per environment that by definition vary across organisms, traits and studies, and makes complex the comparison of how does plasticity vary across biological units, especially when linear versus quadratic reaction norms are considered. A clear methodology to quantify phenotypic plasticity in a way that allow for comparison across traits, organisms and environments is lacking. In this contribution, Pierre de Villemereuil and Luis-Miguel Chevin clarify key concepts about variability and evolutionary potential of plasticity, and propose an efficient method to partition phenotypic variance between genotype and environment. Expanding from the classical (too) simple regression slope approach, and directly integrating the genetic variability of plasticity, they provide a clear framework to quantify the part of phenotypic variance resulting from phenotypic plasticity, integrate the role of the shape of reaction norms, and estimate the heritable variation of trait plasticity. They integrate this method in a R package named Reacnorm, with step by step decision tree, that should greatly help the applicability of this framework. The authors here propose a contribution that simultaneously clarify key concepts and challenges about plasticity and reaction norms, being very interesting on the theoretical side, and is directly and quite simply applicable to any trait and organism. This should help and stimulate comparative studies of how does plasticity vary across traits, organisms and environmental contexts, both using already published datasets and through new experiments. References Pierre de Villemereuil, Luis-Miguel Chevin (2025) Partitioning the phenotypic and genetic variances of reaction norms. EcoEvorxiv, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evol Biol https://doi.org/10.32942/X2NC8B | Partitioning the phenotypic and genetic variances of reaction norms | Pierre de Villemereuil, Luis-Miguel Chevin | <p>Many traits show plastic phenotypic variation across environments, captured by their norms of reaction. These reaction norms may be discrete or continuous, and can substantially vary in shape across organisms and traits, making it difficult to ... |  | Evolutionary Ecology, Phenotypic Plasticity, Quantitative Genetics | Staffan Jacob | 2023-09-01 16:42:45 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Dustin Brisson
Julien Dutheil
Marianne Elias
Inês Fragata
François Rousset
Sishuo Wang










