Strong habitat and weak genetic effects shape the lifetime reproductive success in a wild clownfish population
Océane C. Salles, Glenn R. Almany, Michael L. Berumen, Geoffrey P. Jones, Pablo Saenz-Agudelo, Maya Srinivasan, Simon Thorrold, Benoit Pujol, Serge Planes
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3476529
Habitat variation of wild clownfish population shapes selfrecruitment more than genetic effects
Recommended by Philip Munday ? based on reviews by Juan Diego Gaitan-Espitia and Loeske Kruuk
Estimating the genetic and environmental components of variation in reproductive success is crucial to understanding the adaptive potential of populations to environmental change. To date, the heritability of lifetime reproductive success (fitness) has been estimated in a handful of wild animal population, mostly in mammals and birds, but has never been estimated for a marine species. The primary reason that such estimates are lacking in marine species is that most marine organisms have a dispersive larval phase, making it extraordinarily difficult to track the fate of offspring from one generation to the next.
In this study, Salles et al. [1] use an unprecedented 10 year data set for a wild population of orange clownfish (Amphiprion percula) to estimate the environmental, maternal and additive genetic components of life time reproductive success for the self-recruiting portion of the local population. Previous studies show that over 50% of juvenile clownfish recruiting to the population of clownfish at Kimbe Island (Kimbe Bay, PNG) are natal to the population. In other words, >50% of the juveniles recruiting to the population at Kimbe Island are offspring of parents from Kimbe Island. The identity and location of every adult clownfish in the Kimbe Island population was tracked over 10 years. At the same time newly recruiting juveniles were collected at regular intervals (biennially) and their parentage assigned with high confidence by 22 polymorphic microsatellite loci. Salles et al. then used a pedigree comprising 1735 individuals from up to 5 generations of clownfish at Kimbe Island to assess the contribution of every breeding pair of clownfish to self-recruitment within the local population. Because clownfish are site attached and live in close association with a host sea anemone, it was also possible to examine the contribution of reef location and host anemones species (either Heteractis magnifica or Stichodactyla gigantea) to reproductive success within the local population.
The study found that breeders from the eastern side of Kimbe Island, and mostly inhabiting S. gigantea sea anemones, produced more juveniles that recruited to the local population than breeders from other location around the island, or inhabiting H. magnifica. In fact, host anemone species and geographic location explained about 97% of the variance in reproductive success within the local population (i.e. excluding successful recruitment to other populations). By contrast, maternal and additive genetic effects explained only 1.9% and 1.3% of the variance, respectively. In other words, reef location and the species of host anemone inhabited had an overwhelming influence on the long-term contribution of breeding pairs of clownfish to replenishment of the local population. This overwhelming effect of the local habitat on reproductive success means that the population is potentially susceptible to rapid environmental changes - for example if S. giganta sea anemones are disproportionately susceptible to global warming, or reef habitats on the eastern side of the island are more susceptible to disturbance. By contrast, the small component of additive genetic variance in local reproductive success translated into low heritability and evolvability of lifetime reproductive success within the local population, as predicted by theory [2] and observed in some terrestrial species. Consequently, fitness would evolve slowly to environmental change.
Establishing the components of variation in fitness in a wild population of marine fishes is an astonishing achievement, made possible by the unprecedented long-term individual-level monitoring of the entire population of clownfish at Kimbe Island. A next step in this research would be to include other clownfish populations that are demographically and genetically connected to the Kimbe Island population through larval dispersal. It would be intriguing to establish the environmental, maternal and additive genetic components of reproductive success in the dispersing part of the Kimbe Island population, to see if this potentially differs among breeders who contribute more or less to replenishment within the local population.
References
[1] Salles, O. C., Almany, G. R., Berumen, M.L., Jones, G. P., Saenz-Agudelo, P., Srinivasan, M., Thorrold, S. R., Pujol, B., Planes, S. (2019). Strong habitat and weak genetic effects shape the lifetime reproductive success in a wild clownfish population. Zenodo, 3476529, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.3476529
[2] Fisher, R.A. (1930). The genetical theory of natural selection. Clarendon Press, Oxford, U.K.
| Strong habitat and weak genetic effects shape the lifetime reproductive success in a wild clownfish population | Océane C. Salles, Glenn R. Almany, Michael L. Berumen, Geoffrey P. Jones, Pablo Saenz-Agudelo, Maya Srinivasan, Simon Thorrold, Benoit Pujol, Serge Planes | <p>Lifetime reproductive success (LRS), the number of offspring an individual contributes to the next generation, is of fundamental importance in ecology and evolutionary biology. LRS may be influenced by environmental, maternal and additive genet... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Ecology, Life History, Quantitative Genetics | Philip Munday | | 2018-10-01 09:00:53 | View |
Deceptive combined effects of short allele dominance and stuttering: an example with Ixodes scapularis, the main vector of Lyme disease in the U.S.A.
Thierry De Meeûs, Cynthia T. Chan, John M. Ludwig, Jean I. Tsao, Jaymin Patel, Jigar Bhagatwala, and Lorenza Beati
https://doi.org/10.1101/622373
New curation method for microsatellite markers improves population genetics analyses
Recommended by Aurelien Tellier based on reviews by Eric Petit, Martin Husemann ? and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Eric Petit, Martin Husemann ? and 2 anonymous reviewers
Genetic markers are used for in modern population genetics/genomics to uncover the past neutral and selective history of population and species. Besides Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) obtained from whole genome data, microsatellites (or Short Tandem Repeats, SSR) have been common markers of choice in numerous population genetics studies of non-model species with large sample sizes [1]. Microsatellites can be used to uncover and draw inference of the past population demography (e.g. expansion, decline, bottlenecks…), population split, population structure and gene flow, but also life history traits and modes of reproduction (e.g. [2,3]). These markers are widely used in conservation genetics [4] or to study parasites or disease vectors [5]. Microsatellites do show higher mutation rate than SNPs increasing, on the one hand, the statistical power to infer recent events (for example crop domestication, [2,3]), while, on the other hand, decreasing their statistical power over longer time scales due to homoplasy [6].
To perform such analyses, however, an excellent and reliable quality of data is required. As emphasized in the article by De Meeûs et al. [7] three main issues do bias the observed heterozygosity at microsatellites: null alleles, short allele dominance (SAD) and stuttering. These originates from poor PCR amplification. As a result, an excess of homozygosity is observed at the microsatellite loci leading to overestimation of the variation statistics FIS and FST as well as increased linage disequilibrium (LD). For null alleles, several methods and software do help to reduce the bias, and in the present study, De Meeûs et al. [7] propose a way to tackle issues with SAD and stuttering.
The authors study a dataset consisting of 387 samples from 61 subsamples genotyped at nine loci of the species Ixodes scapularis, i.e. ticks transmitting the Lyme disease. Based on correlation methods and FST, FIS they can uncover null alleles and SAD. Stuttering is detected by evaluating the heterozygote deficit between alleles displaying a single repeat difference. Without correction, six loci are affected by one of these amplification problems generating a large deficit of heterozygotes (measured by significant FIS and FST) remaining so after correction for the false discovery rate (FDR). These results would be classically interpreted as a strong Wahlund effect and/or selection at several loci.
After correcting for null alleles, the authors apply two novel corrections: 1) a re-examination of the chromatograms reveals previously disregarded larger alleles thus decreasing SAD, and 2) pooling alleles close in size decreasing stuttering. The corrected dataset shows then a significant excess of heterozygotes as could be expected in a dioecious species with strong population structure. The FDR correction removes then the significant excess of homozygotes and LD between pairs of loci. FST on the cured dataset is used to demonstrate the strong population structure and small effective subpopulation sizes. This is confirmed by a clustering analysis using discriminant analysis of principal components (DAPC).
While based on a specific dataset of ticks from different populations sampled across the USA, the generality of the authors’ approach is presented in Figure 6 in which they provide a step by step flowchart to cure microsatellite datasets from null alleles, SAD and stuttering. Several criteria based on FIS, FST and LD between loci are used as decision keys in the flowchart. An excel file is also provided as help for the curation steps. This study and the proposed methodology are thus extremely useful for all population geneticists working on non-model species with large number of samples genotyped at microsatellite markers. The method not only allows more accurate estimates of heterozygosity but also prevents the thinning of datasets due to the removal of problematic loci. As a follow-up and extension of this work, an exhaustive simulation study could investigate the influence of these data quality issues on past demographic and population structure inference under a wide range of scenarios. This would allow to quantify the current biases in the literature and the robustness of the methodology devised by De Meeûs et al. [7].
References
[1] Jarne, P., and Lagoda, P. J. (1996). Microsatellites, from molecules to populations and back. Trends in ecology & evolution, 11(10), 424-429. doi: 10.1016/0169-5347(96)10049-5
[2] Cornille, A., Giraud, T., Bellard, C., Tellier, A., Le Cam, B., Smulders, M. J. M., Kleinschmit, J., Roldan-Ruiz, I. and Gladieux, P. (2013). Postglacial recolonization history of the E uropean crabapple (Malus sylvestris M ill.), a wild contributor to the domesticated apple. Molecular Ecology, 22(8), 2249-2263. doi: 10.1111/mec.12231
[3] Parat, F., Schwertfirm, G., Rudolph, U., Miedaner, T., Korzun, V., Bauer, E., Schön C.-C. and Tellier, A. (2016). Geography and end use drive the diversification of worldwide winter rye populations. Molecular ecology, 25(2), 500-514. doi: 10.1111/mec.13495
[4] Broquet, T., Ménard, N., & Petit, E. (2007). Noninvasive population genetics: a review of sample source, diet, fragment length and microsatellite motif effects on amplification success and genotyping error rates. Conservation Genetics, 8(1), 249-260. doi: 10.1007/s10592-006-9146-5
[5] Koffi, M., De Meeûs, T., Séré, M., Bucheton, B., Simo, G., Njiokou, F., Salim, B., Kaboré, J., MacLeod, A., Camara, M., Solano, P., Belem, A. M. G. and Jamonneau, V. (2015). Population genetics and reproductive strategies of African trypanosomes: revisiting available published data. PLoS neglected tropical diseases, 9(10), e0003985. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003985
[6] Estoup, A., Jarne, P., & Cornuet, J. M. (2002). Homoplasy and mutation model at microsatellite loci and their consequences for population genetics analysis. Molecular ecology, 11(9), 1591-1604. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294X.2002.01576.x
[7] De Meeûs, T., Chan, C. T., Ludwig, J. M., Tsao, J. I., Patel, J., Bhagatwala, J., and Beati, L. (2019). Deceptive combined effects of short allele dominance and stuttering: an example with Ixodes scapularis, the main vector of Lyme disease in the USA. bioRxiv, 622373, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/622373
| Deceptive combined effects of short allele dominance and stuttering: an example with Ixodes scapularis, the main vector of Lyme disease in the U.S.A. | Thierry De Meeûs, Cynthia T. Chan, John M. Ludwig, Jean I. Tsao, Jaymin Patel, Jigar Bhagatwala, and Lorenza Beati | <p>Null alleles, short allele dominance (SAD), and stuttering increase the perceived relative inbreeding of individuals and subpopulations as measured by Wright’s FIS and FST. Ascertainment bias, due to such amplifying problems are usually caused ... | 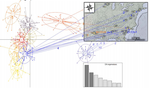 | Evolutionary Ecology, Other, Population Genetics / Genomics | Aurelien Tellier | | 2019-05-02 20:52:08 | View |
The discernible and hidden effects of clonality on the genotypic and genetic states of populations: improving our estimation of clonal rates
Solenn Stoeckel, Barbara Porro, Sophie Arnaud-Haond
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1902.09365
How to estimate clonality from genetic data: use large samples and consider the biology of the species
Recommended by Myriam Heuertz based on reviews by David Macaya-Sanz, Marcela Van Loo and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by David Macaya-Sanz, Marcela Van Loo and 1 anonymous reviewer
Population geneticists frequently use the genetic and genotypic information of a population sample of individuals to make inferences on the reproductive system of a species. The detection of clones, i.e. individuals with the same genotype, can give information on whether there is clonal (vegetative) reproduction in the species. If clonality is detected, population geneticists typically use genotypic richness R, the number of distinct genotypes relative to the sample size, to estimate the rate of clonality c, which can be defined as the proportion of reproductive events that are clonal. Estimating the rate of clonality based on genotypic richness is however problematic because, to date, there is no analytical, nor simulation-based, characterization of this relationship. Furthermore, the effect of sampling on this relationship has never been critically examined.
The paper by Stoeckel, Porro and Arnaud-Haond [1] contributes significantly to the characterization of the relationship between rate of clonality and genetic and genotypic parameters in a population. The authors use an extensive individual-based simulation approach to assess the effects of rate of clonality (fully sexual, fully clonal and a range of intermediate levels of clonality, i.e., partial clonality) on genetic and genotypic parameters, considering variable population size, sample size, and numbers of generations elapsed since population initiation. Based on their simulations, they derive empirical formulae that link for the first time the rate of clonality to the genotypic richness and to the size distribution of clones (genotypic parameters), as well as to the population inbreeding coefficient and to a metric of linkage disequilibrium (genetic parameters). They then use the simulated data to assess the accuracy of their predictions. In a second phase, the authors use a Bayesian supervised learning algorithm to estimate rates of clonality from the simulated data.
The authors show that the relationship between rate of clonality and genotypic richness is not linear: genotypic richness decreases slowly with increasing clonality, a large drop in genotypic richness is only seen for rates of clonality ≥ 0.90. Genetic parameters are only sensitive to high rates of clonality. The practical implications of these results are that genotypic and genetic parameters can complement each other for the estimation of rates of clonality, with genotypic parameters most useful throughout most of the range of clonality values and with genetic parameters complementing them meaningfully at higher values. The most meaningful practical result of the paper is the demonstration of sampling bias on the estimation of genotypic richness. Commonly used population sample sizes in population genetics studies (n ≤ 50) lead to great overestimation of genotypic richness, which consequently leads to a severe underestimation of the rate of clonality in most systems, irrespectively of whether they have reached stationary equilibrium. Only in small populations, these effects are attenuated.
Biologists interested in the estimation of the rate of clonality will find this paper highly useful to design their sampling, and to choose their statistics for inference in a meaningful way. This paper also calls for a careful reappraisal of previously published works that infer rates of clonality from genetic data, and highlights the prime importance of complementary information on species life history data for a correct understanding of partial clonality.
References
[1] Stoeckel, S., Porro, B., and Arnaud-Haond, S. (2019). The discernible and hidden effects of clonality on the genotypic and genetic states of populations: improving our estimation of clonal rates. ArXiv:1902.09365 [q-Bio] v4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. Retrieved from http://arxiv.org/abs/1902.09365v4
| The discernible and hidden effects of clonality on the genotypic and genetic states of populations: improving our estimation of clonal rates | Solenn Stoeckel, Barbara Porro, Sophie Arnaud-Haond | <p>Partial clonality is widespread across the tree of life, but most population genetics models are conceived for exclusively clonal or sexual organisms. This gap hampers our understanding of the influence of clonality on evolutionary trajectories... |  | Population Genetics / Genomics, Reproduction and Sex | Myriam Heuertz | | 2019-02-28 10:10:56 | View |
Is adaptation limited by mutation? A timescale-dependent effect of genetic diversity on the adaptive substitution rate in animals
Marjolaine Rousselle, Paul Simion, Marie-Ka Tilak, Emeric Figuet, Benoit Nabholz, Nicolas Galtier
https://doi.org/10.1101/643619
To tinker, evolution needs a supply of spare parts
Recommended by Georgii Bazykin based on reviews by Konstantin Popadin, David Enard and 1 anonymous reviewer
Is evolution adaptive? Not if there is no variation for natural selection to work with. Theory predicts that how fast a population can adapt to a new environment can be limited by the supply of new mutations coming into it. This supply, in turn, depends on two things: how often mutations occur and in how many individuals. If there are few mutations, or few individuals in whom they can originate, individuals will be mostly identical in their DNA, and natural selection will be impotent.
This theoretical prediction has been hard to test. The rate at which new mutations arise in a population can be manipulated experimentally, and some work has shown that the fitness of a population increases more rapidly if more new mutations appear per generation, lending support to the mutation-limitation hypothesis [1]. However, the question remains whether this limitation has played a role in the history of life over the evolutionary timescale. Maybe all natural populations are so large, the mutation rate so high, and/or the environment changes so slowly, that any novel variant required for adaptation is already there when selection starts to act? Some recent work does suggest that when strong selection begins to favor a certain phenotype, multiple distinct genetic variants producing this phenotype spread; this is what has happened, for instance, at the origin of insecticide resistance in wild populations of Drosophila melanogaster [2] or lactose persistence in humans [3]. In many other cases, though, adaptations seem to originate through a single mutation event, suggesting that the time needed for this mutation to arise may be important.
To complicate things, adaptation is hard to quantify. It leaves a trace in differences between individuals of the same species as well as of different species. However, this trace is often masked or confounded by other processes, including natural selection disfavoring newly arising deleterious variants, interference from selection acting at linked sites, and changes in population size. In 1991, McDonald and Kreitman [4] have come up with a method to infer the rate of adaptation in the presence of strong negative selection, and later work has developed upon it to control for some of the other confounders. Still, the method is data-intensive, and previous attempts to employ it to compare the rates of adaptation between species have yielded somewhat contradictory results.
The new paper by Rousselle et al. recommended by PCI Evol Biol [5] fills this gap. The authors use published data as well as their own newly generated dataset to analyze, in a McDonald and Kreitman-like framework, both closely and distantly related species. Importantly, these comparisons cover species with very different polymorphism levels, spanning two orders of magnitude of difference levels.
So is adaptation in fact limited by supply of new mutations? The answer is, it depends. It does indeed seem that the species with a lower level of polymorphism adapt at a lower rate, consistent with the mutation-limitation hypothesis. However, this only is true for those groups of species in which the variability is low. Therefore, if a population is very small or the mutation rate very low, there may be in fact not enough mutations to secure its need to adapt.
In more polymorphic species, and in comparisons of distant species, the data hint instead at the opposite relationship: the rate of adaptations declines with variability. This is consistent with a different explanation: when a population is small, it needs to adapt more frequently, repairing the weakly deleterious mutations that can’t be prevented by selection under small population sizes.
There are quite a few problems small populations have to deal with. Some of them are ecological: e.g., small numbers make populations more vulnerable to stochastic fluctuations in size or sex ratio. Others, however, are genetic. Small populations are prone to inbreeding depression and have an increased rate of genetic drift, leading to spread of deleterious alleles. Indeed, selection against deleterious mutations is less efficient when populations are small, and less numerable species accumulate more of such mutations over the course of evolution [6]. The work by Rouselle et al. [5] suggests that small populations also face an additional burden: a reduced ability to adapt.
Has the rate of adaptation in our own species also been limited by our deficit of diversity? The data hints at this. Homo sapiens, as well as the two other studied extinct representatives of the genus Homo, Neanderthals and Denisovans, belong to the domain of relatively low polymorphism levels, where an increase in polymorphism matters for the rate at which adaptive substitutions accumulate. Perhaps, if our ancestors were more numerous or more mutable, they would have been able to get themselves out of trouble, and there would be multiple human species still alive rather than just one.
References
[1] G, J. A., Visser, M. de, Zeyl, C. W., Gerrish, P. J., Blanchard, J. L., and Lenski, R. E. (1999). Diminishing Returns from Mutation Supply Rate in Asexual Populations. Science, 283(5400), 404–406. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5400.404
[2] Karasov, T., Messer, P. W., and Petrov, D. A. (2010). Evidence that Adaptation in Drosophila Is Not Limited by Mutation at Single Sites. PLOS Genetics, 6(6), e1000924. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000924
[3] Jones, B. L., Raga, T. O., Liebert, A., Zmarz, P., Bekele, E., Danielsen, E. T., Olsen, A. K., Bradman, N., Troelsen, J. T., and Swallow, D. M. (2013). Diversity of Lactase Persistence Alleles in Ethiopia: Signature of a Soft Selective Sweep. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 93(3), 538–544. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.07.008
[4] McDonald, J. H., and Kreitman, M. (1991). Adaptive protein evolution at the Adh locus in Drosophila. Nature, 351(6328), 652–654. doi: 10.1038/351652a0
[5] Rousselle, M., Simion, P., Tilak, M. K., Figuet, E., Nabholz, B., and Galtier, N. (2019). Is adaptation limited by mutation? A timescale-dependent effect of genetic diversity on the adaptive substitution rate in animals. BioRxiv, 643619, ver 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/643619
[6] Popadin, K., Polishchuk, L. V., Mamirova, L., Knorre, D., and Gunbin, K. (2007). Accumulation of slightly deleterious mutations in mitochondrial protein-coding genes of large versus small mammals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(33), 13390–13395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701256104
| Is adaptation limited by mutation? A timescale-dependent effect of genetic diversity on the adaptive substitution rate in animals | Marjolaine Rousselle, Paul Simion, Marie-Ka Tilak, Emeric Figuet, Benoit Nabholz, Nicolas Galtier | <p>Whether adaptation is limited by the beneficial mutation supply is a long-standing question of evolutionary genetics, which is more generally related to the determination of the adaptive substitution rate and its relationship with the effective... | 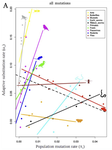 | Adaptation, Evolutionary Theory, Genome Evolution, Molecular Evolution, Population Genetics / Genomics | Georgii Bazykin | | 2019-05-21 09:49:16 | View |
Transgenerational plasticity of inducible defenses: combined effects of grand-parental, parental and current environments
Juliette Tariel; Sandrine Plénet; Emilien Luquet
https://doi.org/10.1101/589945
Transgenerational plasticity through three generations
Recommended by Troy Day based on reviews by Stewart Plaistow and 1 anonymous reviewer
Organisms very often display phenotypic plasticity, whereby the expression of trait (or suite of traits) changes in a consistent way as a function of some environmental variable. Sometimes this plastic response remains labile and so the trait continues to respond to the environment throughout an organism’s life, but there are also many examples in which environmental conditions during a critical developmental window irreversibly set the stage for how a trait will be expressed later in life.
Traditionally, most studies of phenotypic plasticity have considered how an organism’s phenotype is altered by the environment that it experiences (called within-generation plasticity) but there is growing interest in how an organism’s phenotype is altered by the environment experienced by its ancestors (called transgenerational plasticity) [1]. In the simplest cases an organism’s phenotype might be affected by the environmental conditions experienced by its parents. There are several examples of this phenomenon as well, including interesting cases where predator cues experiences by an organism’s parents dictate the extent to which it displays a defensive phenotype.
Tariel et al. [2] present a study that takes these ideas to the next logical step and examines transgenerational plasticity through three generations. They used a well-studied system of snails (Physa acuta) that display inducible defences in response to predator (crayfish) cues. The authors exposed three generations of snails to one of two treatments: the presence or absence of predator cues, and then examined a suite of behavioural and morphological traits associated with predator defence. This allowed them to determine if and how offspring, parental, and grandparental environment influence offspring phenotype.
Interestingly, their results do show that transgenerational plasticity can act across multiple generations. The patterns found were complex though and it is difficult at this stage to assess how likely it is that these responses are adaptive. For example, a behavioural trait appears to respond to grandparental but not parental environment, shell thickness responds to both, and snail weight and a composite index of morphology respond to neither. Exactly what this means in terms of an offspring’s fitness, however, is unclear. It is also not immediately clear from the study how predictive a grandparent’s environment is of the conditions likely to be faced by an individual. Further work will be needed on these issues to better interpret what this transgenerational plasticity means and to assess if it might be an evolved response to cope with varying predation pressure. It would also be useful to delve more deeply into the developmental mechanisms throughout which this plasticity occurs. Irrespective of these issues, however, the study does reveal that transgenerational plasticity across multiple generations can indeed occur and so cannot be ignored as a source of phenotypic variation.
References
[1] West-Eberhard, M. J. (2003). Developmental plasticity and evolution. Oxford University Press.
[2] Tariel, J., Plenet, S., and Luquet, E. (2019). Transgenerational plasticity of inducible defenses: combined effects of grand-parental, parental and current environments. bioRxiv, 589945, ver. 3, peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/589945
| Transgenerational plasticity of inducible defenses: combined effects of grand-parental, parental and current environments | Juliette Tariel; Sandrine Plénet; Emilien Luquet | <p>While an increasing number of studies highlights that parental environment shapes offspring phenotype (transgenerational plasticity TGP), TGP beyond the parental generation has received less attention. Studies suggest that TGP impacts populatio... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Ecology, Non Genetic Inheritance, Phenotypic Plasticity | Troy Day | | 2019-03-29 09:31:53 | View |
Population genomics supports clonal reproduction and multiple gains and losses of parasitic abilities in the most devastating nematode plant pest
Georgios D Koutsovoulos, Eder Marques, Marie-Jeanne Arguel, Laurent Duret, Andressa CZ Machado, Regina MDG Carneiro, Djampa K Kozlowski, Marc Bailly-Bechet, Philippe Castagnone-Sereno, Erika VS Albuquerque, Etienne GJ Danchin
https://doi.org/10.1101/362129
The scandalous pest
Recommended by Nicolas Galtier based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Koutsovoulos et al. [1] have generated and analysed the first population genomic dataset in root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Why is this interesting? For two major reasons. First, M. incognita has been documented to be apomictic, i.e., to lack any form of sex. This is a trait of major evolutionary importance, with implications on species adaptive potential. The study of genome evolution in asexuals is fascinating and has the potential to inform on the forces governing the evolution of sex and recombination. Even small amounts of sex, however, are sufficient to restore most of the population genetic properties of true sexuals [2]. Because rare events of sex can remain undetected in the field, to confirm asexuality in M. incognita using genomic data is an important step. The second reason why M. incognita is of interest is that this nematode is one of the most harmful pests currently living on earth. M. incognita feeds on the roots of many cultivated plants, including tomato, bean, and cotton, and has been of major agricultural importance for decades. A number of races were defined based on host specificity. These have played a key role in attempts to control the dynamic of M. incognita populations via crop rotations. Races and management strategies so far lack any genetic basis, hence the second major interest of this study.
The authors newly sequenced the full genome of eleven strains from Brazil and added nine already available samples from Africa and North-America. They report that, in all likelihood, M. incognita is indeed a purely asexual species. This is supported by (i) the confirmation that the genome is in its major part haploid, and (ii) a spectacularly high level of linkage disequilibrium, which does not decline with genetic distance between loci at a 100kb scale. The absence of sex and recombination is associated in M. incognita with a remarkably low amount of genetic diversity - one order of magnitude less than in typical sexual nematodes - and an heavy load of deleterious mutations, as measured by the ratio of non-synonymous (=amino-acid changing) to synonymous (=amino-acid conservative) diversity in coding sequences. The other important result of this study is that the population substructure in M. incognita is in no way related to host races or geography. The tree genetic clusters that are identified include strains from several continents and feeding on a diversity of host plants.
The implications of this work are numerous. First, the results suggest that M. incognita is an ancient asexual. Asexuality, which was here demonstrated via linkage disequilibrium analysis, must be ancient enough for diploidy (or, in this case, maybe triploidy) to have been lost - i.e., formerly homologous chromosomes have accumulated enough mutations to be assembled as distinct entities. So we are not talking about a highly successful clone having recently spread the world - rather a long-term obligate parthenogen. Asexual organisms are deprived of the source of genetic variation offered by recombination, which is why asexuality is thought to be an evolutionary dead-end. Long-term asexuals are uncommon and even the most famous ones, bdelloid rotifers, are suspected to experience between-individual genetic transfers [3]. M. incognita is apparently a true 'evolutionary scandal', and as such deserves particular attention from molecular evolutionary geneticists.
The lack of any host race effect on the genetic diversity of M. incognita is another important finding. So-called 'races' have largely contributed to shape researchers' view of the structure of the species so far. This study demonstrates that a mental effort is now needed to forget about races, and consider host-specificity for what it is - a phenotypic trait. This result implies that many host shifts must have independently occurred in the three M. incognita genetic lineages, suggesting an arms race between plants and nematodes, which in the absence of sex and recombination must be entirely mutation-driven on the nematode side. Genes functionally involved in the arms race might therefore be expected to have experienced convergent evolution, if distinct M. incognita lineages have adopted the same solutions to overcome plant defenses. The present study paves the way for such a genome scan. The authors rightly discuss that the strong adaptive potential of M. incognita, at least in terms of host shift, despite no sex and tiny amounts of genetic diversity, is a paradox that would deserve to be further investigated.
References
[1] Koutsovoulos, G. D., Marques, E., Arguel, M. J., Duret, L., Machado, A. C. Z., Carneiro, R. M. D. G., Kozlowski, D. K., Bailly-Bechet, M., Castagnone-Sereno, P., Albuquerque, E. V., & Danchin, E. G. J. (2019). Population genomics supports clonal reproduction and multiple gains and losses of parasitic abilities in the most devastating nematode plant pest. bioRxiv, 362129, ver. 5, peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/362129
[2] Hartfield, M. (2016). Evolutionary genetic consequences of facultative sex and outcrossing. Journal of evolutionary biology, 29(1), 5-22. doi: 10.1111/jeb.12770
[3] Debortoli, N., Li, X., Eyres, I., Fontaneto, D., Hespeels, B., Tang, C. Q., Flot, J. F. & Van Doninck, K. (2016). Genetic exchange among bdelloid rotifers is more likely due to horizontal gene transfer than to meiotic sex. Current Biology, 26(6), 723-732. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.01.031
| Population genomics supports clonal reproduction and multiple gains and losses of parasitic abilities in the most devastating nematode plant pest | Georgios D Koutsovoulos, Eder Marques, Marie-Jeanne Arguel, Laurent Duret, Andressa CZ Machado, Regina MDG Carneiro, Djampa K Kozlowski, Marc Bailly-Bechet, Philippe Castagnone-Sereno, Erika VS Albuquerque, Etienne GJ Danchin | <p>The most devastating nematodes to worldwide agriculture are the root-knot nematodes with Meloidogyne incognita being the most widely distributed and damaging species. This parasitic and ecological success seem surprising given its supposed obli... | 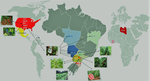 | Adaptation, Bioinformatics & Computational Biology, Evolutionary Ecology, Genome Evolution, Genotype-Phenotype, Molecular Evolution, Phylogenetics / Phylogenomics, Population Genetics / Genomics, Reproduction and Sex | Nicolas Galtier | | 2018-08-24 09:02:33 | View |
A bird’s white-eye view on neosex chromosome evolution
Thibault Leroy, Yoann Anselmetti, Marie-Ka Tilak, Sèverine Bérard, Laura Csukonyi, Maëva Gabrielli, Céline Scornavacca, Borja Milá, Christophe Thébaud, Benoit Nabholz
https://doi.org/10.1101/505610
Young sex chromosomes discovered in white-eye birds
Recommended by Kateryna Makova based on reviews by Gabriel Marais, Melissa Wilson and 1 anonymous reviewer
Recent advances in next-generation sequencing are allowing us to uncover the evolution of sex chromosomes in non-model organisms. This study [1] represents an example of this application to birds of two Sylvioidea species from the genus Zosterops (commonly known as white-eyes). The study is exemplary in the amount and types of data generated and in the thoroughness of the analysis applied. Both male and female genomes were sequenced to allow the authors to identify sex-chromosome specific scaffolds. These data were augmented by generating the transcriptome (RNA-seq) data set. The findings after the analysis of these extensive data are intriguing: neoZ and neoW chromosome scaffolds and their breakpoints were identified. Novel sex chromosome formation appears to be accompanied by translocation events. The timing of formation of novel sex chromosomes was identified using molecular dating and appears to be relatively recent. Yet first signatures of distinct evolutionary patterns of sex chromosomes vs. autosomes could be already identified. These include the accumulation of transposable elements and changes in GC content. The changes in GC content could be explained by biased gene conversion and altered recombination landscape of the neo sex chromosomes. The authors also study divergence and diversity of genes located on the neo sex chromosomes. Here their findings appear to be surprising and need further exploration. The neoW chromosome already shows unique patterns of divergence and diversity at protein-coding genes as compared with genes on either neoZ or autosomes. In contrast, the genes on the neoZ chromosome do not display divergence or diversity patterns different from those for autosomes. This last observation is puzzling and I believe should be explored in further studies. Overall, this study significantly advances our knowledge of the early stages of sex chromosome evolution in vertebrates, provides an example of how such a study could be conducted in other non-model organisms, and provides several avenues for future work.
References
[1] Leroy T., Anselmetti A., Tilak M.K., Bérard S., Csukonyi L., Gabrielli M., Scornavacca C., Milá B., Thébaud C. and Nabholz B. (2019). A bird’s white-eye view on neo-sex chromosome evolution. bioRxiv, 505610, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/505610
| A bird’s white-eye view on neosex chromosome evolution | Thibault Leroy, Yoann Anselmetti, Marie-Ka Tilak, Sèverine Bérard, Laura Csukonyi, Maëva Gabrielli, Céline Scornavacca, Borja Milá, Christophe Thébaud, Benoit Nabholz | <p>Chromosomal organization is relatively stable among avian species, especially with regards to sex chromosomes. Members of the large Sylvioidea clade however have a pair of neo-sex chromosomes which is unique to this clade and originate from a p... |  | Molecular Evolution, Population Genetics / Genomics | Kateryna Makova | | 2019-01-24 14:17:15 | View |
Tell me who you mate with, I’ll tell you what’s going on
Recommended by Sara Magalhaes and Alexandre Courtiol based on reviews by Alexandre Courtiol and 2 anonymous reviewers
The study of sexual selection goes as far as Darwin himself. Since then, elaborate theories concerning both intra- and inter-sexual sexual have been developed, and elegant experiments have been designed to test this body of theory. It may thus come as a surprise that the community is still debating on the correct way to measure simple components of sexual selection, such as the Bateman gradient (i.e., the covariance between the number of matings and the number of offspring)[1,2], or to quantify complex behaviours such as mate choice (the non-random choice of individuals with particular characters as mates)[3,4] and their consequences.
One difficulty in the study of sexual selection is evaluating the consequences of non-random mating. Indeed, when non-random mating is observed in a population, it is often difficult to establish whether such mating pattern leads to i) sexual selection per se (selection pressures favouring certain phenotypes), and/or ii) the non-random association of parental genes in their offspring or not. These two processes differ. In particular, assortative (and disassortative) mating can shape genetic covariances without leading to changes in gene frequencies in the population. Their distinction matters because these two processes lead to different evolutionary outcomes, which can have large ripple effects in the evolution of sexual behaviours, sexual ornamentation, and speciation.
In his paper, entitled “Multi-model inference of non-random mating from an information theoretic approach” [5], Carvajal-Rodríguez tackled this issue. The author generated a simple model in which the consequences of non-random mating can be inferred from information on the population frequencies before and after mating. The procedure is as follows: from the initial population frequencies of phenotypes (or genotypes) of both sexes, the model generates predictions on the frequencies after mating, assuming that particular mating patterns have occurred. This leads to different predictions for the phenotypic (or genotypic) frequencies after mating. The particular mating pattern leading to the best fit with the real frequencies is then identified via a model selection procedure (performing model averaging to combine different mating patterns is also possible).
This study builds on a framework introduced by Carvajal-Rodríguez’s colleagues [6] and encompasses later methodological developments involving the author himself [7]. Compared to early work, the new method proposed by the author builds on the relationship between mating pattern and information [8] to distinguish among scenarios that would lead to non-random mating due to different underlying processes, using simple model selection criterion such as the AICc.
The great asset of the proposed method is that it can be applied to the study of natural populations in which the study of mate choice and sexual selection is notoriously difficult. In the manuscript, the procedure is tested on a population of marine gastropods (Littorina saxatilis). This allows the reader to grasp how the method can be applied to a real system. In fact, anyone can try out the method thanks to the freely available software InfoMating programmed by the author. One important assumption underlying the current method is that the frequencies of unmated individuals do not change during the mating season. If this is not the case, the reader may refer to another publication of the same author which relaxes this assumption [9]. These papers are both instrumental for empiricists interested in testing sexual selection theory.
References
[1] Bateman, A. J. (1948). Intra-sexual selection in Drosophila. Heredity, 2(3), 349-368. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1948.21
[2] Jones, A. G. (2009). On the opportunity for sexual selection, the Bateman gradient and the maximum intensity of sexual selection. Evolution: International Journal of Organic Evolution, 63(7), 1673-1684. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2009.00664.x
[3] Andersson, M., & Simmons, L. W. (2006). Sexual selection and mate choice. Trends in ecology & evolution, 21(6), 296-302. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2006.03.015
[4] Kuijper, B., Pen, I., & Weissing, F. J. (2012). A guide to sexual selection theory. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 43, 287-311. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110411-160245
[5] Carvajal-Rodríguez, A. (2019). Multi-model inference of non-random mating from an information theoretic approach. bioRxiv, 305730, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/305730
[6] Rolán‐Alvarez, E., & Caballero, A. (2000). Estimating sexual selection and sexual isolation effects from mating frequencies. Evolution, 54(1), 30-36. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2000.tb00004.x
[7] Carvajal-Rodríguez, A., & Rolan-Alvarez, E. (2006). JMATING: a software for the analysis of sexual selection and sexual isolation effects from mating frequency data. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 6(1), 40. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-6-40
[8] Carvajal-Rodríguez, A. (2018). Non-random mating and information theory. Theoretical population biology, 120, 103-113. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2018.01.003
[9] Carvajal-Rodríguez, A. (2019). A generalization of the informational view of non-random mating: Models with variable population frequencies. Theoretical population biology, 125, 67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2018.12.004
| Multi-model inference of non-random mating from an information theoretic approach | Antonio Carvajal-Rodríguez | <p>Non-random mating has a significant impact on the evolution of organisms. Here, I developed a modelling framework for discrete traits (with any number of phenotypes) to explore different models connecting the non-random mating causes (mate comp... | 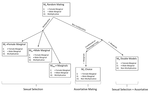 | Evolutionary Ecology, Evolutionary Theory, Sexual Selection | Sara Magalhaes | | 2019-02-08 19:24:03 | View |
Thermal regimes, but not mean temperatures, drive patterns of rapid climate adaptation at a continent-scale: evidence from the introduced European earwig across North America
Jean-Claude Tourneur, Joël Meunier
https://doi.org/10.1101/550319
Temperature variance, rather than mean, drives adaptation to local climate
Recommended by Fabien Aubret based on reviews by Ben Phillips and Eric Gangloff
Climate change is impacting eco-systems worldwide and driving many populations to move, adapt or go extinct. It is increasingly appreciated, for example, that species may adjust their phenology in response to climate change, although empirical data is scarce. In this preprint [1], Tourneur and Meunier report an impressive sampling effort in which life-history traits were measured across introduced populations of earwig in North America. The authors examine whether variation in life-history across populations is correlated with aspects of the thermal climate experienced by each population: mean temperature and seasonality of temperature. They find some fascinating correlations between life-history and thermal climate; correlations with the seasonality of temperature, but not with mean temperature. This study provides relatively uncommon data, in the sense that where most of the literature looking at adaptation in animals in response to climate change has focused on physiological traits [2, 3], this study examines changes in life-history traits with time scales relevant to impending climate change, and provides a reasonable argument that this is adaptation, not just constraint.
References
[1] Tourneur, J.-C. and Meunier, J. (2019). Thermal regimes, but not mean temperatures, drive patterns of rapid climate adaptation at a continent-scale: evidence from the introduced European earwig across North America. BioRxiv, 550319, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/550319
[2] Kellermann, V., Overgaard, J., Hoffmann, A. A., Fløjgaard, C., Svenning, J. C., & Loeschcke, V. (2012). Upper thermal limits of Drosophila are linked to species distributions and strongly constrained phylogenetically. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(40), 16228-16233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1207553109
[3] Hoffmann, A. A., & Sgro, C. M. (2011). Climate change and evolutionary adaptation. Nature, 470(7335), 479. doi: 10.1038/nature09670
| Thermal regimes, but not mean temperatures, drive patterns of rapid climate adaptation at a continent-scale: evidence from the introduced European earwig across North America | Jean-Claude Tourneur, Joël Meunier | <p>The recent development of human societies has led to major, rapid and often inexorable changes in the environment of most animal species. Over the last decades, a growing number of studies formulated predictions on the modalities of animal adap... |  | Adaptation, Evolutionary Ecology, Life History | Fabien Aubret | | 2019-02-15 09:12:11 | View |
Transcriptomic response to divergent selection for flowering time in maize reveals convergence and key players of the underlying gene regulatory network
Maud Irène Tenaillon, Khawla Sedikki, Maeva Mollion, Martine Le Guilloux, Elodie Marchadier, Adrienne Ressayre, Christine Dillmann
https://doi.org/10.1101/461947
Early and late flowering gene expression patterns in maize
Recommended by Tanja Pyhäjärvi based on reviews by Laura Shannon ? and 2 anonymous reviewers
Artificial selection experiments are key experiments in evolutionary biology. The demonstration that application of selective pressure across multiple generations results in heritable phenotypic changes is a tangible and reproducible proof of the evolution by natural selection.
Artificial selection experiments are used to evaluate the joint effects of selection on multiple traits, their genetic covariances and differences in responses in different environments. Most studies on artificial selection experiments report and base their analyses on phenotypic changes [1]. More recently, changes in allele frequency and other patterns of molecular genetic diversity have been used to identify genomic locations where selection has had an effect. However, so far the changes in gene expression have not been in the focus of artificial selection experiment studies (see [2] for an example though).
In plants, one of the most famous artificial selection experiments is the Illinois Corn Experiment where maize (Zea mays) is selected for oil and protein content [3], but in addition, similar experiments have been conducted also for other traits in maize. In Saclay divergent selection experiment [4] two maize inbred lines (F252 and MBS847) have been selected for early and late flowering for 13 generations, resulting in two week difference in flowering time.
In ”Transcriptomic response to divergent selection for flowering time in maize reveals convergence and key players of the underlying gene regulatory network ” [5] Maud Tenaillon and her coworkers study the gene expression differences among these two independently selected maize populations. Their experiments cover two years in field conditions and they use samples of shoot apical meristem at three different developmental stages: vegetative, transitioning and reproductive. They use RNA-seq transcriptome level differences and qRT-PCR for gene expression pattern investigation. The work is continuation to earlier genetic and phenotypic studies on the same material [4, 6].
The reviewers and I agree that dataset is unique and its major benefit is that it has been obtained from field conditions similar to those that species may face under natural setting during selection. Their tissue sampling is supported by flowering time phenotypic observations and covers the developmental transition stage, making a good effort to identify key transcriptional and phenotypic changes and their timing affected by selection.
Tenaillon et al. [5] identify more than 2000 genes that are differentially expressed among early and late flowering populations. Expectedly, they are enriched for known flowering time genes. As they point out, differential expression of thousands of genes does not mean that they all were independently affected by selection, but rather that the whole transcriptional network has shifted, possibly due to just few upstream or hub-genes. Also, the year-to-year variation had smaller effect in gene expression compared to developmental stage or genetic background, possibly indicating selection for stability across environmental fluctuation for such an important phenotype as flowering time.
Another noteworthy observation is that they find convergent patterns of transcriptional changes among the two selected lines. 115 genes expression patterns are shifted due to selection in both genetic backgrounds. This convergent pattern can be a result of either selection on standing variation or de novo mutations. The data does not allow testing which process is underlying the observed convergence. However, their results show that this is an interesting future question that can be addressed using genotype and gene expression data from the same ancestral and derived material and possibly their hybrids.
References
[1] Hill, W. G., & Caballero, A. (1992). Artificial selection experiments. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 23(1), 287-310. doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.23.110192.001443
[2] Konczal, M., Babik, W., Radwan, J., Sadowska, E. T., & Koteja, P. (2015). Initial molecular-level response to artificial selection for increased aerobic metabolism occurs primarily through changes in gene expression. Molecular biology and evolution, 32(6), 1461-1473. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv038
[3] Moose, S. P., Dudley, J. W., & Rocheford, T. R. (2004). Maize selection passes the century mark: a unique resource for 21st century genomics. Trends in plant science, 9(7), 358-364. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.05.005
[4] Durand, E., Tenaillon, M. I., Ridel, C., Coubriche, D., Jamin, P., Jouanne, S., Ressayre, A., Charcosset, A. and Dillmann, C. (2010). Standing variation and new mutations both contribute to a fast response to selection for flowering time in maize inbreds. BMC evolutionary biology, 10(1), 2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-2
[5] Tenaillon, M. I., Seddiki, K., Mollion, M., Le Guilloux, M., Marchadier, E., Ressayre, A. and Dillmann C. (2019). Transcriptomic response to divergent selection for flowering time in maize reveals convergence and key players of the underlying gene regulatory network. BioRxiv, 461947 ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Evolutionary Biology. doi: 10.1101/461947
[6] Durand, E., Tenaillon, M. I., Raffoux, X., Thépot, S., Falque, M., Jamin, P., Bourgais A., Ressayre, A. and Dillmann, C. (2015). Dearth of polymorphism associated with a sustained response to selection for flowering time in maize. BMC evolutionary biology, 15(1), 103. doi: 10.1186/s12862-015-0382-5
| Transcriptomic response to divergent selection for flowering time in maize reveals convergence and key players of the underlying gene regulatory network | Maud Irène Tenaillon, Khawla Sedikki, Maeva Mollion, Martine Le Guilloux, Elodie Marchadier, Adrienne Ressayre, Christine Dillmann | <p>Artificial selection experiments are designed to investigate phenotypic evolution of complex traits and its genetic basis. Here we focused on flowering time, a trait of key importance for plant adaptation and life-cycle shifts. We undertook div... |  | Adaptation, Experimental Evolution, Expression Studies, Quantitative Genetics | Tanja Pyhäjärvi | | 2018-11-23 11:57:35 | View |



 based on reviews by Eric Petit, Martin Husemann ? and 2 anonymous reviewers
based on reviews by Eric Petit, Martin Husemann ? and 2 anonymous reviewers


 based on reviews by David Macaya-Sanz, Marcela Van Loo and 1 anonymous reviewer
based on reviews by David Macaya-Sanz, Marcela Van Loo and 1 anonymous reviewer





 based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers


















